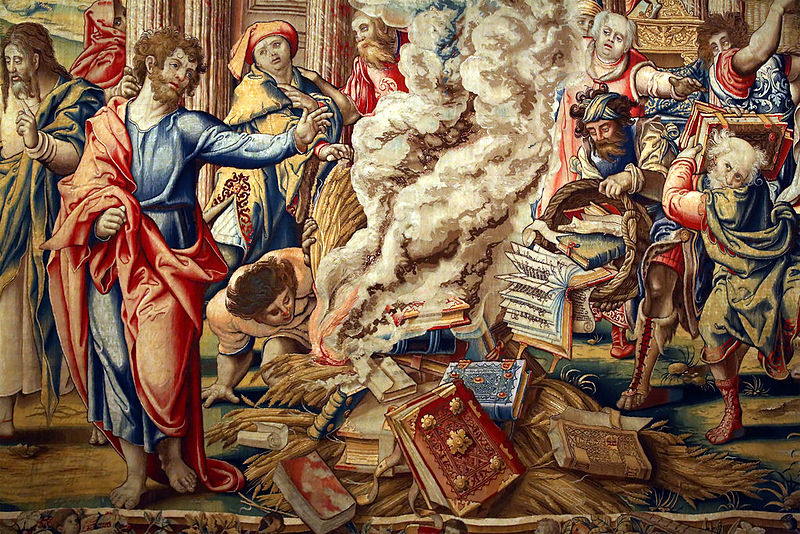
Pieter Coecke van Aelst, Story of Saint Paul: The Burning of the
Books at Ephesus, designed ca. 1529, woven before 1546 (medium:
wool and silk, woven under the direction of Jan van der Vyst).
Editor’s note.Bold-typed emphasis in the last paragraph is mine. In chapter eleven of The Darkening Age: The Christian Destruction of the Classical World, Catherine Nixey wrote:
In Egypt, a fearsome monk and saint named Shenoute entered the house of a man suspected of being a pagan and removed all his books. The Christian habit of book-burning went on to enjoy a long history. A millennium later, the Italian preacher Savonarola wanted the works of the Latin love poets Catullus, Tibullus and Ovid to be banned while another preacher said that all of these ‘shameful books’ should be let go, because if you are Christians you are obliged to burn them’…
* * *
Before there had been competing philosophical schools, all equally valid, all equally arguable. Now, for the first time, there was right—and there was wrong. Now, there was what the Bible said—and there was everything else. And from now on any belief that was ‘wrong’ could, in the right circumstances, put you in grave danger.
As Dirk Rohmann has highlighted, Augustine said that works that opposed Christian doctrine had no place in Christian society and had scant time for much of Greek philosophy. The Greeks, Augustine said dismissively, ‘have no ground for boasting of their wisdom’. The Church’s authors were greater, and more ancient. John Chrysostom went far further. He described pagan philosophy as a madness, the mother of evils and a disease.
Classical literature was filled with the incorrect and demonic and it came under repeated and vicious attack from the Church Fathers. Atheism, science and philosophy were all targeted. The very idea that mankind could explain everything through science was, as Rohmann has shown, disparaged as folly. ‘Stay clear of all pagan books!’ the Apostolic Constitutions advised Christians bluntly. ‘For what do you have to do with such foreign discourses, or laws, or false prophets, which subvert the faith of the unstable?’ If you wish to read about history, it continued, ‘you have the Books of Kings; if philosophy and poetry, you have the Prophets, the Book of Job and the Proverbs, in which you will find greater depth of sagacity than in all of the pagan poets and philosophers because this is the voice of the Lord… Do therefore always stay clear of all such strange and diabolical books!’…
An accusation of ‘magic’ was frequently the prelude to a spate of burnings. In Beirut, at the turn of the sixth century, a bishop ordered Christians, in the company of civil servants, to examine the books of those suspected of this. Searches were made, books were seized from suspects and then brought to the centre of the city and placed in a pyre. A crowd was ordered to come and watch as the Christians lit this bonfire in front of the church of the Virgin Mary. The demonic deceptions and ‘barbarous and atheistic arrogance’ of these books were condemned as ‘everybody’ watched ‘the magic books and the demonic signs burn’. As with the destruction of temples, there was no shame in this…
What did the books burned on such occasions really contain? Doubtless some did contain ‘magic’—such practices were popular prior to Christianity and certainly didn’t disappear with its arrival. But they were not all. The list given in the life of St Simeon clearly refers to the destruction of books of Epicureanism, the philosophy that advocated the theory of atomism. ‘Paganism’ appears to have been a charge in itself—and while it could mean outlawed practices it could, at a stretch, refer to almost any antique text that contained the gods. Christians were rarely good chroniclers of what they burned.
Sometimes, clues to the texts remain. In Beirut, just before the bonfire of the books, pious Christians had gone to the house of a man suspected of owning books that were ‘hateful to God’. The Christians told him that they ‘wanted the salvation and recovery of his soul’; they wanted ‘liberation’. These Christians then entered his home, inspected his books and searched each room. Nothing was found—until the man was betrayed by his slave. Forbidden books were discovered in a secret compartment in a chair. The man whose house it was—clearly well aware of what such ‘liberation’ might involve—‘fell to the ground and begged us, in tears, not to hand him over to the law’. He was spared the law but forced to burn his books. As our chronicler Zachariah records with pleasure, ‘when the fire was lit he threw the books of magic into it with his own hands, and said that he thanked God who had granted him with his visit and liberated him from the slavery and error of demons’. One of the books removed from the house in Beirut is mentioned: it is very possible it was not magic but a history by a disapproved-of Egyptian historian.
Divination and prophecy were often used as pretexts to attack a city’s elite. One of the most infamous assaults on books and thinkers took place in Antioch. Here, at the end of the fourth century, an accusation of treasonous divination led to a full-scale purge that targeted the city’s intellectuals. By sheer chance, Ammianus Marcellinus, a non-Christian and one of the finest historians of the era, happened to be in the city; a wonderful piece of luck for later historians and wretched luck for the man himself, who was horrified. As Ammianus describes it,
the racks were set up, and leaden weights, cords, and scourges put in readiness. The air was filled with the appalling yells of savage voices mixed with the clanking of chains, as the torturers in the execution of their grim task shouted: ‘Hold, bind, tighten, more yet.’
A noble of ‘remarkable literary attainments’ was one of the first to be arrested and tortured; he was followed by a clutch of philosophers who were variously tortured, burned alive and beheaded. Educated men in the city who had considered themselves fortunate now, Damocles-like, realized the fragility of their fortune. Looking up, it was as if they saw ‘swords hung over their heads suspended by horse-hairs from the ceiling’.
And, once again, there was the burning of books as bonfires of volumes were used as post-hoc justification for the slaughter. Ammianus Marcellinus writes with distaste that
innumerable books and whole heaps of documents, which had been routed out from various houses, were piled up and burnt under the eyes of the judges. They were treated as forbidden texts to allay the indignation caused by the executions, though most of them were treatises on various liberal arts and on jurisprudence.
Many intellectuals started to pre-empt the persecutors and set light to their own books. The destruction was extensive and ‘throughout the eastern provinces whole libraries were burnt by their owners for fear of a similar fate; such was the terror which seized all hearts’. Ammianus wasn’t the only intellectual to be scared in these decades. The orator Libanius burned a huge number of his own works…
* * *
The Great Library of Alexandria might have attempted to collect books on every topic, but Christianity was going to be considerably more selective…
One surviving Byzantine manuscript of Ovid has been scarred by a series of ridiculous redactions—even the word ‘girl’ seems to have been considered too racy to remain. In the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, Jesuits were still censoring and bowdlerizing their editions of the classics. Individual abbots, far from Umberto Eco’s avenging intellectual ideal, sometimes censored their own libraries. At some point in the fifteenth century, a note was left in a mutilated manuscript in Vienna. ‘At this point in the book,’ it records, ‘there were thirteen leaves containing works by the apostate Julian; the abbot of the monastery… read them and realised that they were dangerous, so he threw them into the sea.’
Much classical literature was preserved by Christians. Far more was not. To survive, manuscripts needed to be cared for, recopied. Classical ones were not. Medieval monks, at a time when parchment was expensive and classical learning held cheap, simply took pumice stones and scrubbed the last copies of classical works from the page. Rohmann has pointed out that there is even evidence to suggest that in some cases ‘whole groups of classical works were deliberately selected to be deleted and overwritten in around AD 700, often with texts authored by [the fathers of the Church or by] legal texts that criticised or banned pagan literature’. Pliny, Plautus, Cicero, Seneca, Virgil, Ovid, Lucan, Livy and many, many more: all were scrubbed away by the hands of believers…
The texts that suffer in this period are the texts of the wicked and sinful pagans. From the entirety of the sixth century only ‘scraps’ of two manuscripts by the satirical Roman poet Juvenal survive and mere ‘remnants’ of two others, one by the Elder and one by the Younger Pliny.
From the next century there survives nothing save a single fragment of the poet Lucan.
From the start of the next century: nothing at all.
Far from mourning the loss, Christians delighted in it. As John Chrysostom crowed, the writings ‘of the Greeks have all perished and are obliterated’. He warmed to the theme in another sermon: ‘Where is Plato? Nowhere! Where Paul? In the mouths of all!’
The fifth-century writer Theodoret of Cyrrhus observed the decline of Greek literature with similar enthusiasm. ‘Those elaborately decorated fables have been utterly banned,’ he gloated. ‘Who is today’s head of the Stoic heresy? Who is safeguarding the teachings of the Peripatetics?’ No one, evidently, for Theodoret concludes this homily with the observation that ‘the whole earth under the sun has been filled with sermons’.
Augustine contentedly observed the rapid decline of the atomist philosophy in the first century of Christian rule. By his time, he recorded, Epicurean and Stoic philosophy had been ‘suppressed’—the word is his. The opinions of such philosophers ‘have been so completely eradicated and suppressed… that if any school of error now emerged against the truth, that is, against the Church of Christ, it would not dare to step forth for battle if it were not covered under the Christian name’…
Much was preserved. Much, much more was destroyed. It has been estimated that less than ten per cent of all classical literature has survived into the modern era. For Latin, the figure is even worse: it is estimated that only one hundredth of all Latin literature remains. If this was ‘preservation’—as it is often claimed to be—then it was astonishingly incompetent. If it was censorship, it was brilliantly effective. The ebullient, argumentative classical world was, quite literally, being erased.