Editor’s note: I will not translate the entire book on Heartland that Eduardo Velasco published on the now defunct Evropa Soberana site in Spanish (here, here and here). I limit myself to translating only a few paragraphs from the final section:
______ 卐 ______
Johann Gottlieb Fichte’s The Closed Commercial State (1800) is a tedious book, utopian and pedantic in its rationalism, but it is worth our attention. On the one hand, it had a certain influence on the development of what Spengler would call ‘Prussian socialism’ or ‘Prussianism’, and on the other, it defends the exact opposite thesis to that of globalisation, i.e. that a country should seek autarchy to extricate itself from the network of international trade, becoming, so to speak, an endorheic state of exclusively internal (commercial, economic) flow. Thinkers of all political persuasions have seen interesting things in Fichte’s work, liberals as well as socialists, communists, anarchists, fascists and Nazis[1] so it is not a work to be dismissed lightly.
 We return, then, to Prussia, the land that before the Second World War was home, according to Mackinder, to ‘one of the most virile races of mankind’, a race that was to suffer between 1944 and 1946 an ethnic cleansing of extreme brutality. While England was ruled by a cosmopolitan aristocracy of shipping, trade, commerce and banking speculation, Prussia was ruled by a provincial, military, land and productivity aristocracy. Fichte sent a copy of The Closed Commercial State (ECC) to Frederick William III, supposedly to influence his economic policy.
We return, then, to Prussia, the land that before the Second World War was home, according to Mackinder, to ‘one of the most virile races of mankind’, a race that was to suffer between 1944 and 1946 an ethnic cleansing of extreme brutality. While England was ruled by a cosmopolitan aristocracy of shipping, trade, commerce and banking speculation, Prussia was ruled by a provincial, military, land and productivity aristocracy. Fichte sent a copy of The Closed Commercial State (ECC) to Frederick William III, supposedly to influence his economic policy.
Fichte was inspired by the peasant society of the Germanic world and the economic organisation of the old German cities. It is impossible not to see in his work affinities with Lycurgus, Plato and Thomas More. The German philosopher’s economic ideal was a completely self-sufficient state, with ‘nothing to demand from its neighbours and nothing to cede to them’. Fichte says that in such a state, ‘the government does not aim at acquiring commercial predominance, which is a dangerous tendency, but at making the nation completely independent and autonomous. If a single nation has achieved supremacy in commerce, its victims must use every possible means to attenuate this supremacy and restore the balance’: a clear reference to the power of Great Britain.
The danger of the commercial supremacy of a single nation was that the international trade handled by that nation took over all the goods of a rival state until that state had only one commodity left to sell: itself. In this way, ‘the state sells itself, sells its independence, collects a permanent subsidy thus becoming the province of another state and a means to any of its objectives’.
In this regard, it is worth remembering that, although autarchy is today surrounded by taboos, in classical Greece it was the ideal to which people aspired, even if it was not always completely attainable. Aristotle, in his Politics, considered autarchy to be the ideal situation for a state. Hesiod went further and proposed autarchy for each family household. Tellurian Sparta, the most respected state in classical Greece, was a closed, autarchic economy thanks to its conquest of fertile Messenia. Thalassic Athens, by contrast, was heavily urbanised and had to rely on grain markets such as Egypt and southern Ukraine.
Fichte divided society into three strata: producers, merchants and craftsmen. Then came the military, teachers and statesmen. Of all these castes, the most dangerous for Fichte was the merchants since, through their possession of commodities and especially money, they tended to escape the authority of the state and ended up imposing their own rules.
The philosopher thought that Europe had a great commercial advantage over the other continents, tending to take over their labour power and goods. He considered that this state of affairs could not be perpetuated forever and that one day, a large state would have to leave the ‘European commercial society’ to form its own closed productive circuit.
What Fichte was criticising in these reflections was the explosion of Europe, and he advocated an implosion: Europe could not be eternally dependent on overseas ‘backyards’ in the Third World and must one day be able to stand on its own feet. Moreover, a planned economy cannot be planned, nor can a country be like a self-balancing and autonomous microsystem, if it depends on foreign goods and production, the supply, processing and transport of which it does not control, and is thus at the mercy of the whims of the markets: price fluctuations, trade embargoes, competition with the domestic product, etc. Such economic phenomena will tend to turn the country that is subject to them into a mere province in the network of international trade, tending to specialise in one economic sector rather than hosting all of them.
In the 1930s, autarky seemed to be gaining the upper hand over international trade. Three distinctly autarkic geopolitical blocs emerged: the European Axis (Germany, Italy and allied nations), the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere (the vast conquests of the Japanese Empire from Manchuria to Indochina) and the Soviet Union.
With Europe, Asia and the Heartland closed to the US export market (except, in the case of the USSR, the substantial military, economic and oil aid it received from the US and the UK), all that remained on the planet was the British Empire and the impoverished colonial Third World: a de facto and imposed US autarchy. In The Tragedy of American Diplomacy (1959), William Appleman argued that the US ruling oligarchy went to war against Germany and Japan to protect global export markets from the effects of autarky. The dynamics of the autarkic blocs were neutralised with the establishment of the Bretton Woods system (1944), with its three pillars: the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank and the dollar as the reserve currency of international trade. The only bloc that was spared to some extent was the USSR, which formed the economic organisation COMECON, formed in 1949, the same year that NATO was founded.
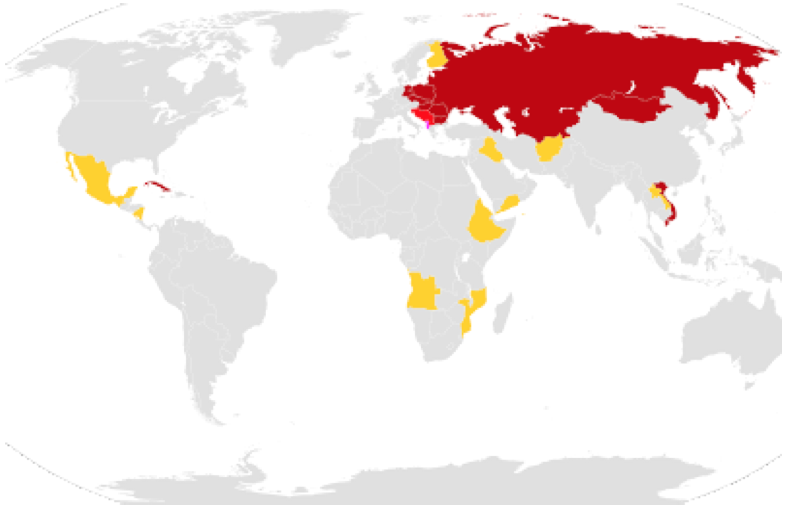
The COMECON bloc, of which the Warsaw Pact was to be the military arm. Red: Member states. Yellow: observer states. Pink: belonged to the organisation but did not participate. (Editor's Note: Compare it with BRICS).
Fichte—who believed that ‘in the beginning was action’ and that property emanates from labour and productive activity, that is, that the earth belongs to whoever pours his blood and sweat upon it—did not recognise the value of money, but the value of the commodities that such money is capable of buying. For him, ‘The total mass of money represents and is worth as much as the total mass of commodities’. No matter how much money is in circulation or is created out of thin air in the form of credit, its purchasing power will always be limited by the actual goods and services that can be bought.
Wealth does not depend on how much money one has, but on how large a fraction of the total existing money one possesses. It is clear that when there is, as today, much more money in circulation (especially electronic money and interest-debt-money) than real commodities, the excess capital floating in ‘the markets’ is devoted to inflating bubbles, opening new artificial markets (for example, by turning the emotions of the individual and human nature itself into a business), manipulating needs and demand with aggressive advertising and speculating to justify its existence. Not to mention that every time the money supply is increased, the creators of money (or rather, counterfeiters of money) increase the proportion of capital they own out of the total money supply, using this capital as if it were a commodity in itself. But ‘In the simple expression “to realise something in money”, the whole falsity of the system is already contained. Nothing can be realised in money because money itself is nothing real. The commodity is the real reality.’
To bring about the closure of the commercial state, Fichte advocated the ‘abolition of the world currency’ which he identifies with gold and silver (Editors’ Note: after the collapse of the British Empire, nowadays the dollar is still the reserve currency of international trade) and the ‘introduction of a national currency’. It is difficult not to see here the influence of Sparta, which forbade the possession of gold and silver by creating a new currency which was not accepted outside the territory of the Lacedaemonian state: rough iron bars, so that they could not be manipulated or moulded, were dipped in vinegar while still red-hot; the idea was to armour against the fluctuating and shifting influence of foreign trade.
In this situation, there is no longer any exchange with foreign states, except for one-off trade pacts based on direct barter, without monetary intermediaries. This is what Germany was doing before World War II in Eastern Europe and South America: a barter trade that did not need to use international currencies in the hands of its enemies. In contrast, initiatives for a world currency have always come from globalist individuals or entities, for example, the Rothschild family. (In this video, Mr. Evelyn de Rothschild proposes an ‘international currency’ to avoid conflict. What he does not say is who will have the power to issue such a currency—presumably himself, for example.)
Another of Fichte’s contributions to geopolitics is his idea that states should not overstep their ‘natural frontiers’, understood as those within which a state can achieve self-sufficiency. Towards the end of his writing, Fichte leaves us with a very politically incorrect reflection:
It is evident that a nation so closed, whose members live only with themselves and very few with foreigners; a nation which preserves by those measures its particular way of life, its institutions and customs; a nation which deeply loves its Fatherland and everything national, very soon a high degree of national honour and a very peculiar national character will emerge. It will become another nation, a completely new nation. That introduction of the national currency is its true creation…
______ 卐 ______
The power of High Finance has decided to base itself in the United Kingdom, North America and to a lesser extent the rest of Western Europe because among other things there is an excellent quality manpower there.
The American troops deployed in Iraq and Afghanistan have a fabulous genetic heritage, perfectly comparable to the Indo-European hordes of antiquity. Even in the faces of many white American convicts, we can discern a potential crusader knight, Viking, sailor, soldier, hard-nosed farmer or hard-headed labourer. These are people gone astray, uprooted by crossing the Atlantic, without the moral and spiritual foundations that only deep Asia, along with inspiring European history—based on heroic examples, war, art, culture, work, beauty and love—can provide.
What is currently being exported from Hollywood and MTV is not American culture, as the saying goes. ‘American culture’ is the love of family and country, the right to defend them with arms, civic sovereignty, religion, liberty and independence: the values of a people whose land was not given to them by a feudal lord, but won by blood and sweat. Neither Thomas Jefferson nor George Washington has anything to do with the toxic rubbish propagated from the meccas of the Yankee subculture, and the sphere of influence of the Pentagon and Wall Street is not an ‘American empire’ any more than the Vatican is the Roman Empire and the City of London is the British Empire.
We know—because we are not deluded or cultural Judeo-Christians, nor do we believe in globalisation or the religion of political correctness—what happens in countries that forget the fundamental laws of reproduction and race improvement: they become vulgarised, corrupt, unserious, undisciplined, disorganised, weakened and Third Worldised. The darkening of the race goes hand in hand with the darkening of the mind and spirit. Parasitic weeds take over the garden and eventually choke out the noblest and most productive trees and plants…
Deliberate and systematic ignorance of human reproduction, of the importance of race and genetics in geopolitics will only have the effect that the ‘myth of blood’ will resurface with greater force and violence. Globalisation pretends to make us believe that we are all equal while at the same time homogenising us racially, a clear proof that it does not consider us all equal. Genetic and anthropological-physical studies, i.e. recognising the difference between people, are therefore an anti-globalisation vector.
____________
[1] Dr. Carl Schmidt, associated with the power groups of Deutsche Bank, IG Farben and Siemens, defended the idea of a Closed Commercial State in Europe led by Germany.
2 replies on “Heartland, 8”
The danger of the merchant class controlling too much commerce and influencing the nation, and of who or how a global currency is managed are the two dangers he mentioned that we face today.
The weakness of modern western governments is that they have capitulated to the merchant class and removed almost all of the monopolization and international trade laws that our ancestors had made to prevent mega-corporations or international corporations harming the nation. A historical error we had already learned!
A merchant class will often devalue blood and soil to make a profit.