The following is my abridgement of chapter 13 of William Pierce’s history of the white race, Who We Are:
Nordic Virtues Led Romans to World Domination
Etruscan Kings Paved Way for Rome’s Fall
Levantines, Decadence, Capitalism Sank Rome

Today, when we speak of “Latins,” we reflexively think of short, swarthy, excitable people who are inordinately fond of loud rhythms, wine, spicy food, and seduction, and who aren’t to be taken very seriously. That is not an accurate image of all speakers of Romance languages, of course. Many individuals of French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, and Romanian nationality are as racially sound as the average Swede or German. Yet, the image persists, and for good reason.
But the Latini, the Northern tribesmen who settled Latium in the ninth century B.C. and founded Rome a century later, were something altogether different. Most of today’s Latins share nothing with those of twenty-eight centuries ago except the name. Not only are the two strikingly different in appearance and temperament, but every element of the culture the original Latins created as an expression of their race-soul has been fundamentally transformed by those who claim that name today.
Above all, the Latini were a people to be taken seriously. They brought with them to Italy the spirit of the northern forests whence they had come. They took themselves and life very seriously indeed.
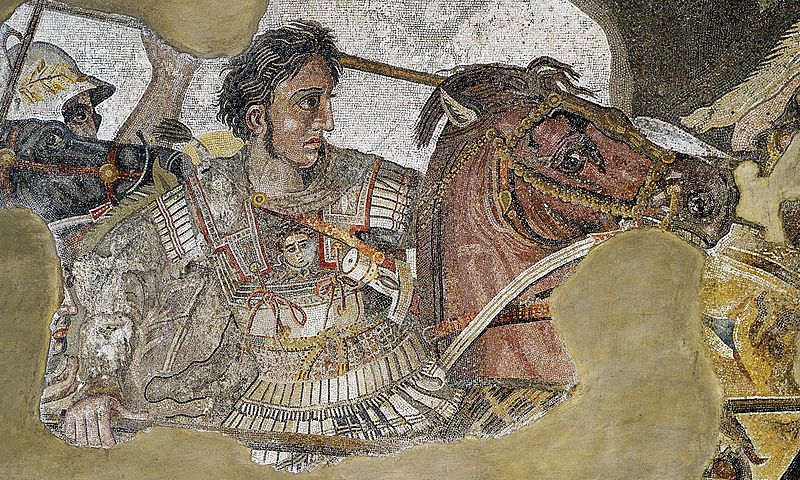
Duty, honor, responsibility: to the early Romans these were the elements which circumscribed a man’s life. Their virtues (the Latin root of the word means “manliness”) were strength of body and will, perseverance, sobriety, courage, hardiness, steadiness of purpose, attentiveness to detail, intelligence, and the characteristically Nordic will to order. Through these virtues they brought the world under their sway and created a civic edifice of such magnificence that it has ever since provided the standard against which all others are measured.
The Romans shaped the world around them—its institution, its politics, its attitudes, and its lifestyles—more extensively and more profoundly than anyone else has, and then they perished. That fact has fascinated and occupied the energies of historical scholars as no other topic. What were the reasons that the Romans rose so high and then fell so far?
Aristocrats only
The populus Romanus, it should be noted, did not include every inhabitant of Rome. Initially, in fact, it included only those persons who were blood members of a gens: i.e., the nobles, or patricians. After the individual households (familiae), the gentes were the fundamental social units among the early Romans, just as among the other Indo-European peoples. Their origin predates the Latin invasion of Italy; those persons born into them were, thus, all descendants of the warrior clans which originally seized the land and subjugated the aborigines.
The members of this warrior nobility, the patricians, were originally the whole people; to them belonged everything: land, livestock, religion, and law. They alone possessed a clan name (nomen gentilicium) and the right to display a coat of arms (jus imaginum).
Those who were not patricians, and, hence, not members of the populus Romanus, were the plebeians (plebs). Although not originally permitted to participate in the political or religious institutions of the populus, the plebeians were technically free. Many of them were the pre-Latin inhabitants of the seven hills beside the Tiber on which Rome was built; some undoubtedly came into the area later, as Rome’s influence grew. No direct evidence remains on the matter, but it nevertheless seems certain that there was a racial as well as a social difference between patricians and plebeians, with the latter having much less Nordic blood than the former.
Several social and political developments worked to diminish the racial distinction between patrician and plebeian with the passage of time. One of these developments was the patron-client relationship; another was the incorporation of an Etruscan element into the Roman population, including the acceptance of a number of gentes of Etruscan nobles into the Roman patrician class; a third was the extension of citizenship to the plebs.
As the social bond between patricians and plebeians grew, the social distance lessened. Many plebeians became, through hard work and good fortune, wealthy enough to rival the patrician class in their standard of living. And, although marriage between patrician and plebeian was strictly forbidden, there was nevertheless a flow of patrician genes into the plebeian class as a result of irregular liaisons between patrician men and plebeian women.
Latins, Sabines, Etruscans. Very early in its history, Romulus’ hilltop village of Latins joined forces with a neighboring village of Sabines, the Titienses. The Sabines and the Latins were of very closely related Indo-European stocks, and the amalgamation did little to change social institutions, other than doubling the number of senators.
A few years later, however, the Etruscan Luceres—of non-Indo-European stock—were absorbed by the growing Rome. Although the Etruscans remained a tribe apart from the Latin and Sabine inhabitants of the city, without patrician status, this condition was destined not to last.
It was Tarquin’s successor, Servius Tullius, who wrought changes which were to have much more profound racial consequences: in essence, Servius made the plebs a part of the populus Romanus. He accomplished this by overshadowing the patrician assembly, the Comitia Curiata, with two new popular assemblies, one civil and one military.
For administrative purposes, Servius divided the city and its territory into 30 “tribes.” These 30 administrative divisions, or wards, were tribal in name only, however; they were based solely on geography, and not on birth.
The patricians still ruled in the new Comitia Tributa, or tribal assembly, and provided the magistrates for the new wards, but Servius had laid the same groundwork for future political gains by the Roman plebs which Cleisthenes, just a few decades later, laid in Athens by reorganizing the tribal basis of the Athenian state along purely geographical lines.
Servius certainly cannot be accused of being a democrat. Yet he clearly initiated the process which eventually led to the ascendancy of gold over blood in Roman society, just as Solon had done in Athens a few years earlier.
The successor of Servius Tullius, Tarquinius Superbus (Tarquin the Proud), partly repealed the changes the former had made. And Tarquin the Proud’s reign marked the end of Etruscan domination of Rome, as well as the end of the monarchy. The Tarquins were driven out of Rome by the Latins and Sabines in 509 B.C. (according to tradition), and the Roman Republic was born.
But the Etruscan kings (among whom Servius is included, although his origins and ethnicity are uncertain) had brought about two lasting changes which were racially significant: the Roman aristocracy of Indo-European Latins and Sabines had received a substantial non-Indo-European admixture by the admission of the nobility of the Luceres to patrician status, and the principle that citizenship (and its attendant rights and powers) should belong solely to the members of a racial elite had been compromised.
The following centuries saw the political power of the plebs increase greatly relative to that of the patricians, while wealth continued to gain weight relative to race and family.
The Romans survived the founding of the Republic by roughly a millennium, but we are not concerned in this series with the political and cultural details of their history, except as these details have a salient racial significance. Therefore, the emphasis in the following historical summary is rather different than that found in most textbooks on Roman history.
Let us focus on four factors: first, the growing racial diversity of the Roman state; second, the eventual decadence of Rome’s patricians; third, the differential in birthrates between Rome’s patrician and plebeian classes; and fourth, the effects on the Roman peasantry of large-scale slavery as a capitalist institution.
Non-white immigration
The Romans were an energetic and martial people, and the power, influence, and wealth which they wielded grew enormously during the period from the end of the sixth to the last quarter of the first century B.C., the life-span of the Republic. First all of Italy, then the rest of the Mediterranean world and the Middle East, and finally much of Nordic Europe came into their possession.
This vast area under Roman rule was inhabited by a great diversity of races and peoples. As time passed, the rights of citizenship were extended to more and more of them. Citizens or not, there was a huge influx of foreign peoples into Rome and the other parts of Italy. Some came as slaves, the spoils of Rome’s victorious wars, and many came voluntarily, attracted by Rome’s growing wealth.
After the Republic became the Empire, in the last quarter of the first century B.C., the flow of foreigners into Italy increased still further. The descendants of the Latin founders of Rome became a minority in their own country. Above all other factors, this influx of alien immigrants led to Rome’s demise and the extinction of the race which built her into the ruler of the world.
The importance of the immigration factor is, of course, barely mentioned, if at all, in the school history texts being published today, because those who control the content of the textbooks have planned the same fate for White America as that which overtook White Rome.
Nevertheless, the writers of Classical antiquity themselves clearly recognized and wrote about the problem, as do those few of today’s professional historians with courage enough to buck the blackout on the mention of race in history. An example of the latter is the distinguished Swedish historian Martin Nilsson, for many years professor at the University of Lund. In his Imperial Rome, Nilsson wrote:
Of greater variety than elsewhere was the medley of races in the capital, where individuals congregated from all quarters, either on business with the rulers and the government or as fortune seekers in the great city, where great possibilities were open to all. It is almost impossible for us to realize the extraordinarily motley character of the Roman mob. The only city in our own day which can rival it is Constantinople, the most cosmopolitan town in the world. Numerous passages in the works of Classical authors refer to it, from Cicero, who calls Rome a city formed by the confluence of nations, to Constantius, who, when he visited Rome, marveled at the haste with which all the human beings of the world flocked there….
There were Romans who viewed the population of the capital with deep pessimism. In Nero’s time (37-68 A.D.) Lucan said that Rome was not peopled by its own citizens but filled with the scourings of the world. The Oriental [by Oriental, Nilsson means Levantine, not Mongoloid] element seems to have been especially strong.
Jews, in particular, in order to get their hands on the wealth there, flocked to Rome in such enormous numbers that Emperor Tiberius, under pressure from the common people on whom the Jews were preying, was obliged to order them all deported in 19 A.D. The Jews sneaked back in even greater numbers, and Tiberius’ brother, Emperor Claudius, was forced to renew the deportation order against them a few years later, but without success. They had become so numerous and so well entrenched that the emperor did not have the energy to dislodge them.
Another distinguished historian, the late Tenney Frank, professor at Bryn Mawr and Johns Hopkins, made a careful survey of Roman tomb inscriptions. He studied 13,900 inscriptions, separating them into categories based on the ethnicity or probable ethnicity indicated by the names and corollary evidence. Professor Frank estimated that by the end of the first century A.D. 90 per cent of the free plebeians in Rome were Levantines or part-Levantines. Fewer than ten per cent could claim unmixed Italian ancestry, and of these even fewer were of pure Indo-European stock.
One problem which Frank ran into was the tendency of non-Italians to disguise their ancestry by changing their names. It was easy enough to separate Greek and Syrian and Hebrew names from Latin ones, but a Latin name which had been adopted rather than inherited could often only be detected by noting the non-Latin names of the parents on the same tomb.
Then too, just as Jewish name-changers today often give themselves away by choosing a non-Jewish first name which has become so popular among their brethren that few non-Jews would dream of burdening their own children with it (Murray, Seymour, Irving are examples), Frank found the same clues among many “Latin” names.
As for the Greek names, the great majority of them did not belong to Hellenes but to Levantines from the remnants of Alexander’s Oriental empire. The Roman poet Juvenal (62-142 A.D.) alluded to this when he wrote:
Sirs, I cannot bear
This Rome made Grecian; yet of all her dregs
How much is Greek? Long since Orontes’ [a river] stream
Hath fouled our Tiber with his Syrian waters,
Bearing upon his bosom foreign speech
And foreign manners…
C. Northcote Parkinson, the noted author and historian, sums up the effect of centuries of uncontrolled immigration in his East and West (1963): “Rome came to be peopled very largely by Levantines, Egyptians, Armenians, and Jews; by astrologers, tipsters, idlers, and crooks.” The name “Roman,” in other words, came to mean as little as the name “American” is coming to mean today. And yet, just as White Americans are bringing about their downfall through greed and timidity and indifference, so did Rome’s patricians cause their own end.
In Rome’s earliest days, when the populus Romanus was entirely of noble birth, duty, honor, and responsibility counted for everything, as mentioned above. A Roman valued nothing above his honor, put nothing before his obligations to the community. Even after Rome’s conquests brought wealth and luxury to her citizens, her patricians could still produce men like Regulus, stern, honorable, unyielding.
Bread and circuses
But wealth inexorably undermined the old virtues. Decadence rotted the souls of the noble Romans. While the mongrel mobs were entertained by the debased spectacles in the Colosseum (not unlike the distraction of today’s rabble by non-stop television), the patricians indulged themselves with every new vice and luxury that money and a resourceful merchant class could provide. Pampered, perfumed, manicured, and attended by numerous slaves, the effete aristocracy of the first century A.D. was a far cry from the hard and disciplined ruling class of a few centuries earlier.
 Just as there are Americans today who understand where the weakness and lack of discipline of their people are leading them and who speak out against these things, so were there Romans who tried to stem the tide of decadence engulfing the Republic. One of these was M. Porcius Cato (“the Censor”), whose public career spanned the first half of the second century B.C.
Just as there are Americans today who understand where the weakness and lack of discipline of their people are leading them and who speak out against these things, so were there Romans who tried to stem the tide of decadence engulfing the Republic. One of these was M. Porcius Cato (“the Censor”), whose public career spanned the first half of the second century B.C.
Cato was born and raised on his father’s farm and then spent 26 years fighting in Rome’s legions before entering politics. Early in his career, having been appointed governor (praetor) of Sardinia, Cato set the pattern he would follow the rest of his life: he expelled all the moneylenders from the island, earning the undying hatred of the Jews and a reputation as a fierce anti-Semite.
Later Cato was elected censor in Rome. The duties of a censor were to safeguard public morality and virtue and to conduct a periodic census of people and property for military and tax purposes. Cato took these duties very seriously. He assessed jewelry and other luxury items at ten times their actual value, and he dealt promptly and severely with disorder and degeneracy.
In the Senate Cato spoke out repeatedly against the foreign influences in philosophy, religion, and lifestyle which were encroaching on the traditional Roman attitudes and manners. As a result, Rome’s “smart set” condemned him (privately, for he was too powerful to attack openly) as an archreactionary and an enemy of “progress.”
In the field of foreign policy, Cato was adamantly opposed to the integration of the Semitic East into the Roman world. He wanted Rome to concentrate on the western Mediterranean and to deal with the Levant only at sword point. Unfortunately, there were few men of Cato’s fiber left among the Romans by the second century.
Declining Birthrate. One of the most fateful effects of decadence was the drastic decline in the birthrate of the Roman nobility. Decadence is always accompanied by an increase in egoism, a shifting of focus from race and nation to the individual. Instead of looking on bearing and raising children as a duty to the state and a necessity for the perpetuation of their gens and tribe, upper-class Romans came to regard children as a hindrance, a limitation on their freedom and pleasure. The “liberation” of women also contributed heavily to this change in outlook.
The failure of the patrician class to reproduce itself alarmed those Roman leaders with a sense of responsibility to the future. Emperor Augustus tried strenuously to reverse the trend by issuing several decrees regarding family life. Heavy penalties were set for celibacy or for marriage with the descendants of slaves. Eventually, Augustus ordered that every noble Roman between the ages of twenty-five and sixty must be married or, at least, betrothed.
Suicide of the Nobility. In 9 A.D. tax advantages and other preferences were granted to the parents of three or more children; unmarried persons were barred from the public games and could not receive inheritances, while the childless married person could receive only half of any inheritance left to him.
All these measures failed. Augustus’ own daughter, Julia, was a thoroughly liberated member of the “jet set” of her time, who considered herself far too sophisticated to be burdened with motherhood; in embarrassment, Augustus banished her to an island.
From the dictatorship of Julius Caesar to the reign of Emperor Hadrian, a century and a half, one can trace the destinies of forty-five leading patrician families: all but one died out during that period. Of 400 senatorial families on the public records in 65 A.D., during the reign of Nero, all trace of half of them had vanished by the reign of Nerva, a single generation later.
Rise of Capitalism. As the patricians declined in numbers, the Roman peasantry also suffered, but for a different reason. The later years of the Republic saw the rise of agricultural capitalism, with wealthy entrepreneurs buying up vast estates, working them with slaves and driving the freeborn small farmers out of the marketplace.
By the tens of thousands the Latin and Sabine yeomen were bankrupted and forced to abandon their farms. They fled to the city, where most of them were swallowed up in the urban mob.
The capitalist nouveaux riches who came to wield much of the power and influence in Rome lost by the dwindling patricians were an altogether new type of Roman. Petronius’ fictional character Trimalchio is their archetype. Tenney Frank wrote of these “new Romans”:
It is apparent that at least the political and moral qualities which counted most in the building of the Italian federation, the army organization, the provincial administrative system of the Republic, were the qualities most needed in holding the Empire together. And however brilliant the endowment of the new citizens, these qualities they lacked. The Trimalchios of the Empire were often shrewd and daring businessmen, but their first and obvious task, apparently was to climb by the ladder of quick profits to a social position in which their children, with Romanized names, could comfortably proceed to forget their forebears. The possession of wealth did not, as in the Republic, suggest certain duties toward the commonwealth.
Many historians have remarked on the fact that the entire spirit of the Roman Empire was radically different from that of the Roman Republic. The energy, foresight, common sense, and discipline which characterized the Republic were absent from the Empire. But that was because the race which built the Republic was largely absent from the Empire; it had been replaced by the dregs of the Orient.
The change in attitudes, values, and behavior was due to a change in blood. The changing racial composition of Rome during the Republic paved the way for the unchecked influx of Levantine blood, manners, and religion during the Empire.
But it also set the stage for a new ascendancy of the same Northern blood which had first given birth to the Roman people. We will look at the conquest of Rome by the Germans. First, however, we must backtrack and see what had been happening in the North during the rise and fall of Rome.
 The earliest known
The earliest known