Léon Degrelle was a Belgian Rexist leader, SS officer, decorated combatant on the Eastern Front. Of the first eight hundred Walloon volunteers who left for the Axis campaign against the Soviet Union and Stalinist Marxism, only three survived the war—one of them Degrelle. He died in 1994, while still in exile in Spain.
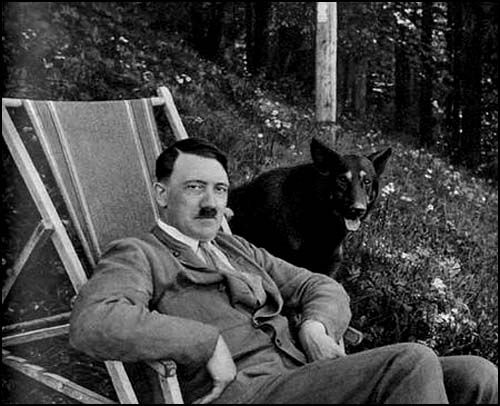

“Hitler—you knew him—what was he like?” I have been asked that question a thousand times since 1945, and nothing is more difficult to answer.
Approximately two hundred thousand books have dealt with the Second World War and with its central figure, Adolf Hitler. But has the real Hitler been discovered by any of them? “The enigma of Hitler is beyond all human comprehension,” the left-wing German weekly Die Zeit once put it.
Salvador Dalí, art’s unique genius, sought to penetrate the mystery in one of his most intensely dramatic paintings. Towering mountain landscapes all but fill the canvas, leaving only a few luminous meters of seashore dotted with delicately miniaturized human figures: the last witness to a dying peace. A huge telephone receiver dripping tears of blood hangs from the branch of a dead tree; and here and there hang umbrellas and bats whose portent is visibly the same. As Dalí tells it, “Chamberlain’s umbrella appeared in this painting in a sinister light, made evident by the bat, and it struck me when I painted it as a thing of enormous anguish.”
He then confided: “I felt this painting to be deeply prophetic. But I confess that I haven’t yet figured out the Hitler enigma either. He attracted me only as an object of my mad imaginings and because I saw him as a man uniquely capable of turning things completely upside down.”
What a lesson in humility for the braying critics who have rushed into print since 1945 with their thousands of “definitive” books, most of them scornful, about this man who so troubled the introspective Dalí that forty years later he still felt anguished and uncertain in the presence of his own hallucinatory painting. Apart from Dalí, who else has ever tried to present an objective portrayal of this extraordinary man whom Dalí labeled the most explosive figure in human history? (Dalí was ejected from the Surrealist Movement in 1934 because of his fascination with Hitler and his fascist sympathies.)
Like Pavlov’s Bell
The mountains of Hitler books based on blind hatred and ignorance do little to describe or explain the most powerful man the world has ever seen. How, I ponder, do these thousands of disparate portraits of Hitler in any way resemble the man I knew? The Hitler seated beside me, standing up, talking, listening. It has become impossible to explain to people fed fantastic tales for decades that what they have read or heard on television just does not correspond to the truth.
People have come to accept fiction, repeated a thousand times over, as reality. Yet they have never seen Hitler, never spoken to him, never heard a word from his mouth. The very name of Hitler immediately conjures up a grimacing devil, the fount of all of one’s negative emotions. Like Pavlov’s bell, the mention of Hitler is meant to dispense with substance and reality. In time, however, history will demand more than these summary judgements.
Strangely Attractive
Hitler is always present before my eyes: as a man of peace in 1936, as a man of war in 1944. It is not possible to have been a personal witness to the life of such an extraordinary man without being marked by it forever. Not a day goes by but Hitler rises again in my memory, not as a man long dead, but as a real being who paces his office floor, seats himself in his chair, pokes the burning logs in the fireplace.
The first thing anyone noticed when he came into view was his small mustache. Countless times he had been advised to shave it off, but he always refused: people were used to him the way he was.
He was not tall—no more than was Napoleon or Alexander the Great.
Hitler had deep blue eyes that many found bewitching, although I did not find them so. Nor did I detect the electric current his hands were said to give off. I gripped them quite a few times and was never struck by his lightning.
His face showed emotion or indifference according to the passion or apathy of the moment. At times he was as though benumbed, saying not a word, while his jaws moved in the meanwhile as if they were grinding an obstacle to smithereens in the void. Then he would come suddenly alive and launch into a speech directed at you alone, as though he were addressing a crowd of hundreds of thousands at Berlin’s Tempelhof airfield. Then he became as if transfigured. Even his complexion, otherwise dull, lit up as he spoke. And at such times, to be sure, Hitler was strangely attractive and as if possessed of magic powers.
Exceptional Vigor
Anything that might have seemed too solemn in his remarks, he quickly tempered with a touch of humor. The picturesque word, the biting phrase were at his command. In a flash he would paint a word-picture that brought a smile, or come up with an unexpected and disarming comparison. He could be harsh and even implacable in his judgments and yet almost at the same time be surprisingly conciliatory, sensitive and warm.
After 1945 Hitler was accused of every cruelty, but it was not in his nature to be cruel. He loved children. It was an entirely natural thing for him to stop his car and share his food with young cyclists along the road. Once he gave his raincoat to a derelict plodding in the rain. At midnight he would interrupt his work and prepare the food for his dog Blondi.
He could not bear to eat meat, because it meant the death of a living creature. He refused to have so much as a rabbit or a trout sacrificed to provide his food. He would allow only eggs on his table, because egg-laying meant that the hen had been spared rather than killed.
Hitler’s eating habits were a constant source of amazement to me. How could someone on such a rigorous schedule, who had taken part in tens of thousands of exhausting mass meetings from which he emerged bathed with sweat, often losing two to four pounds in the process; who slept only three to four hours a night; and who, from 1940 to 1945, carried the whole world on his shoulders while ruling over 380 million Europeans: how, I wondered, could he physically survive on just a boiled egg, a few tomatoes, two or three pancakes, and a plate of noodles? But he actually gained weight!
He drank only water. He did not smoke and would not tolerate smoking in his presence. At one or two o’clock in the morning he would still be talking, untroubled, close to his fireplace, lively, often amusing. He never showed any sign of weariness. Dead tired his audience might be, but not Hitler.
He was depicted as a tired old man. Nothing was further from the truth. In September 1944, when he was reported to be fairly doddering, I spent a week with him. His mental and physical vigor were still exceptional. The attempt made on his life on July 20th had, if anything, recharged him. He took tea in his quarters as tranquilly as if we had been in his small private apartment at the chancellery before the war, or enjoying the view of snow and bright blue sky through his great bay window at Berchtesgaden.
Iron Self-Control
At the very end of his life, to be sure, his back had become bent, but his mind remained as clear as a flash of lightening. The testament he dictated with extraordinary composure on the eve of his death, at three in the morning of April 29, 1945, provides us a lasting testimony. Napoleon at Fontainebleau was not without his moments of panic before his abdication. Hitler simply shook hands with his associates in silence, breakfasted as on any other day, then went to his death as if he were going on a stroll. When has history ever witnessed so enormous a tragedy brought to its end with such iron self-control?
Hitler’s most notable characteristic was ever his simplicity. The most complex of problems resolved itself in his mind into a few basic principles. His actions were geared to ideas and decisions that could be understood by anyone. The laborer from Essen, the isolated farmer, the Ruhr industrialist, and the university professor could all easily follow his line of thought. The very clarity of his reasoning made everything obvious.
His behavior and his lifestyle never changed even when he became the ruler of Germany. He dressed and lived frugally. During his early days in Munich, he spent no more than a mark per day for food. At no stage in his life did he spend anything on himself. Throughout his thirteen years in the chancellery he never carried a wallet or ever had money of his own.
Intellectual Curiosity
Hitler was self-taught and made not attempt to hide the fact. The smug conceit of intellectuals, their shiny ideas packaged like so many flashlight batteries, irritated him at times. His own knowledge he had acquired through selective and unremitting study, and he knew far more than thousands of diploma-decorated academics.
I don’t think anyone ever read as much as he did. He normally read one book every day, always first reading the conclusion and the index in order to gauge the work’s interest for him. He had the power to extract the essence of each book and then store it in his computer-like mind. I have heard him talk about complicated scientific books with faultless precision, even at the height of the war.
His intellectual curiosity was limitless. He was readily familiar with the writings of the most diverse authors, and nothing was too complex for his comprehension. He had a deep knowledge and understanding of Buddha, Confucius, and Jesus Christ, as well as Luther, Calvin, and Savonarola; of literary giants such as Dante, Schiller, Shakespeare, and Goethe; and of analytical writers such as Renan and Gobineau, Chamberlain and Sorel.
He had trained himself in philosophy by studying Aristotle and Plato. He could quote entire paragraphs of Schopenhauer from memory, and for a long time carried a pocked edition of Schopenhauer with him. Nietzsche taught him much about the willpower.
His thirst for knowledge was unquenchable. He spent hundreds of hours studying the works of Tacitus and Mommsen, military strategists such as Clausewitz, and empire builders such as Bismarck. Nothing escaped him: world history or the history of civilizations, the study of the Bible and the Talmud, Thomistic philosophy and all the master- pieces of Homer, Sophocles, Horace, Ovid, Titus Livius and Cicero. He knew Julian the Apostate as if he had been his contemporary.
His knowledge also extended to mechanics. He knew how engines worked; he understood the ballistics of various weapons; and he astonished the best medical scientists with his knowledge of medicine and biology.
The universality of Hitler’s knowledge may surprise or displease those unaware of it, but it is nonetheless a historical fact: Hitler was one of the most cultivated men of this century. Many times more so than Churchill, an intellectual mediocrity; or than Pierre Laval, with his mere cursory knowledge of history; or than Roosevelt; or Eisenhower, who never got beyond detective novels.
Artist and Architect
Even during his earliest years, Hitler was different than other children. He had an inner strength and was guided by his spirit and his instincts.
He could draw skillfully when he was only eleven years old. His sketches made at that age show a remarkable firmness and liveliness.
His first paintings and watercolors, created at age 15, are full of poetry and sensitivity. One of his most striking early works, “Fortress Utopia,” also shows him to have been an artist of rare imagination. His artistic orientation took many forms. He wrote poetry from the time he was a lad. He dictated a complete play to his sister Paula who was amazed at his presumption. At the age of 16, in Vienna, he launched into the creation of an opera. He even designed the stage settings, as well as all the costumes; and, of course, the characters were Wagnerian heroes.
More than just an artist, Hitler was above all an architect. Hundreds of his works were notable as much for the architecture as for the painting. From memory alone he could reproduce in every detail the onion dome of a church or the intricate curves of wrought iron. Indeed, it was to fulfill his dream of becoming an architect that Hitler went to Vienna at the beginning of the century.
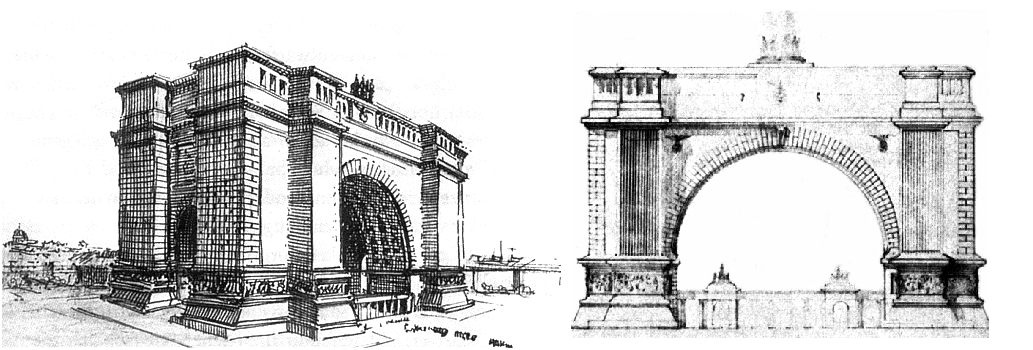 When one sees the hundreds of paintings, sketches and drawings he created at the time, which reveal his mastery of three dimensional figures, it is astounding that his examiners at the Fine Arts Academy failed him in two successive examinations. German historian Werner Maser, no friend of Hitler, castigated these examiners: “All of his works revealed extraordinary architectural gifts and knowledge. The builder of the Third Reich gives the former Fine Arts Academy of Vienna cause for shame.”
When one sees the hundreds of paintings, sketches and drawings he created at the time, which reveal his mastery of three dimensional figures, it is astounding that his examiners at the Fine Arts Academy failed him in two successive examinations. German historian Werner Maser, no friend of Hitler, castigated these examiners: “All of his works revealed extraordinary architectural gifts and knowledge. The builder of the Third Reich gives the former Fine Arts Academy of Vienna cause for shame.”
Humble Origins
Impressed by the beauty of the church in a Benedictine monastery where he was part of the choir and served as an altar boy, Hitler dreamt fleetingly of becoming a Benedictine monk. And it was at that time, too, interestingly enough, that whenever he attended mass, he always had to pass beneath the first swastika he had ever seen: it was graven in the stone escutcheon of the abbey portal.
Hitler’s father, a customs officer, hoped the boy would follow in his footsteps and become a civil servant. His tutor encouraged him to become a monk. Instead the young Hitler went, or rather he fled, to Vienna. And there, thwarted in his artistic aspirations by the bureaucratic mediocraties of academia, he turned to isolation and meditation. Lost in the great capital of Austria-Hungary, he searched for his destiny.
During the first thirty years of Hitler’s life, the date April 20, 1889, meant nothing to anyone. He was born on that day in Branau, a small town in the Inn valley. During his exile in Vienna, he often thought of his modest home, and particularly of his mother. When she fell ill, he returned home from Vienna to look after her. For weeks he nursed her, did all the household chores, and supported her as the most loving of sons. When she finally died, on Christmas eve, his pain was immense. Wracked with grief, he buried his mother in the little country cemetery: “I have never seen anyone so prostrate with grief,” said his mother’s doctor, who happened to be Jewish.
In his room, Hitler always displayed an old photograph of his mother. The memory of the mother he loved was with him until the day he died. Before leaving this earth, on April 30, 1945, he placed his mother’s photograph in front of him. She had blue eyes like his and a similar face. Her maternal intuition told her that her son was different from other children. She acted almost as if she knew her son’s destiny. When she died, she felt anguished by the immense mystery surrounding her son.
Throughout the years of his youth, Hitler lived the life of a virtual recluse. He greatest wish was to withdraw from the world. At heart a loner, he wandered about, ate meager meals, but devoured the books of three public libraries. He abstained from conversations and had few friends.
It is almost impossible to imagine another such destiny where a man started with so little and reached such heights. Alexander the Great was the son of a king. Napoleon, from a well-to-do family, was a general at twenty-four. Fifteen years after Vienna, Hitler would still be an unknown corporal. Thousands of others had a thousand times more opportunity to leave their mark on the world.
Hitler was not much concerned with his private life. In Vienna he had lived in shabby, cramped lodgings. But for all that he rented a piano that took up half his room, and concentrated on composing his opera. He lived on bread, milk, and vegetable soup. His poverty was real. He did not even own an over-coat. He shoveled streets on snowy days. He carried luggage at the railway station. He spent many weeks in shelters for the homeless. But he never stopped painting or reading.
Despite his dire poverty, Hitler somehow managed to maintain a clean appearance. Landlords and landladies in Vienna and Munich all remembered him for his civility and pleasant disposition. His behavior was impeccable. His room was always spotless, his meager belongings meticulously arranged, and his clothes neatly hung or folded. He washed and ironed his own clothes, something which in those days few men did. He needed almost nothing to survive, and money from the sale of a few paintings was sufficient to provide for all his needs.
Summing Things Up
Hitler had not yet focused on politics, but without his rightly knowing, that was the career to which he was most strongly called. Politics would ultimately blend with his passion for art. People, the masses, would be the clay the sculptor shapes into an immortal form. The human clay would become for him a beautiful work of art like one of Myron’s marble sculptures, a Hans Makart painting, or Wagner’s Ring Cycle.
His love of music, art, and architecture had not removed him from the political life and social concerns of Vienna. In order to survive, he worked as a common laborer side by side with other workers. He was a silent spectator, but nothing escaped him: not the vanity and egoism of the bourgeoisie, not the moral and material misery of the people, nor yet the hundreds of thousands of workers who surged down the wide avenues of Vienna with anger in their hearts.
He had also been taken aback by the growing presence in Vienna of bearded Jews wearing caftans, a sight unknown in Linz. “How can they be Germans?” he asked himself. He read the statistics: in 1860 there were sixty-nine Jewish families in Vienna; forty years later there were two hundred thousand. They were everywhere. He observed their invasion of the universities and the legal and medical professions, and their takeover of the newspapers.
Hitler was exposed to the passionate reactions of the workers to this influx, but the workers were not alone in their unhappiness. There were many prominent persons in Austria and Hungary who did not hide their resentment at what they believed was an alien invasion of their country. The mayor of Vienna, a Christian-Democrat and a powerful orator, was eagerly listened to by Hitler.
Hitler was also concerned with the fate of the eight million Austrian Germans kept apart from Germany, and thus deprived of their rightful German nationhood. He saw Emperor Franz Josef as a bitter and petty old man unable to cope with the problems of the day and the aspirations of the future.
Quietly, the young Hitler was summing things up in his mind.
First: Austrians were part of Germany, the common fatherland.
Second: The Jews were aliens within the German community.
Third: Patriotism was only valid if it was shared by all classes. The common people with whom Hitler had shared grief and humiliation were just as much a part of the fatherland as the millionaires of high society.
Fourth: Class war would sooner or later condemn both workers and bosses to ruin in any country. No country could survive class war; only cooperation between workers and bosses can benefit the country. Workers must be respected and live with decency and honor. Creativity must never be stifled.
When Hitler later said that he had formed his social and political doctrine in Vienna, he told the truth. Ten years later his observations made in Vienna would become the order of the day.
Thus Hitler was to live for several years in the crowded city of Vienna as a virtual outcast, yet quietly observing everything around him. His strength came from within. He did not rely on anyone to do his thinking for him. Exceptional human beings always feel lonely amid the vast human throng. Hitler saw his solitude as a wonderful opportunity to meditate and not to be submerged in a mindless sea. In order not to be lost in the wastes of a sterile desert, a strong soul seeks refuge within himself. Hitler was such a soul.
Lightning and the Word
The lightning in Hitler’s life would come from the Word.
All his artistic talent would be channeled into his mastery of communication and eloquence. Hitler would never conceive of popular conquests without the power of the Word. He would enchant and be enchanted by it. He would find total fulfillment when the magic of his words inspired the hearts and minds of the masses with whom he communed. He would feel reborn each time he conveyed with mystical beauty the knowledge he had acquired in his lifetime.
Hitler’s incantory eloquence will remain, for a very long time, a vast field of study for the psychoanalyst. The power of Hitler’s word is the key. Without it, there would never have been a Hitler era.
Transcendent Faith
Did Hitler believe in God? He believed deeply in God. He called God the Almighty, master of all that is known and unknown.
Propagandists portrayed Hitler as an atheist. He was not. He had contempt for hypocritical and materialistic clerics, but he was not alone in that. He believed in the necessity of standards and theological dogmas, without which, he repeatedly said, the great institution of the Christian church would collapse. These dogmas clashed with his intelligence, but he also recognized that it was hard for the human mind to encompass all the problems of creation, its limitless scope and breathtaking beauty. He acknowledged that every human being has spiritual needs.
The song of the nightingale, the pattern and color of a flower, continually brought him back to the great problems of creation. No one in the world has spoken to me so eloquently about the existence of God. He held this view not because he was brought up as a Christian, but because his analytical mind bound him to the concept of God. Hitler’s faith transcended formulas and contingencies. God was for him the basis of everything, the ordainer of all things, of his destiny and that of all others.
Note
Excerpted from volume two of Degrelle’s uncompleted multi-volume series on the life and legacy of Adolf Hitler, Hitler: Born at Versailles (Costa Mesa, Cal.: Institute for Historical Review, 1987). The examples of Hitler’s art have been scanned from Adolf Hitler: The Unknown Artist (Houston: Billy F. Price, 1984).
Source: Irmin Vinson’s site.