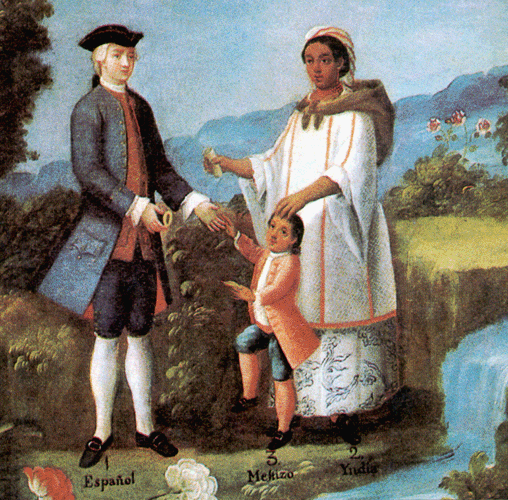Half a year ago the admin of a Catholic, counter-Jihad website in Spain commented in this blog.
Mexico’s backwardness has been the result of its governments after independence, which has been mostly in the hands of whites. Its historical demise is due to the fact that the whites are not breeding, as it is the case, unfortunately, of so many white nationalists.
I quote this friend because his Catholic views reflect exactly the ideology that ruined this part of the American continent: blaming the few whites in charge of a nation consisting of a sea of brown people and sparing the Catholic, Universal ethics that caused the non-white population explosion in the first place.
Arthur Kemp’s March of the Titans is a comprehensive book about the odyssey of the white race, presently available only in printed format. After a long transcontinental research Kemp concludes that colonization is only successful when the colonizers ensure that they demographically replace the native population. “Anything less than that will cause the colonial experiment to fail.” Kemp demonstrates his thesis not only through the paradigm of his native Rhodesia, but of every other geographical entity that had been conquered by whites in the last millennia only to be re-conquered by the natives after overwhelming the white conquerors demographically.
William Pierce had reached identical conclusions in Who We Are: ethnic cleansing is the only way to succeed, and, as he hinted in other texts, to do that we must abandon Christian meta-ethics altogether.
Over the boards I’ve said it many times and will say it again: Pace my Christian friends, the price to save the West is to give up Christian axiology, and its secular offshoots, that presently are infecting our minds and our sense of decency.
* * *
Excerpted from the 22nd article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
The native Amerinds found by the Spaniards in the West Indies were, like those of the mainland, of Mongoloid derivation, being the descendants of Mongoloid peoples who had begun crossing the Bering Strait from Siberia to North America some 12,000 years ago and had then gradually propagated throughout the empty North and South American continents and the adjacent islands.
Since the Spaniards’ entire purpose in the New World was economic exploitation, not the propagation of their own race, they did not deliberately liquidate the native population. In some areas, however, that was the inadvertent effect of the Spanish conquest. The Indians were not constitutionally suited to the unremitting slave labor in the gold and silver mines and on the sugar plantations which was forced on them by their new masters, and they died like flies under the Spanish yoke.
An enormous toll was also taken by smallpox, a disease endemic among the Europeans but one to which the Amerinds, isolated as they had been for thousands of years, had no natural immunity. It virtually depopulated the Caribbean islands and then wreaked havoc among the mainland Indians. (The Indian revenge was syphilis, a New World disease entirely new to the Europeans—at least, in the new and virulent form in which it existed among the Amerinds.)
Beginning of the Black Tide
Because of the inadequacy of the Indians as a local labor force, the Spaniards almost immediately began importing Negro slaves from West Africa. The latter belong to a race ideally suited to the plantation labor of that era. The Blacks were first used in the West Indies, then on the Brazilian mainland. Approximately a million of them were imported in the period 1550-1650, and by the latter date they had completely replaced the Amerind natives as a slave labor force on the Caribbean islands.
(Spanish-English translation of the painting footnote: Spaniard, Mestizo, Indian)
Approximately 150,000 Spaniards and Portuguese had migrated to the New World by the middle of the 17th century, and natural increase had raised their number to about 400,000. They ruled over about 9,000,000 Indians—and a growing population of mestizos (Indian-White mixed breeds), Blacks, mulattos, and Indian-Black mixed breeds. Only on the island of Cuba was there anything approaching a truly White Spanish or Portuguese community.
Northerners Arrive
From the beginning of the 17th century, however, Northern Europeans—English, French, and Dutch—began seriously contesting the Iberians’ claims on the New World. By 1650 nearly 50,000 English (and a few thousand French and Dutch) immigrants were settled on Caribbean land wrested away from the Spaniards, and another 50,000 had landed in North America.
In sharp contrast to the Spanish and Portuguese colonists, the great bulk of the Northern Europeans came to the New World not to exploit non-White labor and make money, but to settle and work the land themselves, in all-White communities. Thus, colonialism acquired two quite distinct meanings in the 17th and 18th centuries: a strictly economic meaning, which applied to all the Southern European and some of the Northern European colonies; and a racial meaning, which applied almost exclusively to the colonies of the Northerners.
The Pollution of the South
Today the only countries in South America which are substantially White are Uruguay (nearly 100 per cent), Argentina (between 80 and 90 per cent), and Chile (approximately 50 per cent).
Women and Plows
Most of the Northern Europeans who came to the New World had quite different motives than did the Spanish and Portuguese. Most of the latter came only to make money, and relatively few brought their women with them; from the beginning miscegenation was common in the areas controlled by the Iberians.
The Northerners, on the other hand, came for the land and the opportunity for a new life on a new frontier. They brought their women and their plows with them, and for the most part, they did their own labor. They saw in the Indians no opportunity for economic exploitation, but only a danger to their families. Until missionaries began making Christians of the Indians and taking their side against the Whites, the latter just pushed them aside, took their land, and formed all-White communities of farmers, craftsmen, and tradesmen, as they had in Europe.