Excerpted from the 15th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Closely related to the Celts, whose fortunes we traced in the previous installment, and settled into the area of Europe directly north of them, were the Germans. Like the Celts, they immigrated into northern Europe over a period of many centuries. It would be incorrect, of course, to refer to these earliest Nordic immigrants as “Germans.” All that can be said of them, just as of those immigrants south of them who later gave birth to the Celts, is that they were Indo-Europeans.
Celtic Buffer
Was there some quality which distinguished the Germans from the Celts, so that the former were able to prevail over the decaying civilization to the south and the latter were not? Certainly not initially, for the two were of the same stock. Nevertheless, the Germans had two enormous advantages over the Celts.
First, the proto-German homeland was buffered from the imperialistic designs of the Romans by the Celts; the latter took the full brunt of the Roman armies, while the German homeland remained relatively inviolate. And yet the Germans, unlike the Balts and the Slavs, had just enough contact with the Romans to serve as a stimulus for their later invasions and conquest of the Roman Empire.
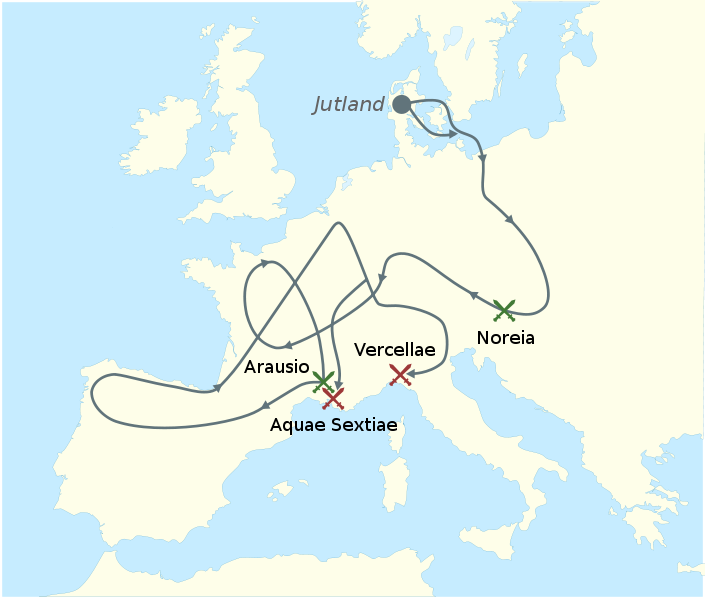
The death struggle between Latins and Germans began even before Caesar’s subjection of Gaul. Late in the second century two neighboring German tribes, the Cimbrians and the Teutons, left their homes in the Danish peninsula because, they said, of the sinking of much of their low-lying land into the sea. Some 300,000 in number, they headed south, crossing the Tyrolese Alps into northern Italy in 113 B.C., where they asked the Romans for permission either to settle or to cross Roman territory into the Celtic lands to the west.
A Tragic End
The Roman consul, Papirius Carbo, attempted to halt them, and they defeated his army. The Germans then proceeded westward into Gaul and went as far as Spain, where they raised havoc. Ten years later, however, they returned to northern Italy.
(Part of the Cimbrian War)
This time they were met by a more competent Roman general, the consul Gaius Marius. In two horrendous battles, in 102 and 101 B.C., Marius virtually exterminated the Teutons and the Cimbrians. So many Teutons were massacred at Aquae Sextiae in 102 that, according to a contemporary Roman historian, their blood so fertilized the earth that the orchards there were especially fruitful for years afterward, and German bones were used to build fences around the vineyards.
More Conflict
At Vercelli the Cimbrians met a similar fate the following year; more than 100,000 were slaughtered. When the German women saw their men being defeated, they first slew their children and then killed themselves in order to avoid the shame of slavery.
The annihilation of these two German nations was followed by a few decades in which Italy remained relatively safe from further incursions from the north. The Germans’ territory was bounded, roughly, on the east by the Vistula and on the south by the Danube. In the west the boundary was less definite, and the Germans west of the Rhine came into repeated conflict with Roman armies in Gaul.
Tacitus on the Germans
The Romans were naturally curious about the teeming tribes of fierce, warlike people beyond the Rhine who dared contest their conquest of the lands in northern Gaul, and several Roman writers enumerated them and described their way of life, most notably the historian Gaius Cornelius Tacitus. Writing in a first-century Rome which was thoroughly mongrelized, Tacitus was strongly impressed by the Germans’ apparent racial homogeneity:
I concur in opinion with those who deem the Germans never to have intermarried with other nations but to be a pure and unmixed race, stamped with a distinct character. Hence, a family likeness pervades the whole, though their numbers are so great. Their eyes are stern and blue, their hair ruddy, and their bodies large, powerful in sudden exertion, but impatient of toil and not at all capable of sustaining thirst and heat. They are accustomed by their climate to endure cold and hunger.
Tacitus added: “Traitors and deserters are hanged; cowards and those guilty of unnatural practices are suffocated in mud under a hurdle.” Subject to the same punishment as cowards and homosexuals were draft dodgers: those who failed to present themselves for military service when summoned.
The education of the German youth stressed not only bravery and skill in arms, but loyalty in the highest degree. Tacitus gives an interesting description of the mutual obligations between a German leader and his companions in arms:
The Germans transact no business, public or private, without being armed, but it is not customary for any person to assume arms until the state has approved his ability to use them. Then, in the midst of the assembly, either one of the chiefs, or the father, or a relative, equips the youth with a shield and a spear. These are to them the manly gown (toga virilis); this is the first honor conferred on youth. Before, they are considered as part of a household; afterwards, of the state.


2 replies on “Germanic People and the Romans (1)”
Another fascinating article by Dr. Pierce.
While the customs of Barbarian tribes were rough — from the point of view of decadent and feminine Rome —, their mastery of iron forging, clothe milling, tool-making and agriculture tends to disprove the common idea they were unsophisticated savages.
The defining characteristic of Aryans: refusal of slavery, and cold pragmatism where “hope” has no place.
Contrast that with the current attitude of westerners, who’d rather prefer a miserable life for eternity over a dangerous rebellion or a quick death.
this:
“the Germans, … had just enough contact with the Romans to serve as a stimulus for their later invasions and conquest of the Roman Empire.”
is not really accurate. The Germans did not set off to conquer the empire; they wanted into it, they wanted to benefit from it, same way everybody wants into the USA today to get their piece of pie. The Goths were let across the Danube as refugees; it was only because they were treated so badly by the local Roman administrators that they revolted and discovered they could stand up to Roman power. The various tribes that came across the Rhine did so primarily as foederatii and were settled in areas of Gaul to hold it, since the local population was either incapable or unwilling to do so – the warlike raids across the Rhine were only for destruction and looting, never conquest. Germanic political authorities originated in the groups settled within the bounds of the empire, not with those transgressing the borders, which is what one would expect from a conquest.
Compare with what happened to the Eastern Empire in Syria and Asia Minor over the following centuries. THAT was conquest.
So talk of the Germans conquering the Western empire is just not accurate. They came in and took over, but they did so because of a vacuum (societal, demographic, political, and military) that the Romans themselves allowed to come into existence. Had the Roman collapse not been so drastic, the Germans would have stayed right where they were.