Below, “The Conspiracy of Man,” forward to The Tabernacle and its Sacrificial System, posted by Arch Stanton as a comment in this blog:
The problem with Christianity is that people do not understand the Jewish mind behind it. To understand the New Testament, one must understand Jewish culture, history and religion. Of course the Jews make no effort to enlighten the ignorant goyim on these subjects. In fact they prohibit the transference of their religious texts under penalty of death!
Long before the Temple came the era of the Tabernacle, where the sacrifice was ceremonial bloodlust. It was a place where priests butchered animals to atone for sins against their God, Yahweh.
The Torah originally referred to the first five books of the Old Testament. The books of Leviticus and Deuteronomy are Levirate laws forming the basis for Judaism’s sacrificial system. This system is naturally founded on the sacrifice of both blood offerings, in the form of specified animals, and non-blood offerings in the form of specified grains. In the early days of the sacrificial system, the Tabernacle was nothing more than a moving slaughterhouse, a place where priests butchered animals. It is telling that only the best animals, the least “blemished,” could be offered for sacrifice.
The indication as to the true purpose of the sacrificial system lay in the fact that priests took ten percent of the choicest cuts of meat for themselves and burned only the fat and viscera upon the altar as “sweet savor” to the Lord. The remaining meat was then returned to the sinner. Think about this for a moment, the Lord preferred fat and viscera to the prime cuts commanded by the priests.
Imagine for a moment, your priest as a butcher. Imagine going to church on Sunday and seeing your priest at the altar slitting the throat of various parishioners’ pets, catching their blood in a golden bowl and then splashing it around the altar as he dances around in a trance-like state chanting pleas to God for the forgiveness of sins and begging for salvation. After the service, you say to your spouse, “Boy that certainly was a different sermon this week wasn’t it dear?” Your spouse replies, “Oh I don’t know, next week is communion, when we eat the body Christ and drink his blood. Speaking of that, let’s hurry to the restaurant before the church crowd gets there.”
 After making their sacrifice, the Hebrew sinner was marked with blood, mixed with other bodily fluids, on either the forehead or the big toe. This mixture ensured longevity of the mark. The blood marking was visible proof that a tribesman had paid his “sin tax.” Later, this mark was washed off in a ritual purification bath called the Mikveh, at which time the sacrificial cycle began anew.
After making their sacrifice, the Hebrew sinner was marked with blood, mixed with other bodily fluids, on either the forehead or the big toe. This mixture ensured longevity of the mark. The blood marking was visible proof that a tribesman had paid his “sin tax.” Later, this mark was washed off in a ritual purification bath called the Mikveh, at which time the sacrificial cycle began anew.
However, this marking system had one obvious, glaring drawback. Blood is a commonly available substance produced by the higher organisms. In their attempt to control the easily counterfeited blood marking, priests forbade their followers from butchering their own animals or even possessing the instruments for doing so. This was the primary reason for the kosher slaughter, a process where the living animal’s throat is slit to ensure the pumping heart will drain the blood as completely as possible. This also led to the prohibition of various implements and practices used in the butchering process. The priests defined these as “clean” or “unclean,” but think “legal” or “illegal,” as these are in fact legalistic dictates that have almost nothing to do with hygiene.
Any contact with blood was strictly prohibited, like that produced by menstruating women or “lepers,” which meant anyone with running sores. As a result, a Byzantine legal structure arose to control the minutiae of everyday life. There is a forgettable tract in the Mishna that elaborates on the cleanliness of a bowl. The upshot of this legal commandment is that if a bowl in intact, then it is unclean; but if the bowl is smashed into pieces of which the largest piece is no larger than the tip of a man’s finger, then it is clean. This makes absolutely no sense unless one understands the bowl in question can be used to hold and mix blood products.
Eventually the phylactery replaced the blood marking. This was a small box attached to the forehead or the back of the wrist holding a scroll with a passage from the Torah. The scroll changed in accordance with the sacrificial cycle; and like tabs on a license plate, it could be checked as proof that Temple followers were current on their sacrificial tribute. Despite this modification, Levirite laws concerning blood products remained in full force.
♣
Imagine yourself as a very young child of a primitive, nomadic, tribesman. Having heard only stories, you are dimly aware of the importance of a much talked about, upcoming ritual. You are aware this ritual occurs on regular basis and the anxiousness of your parents is palpable when discussing the subject.
On the prescribed day, the day the ritual begins. You follow your parents down to a running stream. A man richly attired in strange garb stands in the middle of the stream. One by one, your neighbors walk into the stream where the man mutters strange words as he immerses them in the water while rubbing their forehead with the palm of his hand. After your father has undergone the ritual immersion, you note the red mark he always wears on is forehead has disappeared. The ritual continues until every adult in the village has undergone immersion. You hear someone nearby whispering that the sacred cycle has ended.
The following day, your mother wakes you earlier than usual and your family spends the morning in careful preparation for the day’s activities. You want to play with your friends, but your mother insists you attended to her demands. You accompany your father as he goes out among his meager collection of animals. He spends quite a bit of time inspecting the herd until he finally chooses a prized sheep. This animal happens to be one of your favorites. You have often played with the sheep, chasing them around the meadows and finally catching one, you buried your face in its soft wool. Your nose takes delight in the earthy smell of the sheep. It is the smell of life, and life seems to be everywhere among the hills where the herds roam.
 Later that morning, your father takes you by the hand and with animal in tow, you are dragged to a portable slaughterhouse your parents refer to as the “Tabernacle.” Here you are to witness the important ritual they have been discussing over the preceding weeks. You enter a large enclosure surrounded by a fence made of cloth. In the middle of the enclosure is an odd tent-like structure with rude wooden columns and entry doors. A number of wooden tables, sagging oddly along the longitudinal center line, are set up in the makeshift courtyard directly in front of the tent. Soon, other families begin arriving with their animals.
Later that morning, your father takes you by the hand and with animal in tow, you are dragged to a portable slaughterhouse your parents refer to as the “Tabernacle.” Here you are to witness the important ritual they have been discussing over the preceding weeks. You enter a large enclosure surrounded by a fence made of cloth. In the middle of the enclosure is an odd tent-like structure with rude wooden columns and entry doors. A number of wooden tables, sagging oddly along the longitudinal center line, are set up in the makeshift courtyard directly in front of the tent. Soon, other families begin arriving with their animals.
Finally, the ceremony begins. A neighbor of yours steps forward and presents a prized calf to one of several strangely dressed men, like the men you saw at the stream the day before. Your parents refer to these men as “priests.” One by one, the sinners step forward and present their animal to a priest who then hoists it upon one of the many tables. Your neighbor drops to his knees in front of the priest, closes his eyes and begins chanting something unintelligible. As you are witnessing this, your father grabs your hand and places it alongside his on the prized sheep. You can feel its heart racing. The animal transmits its terror though the palm of your hand. The priest takes hold of the struggling animal and with quick, practiced motion, slits its throat with a razor sharp knife. The animal struggles, kicking and bellowing in protest, as geysers of blood erupts from its jugular vein. A froth of blood spews forth, splattering you and everyone present. You can feel the spark of life draining through its hide as the stillness of death overcomes the animal. You look down at the viscous red fluid splattered on the front of your robe. You stare with revulsion at the red stains soaking into the fibers as the stench of death assaults your nostrils and addles your sense.

Even before the animal has ceased struggling, you look up from your bloodstained robe to see the head priest/butcher moving quickly to catch the animal’s blood in a golden bowl. Now you realize the sagging tabletop forms a trough that allows the blood to flow from the end, where the priest awaits with his bowl. With eyelids half closed and muttering some strange incantation, he seems to be in a trance. Shouting, he lifts the golden bowl skyward at arms’ length before splashing the rapidly congealing blood over and around the base of the altar. The priest then comes out of his trance and begins eviscerating the animal. During this process, the animal’s bloody guts are laid aside so they can later be burned on the altar as sweet savor to the lord, who evidently has an abiding taste for burnt fat and viscera.
In just a few strokes, the priest/butcher finishes his gory task. Working rapidly, he begins cutting the animal’s joints. As he separates the portions of meat, he carefully lays aside a large portion of the best cuts for himself. He then returns the remaining meat to your neighbor, who by now has given the priest full admission of his sins.
After the sacrifice is complete, the priest produces a smaller bowl with a cupful of the animal’s blood. The priest mixes it with another bodily fluid that appears to be semen. He uses his thumb to smear a large daub of the mixture on the forehead of the entranced, chanting sinner kneeling before him with closed eyes. Then, with a loud shout, the priest/butcher declares that by this act, your neighbor’s sins have been atoned. Your neighbor staggers to his feet and like a drunk, lurches away from the butchering table with a beatific look on his face, even as the priest calls for the next sinner to step forward with his animal.
Suddenly you feel the full emotional horror of the fate awaiting the other animals brought to the ritual. All the while, these men called priests, howl, chant and dance about, reciting their ritualistic incantations that beg god’s forgiveness; it must have been a bloody spectacle. The bloodlust continues well into evening.
 What you never witness is the secret ceremony inside the Tabernacle’s tent where the high priest in a final act of crazed bloodlust drinks the sacrificial blood before the mercy seat. The Levirate injunction against consuming blood is a public admonishment to restrict the use of blood products. However, the priesthood exempted itself from its own laws and secretly does not observe such restrictions. This covert act, along with the acceptable act of consuming sacrificial meat, will later be replayed by Yeshu during his last supper, when he symbolically offers wine and bread representing his blood and body to his disciples.
What you never witness is the secret ceremony inside the Tabernacle’s tent where the high priest in a final act of crazed bloodlust drinks the sacrificial blood before the mercy seat. The Levirate injunction against consuming blood is a public admonishment to restrict the use of blood products. However, the priesthood exempted itself from its own laws and secretly does not observe such restrictions. This covert act, along with the acceptable act of consuming sacrificial meat, will later be replayed by Yeshu during his last supper, when he symbolically offers wine and bread representing his blood and body to his disciples.
 A few days later the priests fold their Tabernacle tent and move on. They will move to the next tribe where the sacrificial cycle will be played out once again.
A few days later the priests fold their Tabernacle tent and move on. They will move to the next tribe where the sacrificial cycle will be played out once again.
Consider the effect of this gruesome spectacle on a child. Blood spewing everywhere, chanting priests mesmerized in their crazed bloodlust, driven by the howling and grunting of animals bleeding out the last of their life on the ground. The restless bleating of animals, now aware of their fate. Sinners raising their hands towards the heavens as they cry out for god’s forgiveness. Imagine your parents continually consumed with the thought of blood and the avoidance of it, thoughts that translate into an unnatural obsession about the stuff.
Extrapolate this horror out over the generational millennium and you have the foundations of a psychopathic bloodlust that is not a preference, not a peculiar, incidental twist in a few exceptional personalities: it is a culturally inbred condition, one that can neither be altered nor escaped. This culture of blood has permeated the very core of Judaism until it has become a genetic component of their race.
♣
The Bible is a book whose stories have influenced humanity in the most profound manner. Few would argue the statement that it has been the single most influential book in history. Yet few truly comprehend the true breadth and depth of its influence. Fewer still stop to consider why this ancient book has had such a powerful influence when other similar books of antiquity faded into complete obscurity; curious artifacts examined only by experts. What is it about the Bible that is different? Why is this particular book considered relevant to modern man, when its contemporaries are considered irrelevant, archaic works of ancient, primitive, tribes? What is it about these stories that drive modern man in the same manner as they drove the men of ancient times?
The original book was known to Jews as the Torah. These were the first five books attributed to Moses. “Torah” is an interesting word. Many words in Jewish culture have multiple constructs. Therefore, to understand the intent, such words must be taken within the frame of reference to the context in which they are used. To Jews, Torah can refer to anything from the first five books of Moses to the entire linage of Hebraic religious works, ranging from Genesis to the last volume of the Talmud. For our purpose, Torah will refer to those five books of the Old Testament attributed to Moses. This collection is commonly known to Christians as the “Pentateuch.”

The actual definition of “Torah” is likewise interesting. Again, we find a double definition in that the word is defined as both “law or legal” as well as “instruction.” From this definition, we find the Torah is in fact books of legal instruction. The reader is asked to keep this definition in mind while reading this book.
The Torah spawned three of the most influential religions on the planet today: Judaism and her unwanted daughters, Islam and Christianity; unwanted because the Jews never intended their book or beliefs to be adopted by non-Jews. It is truly ironic how few Christians realize that these two daughters have far more in common with each other than they do with their mother religion. All three religions are based on the original stories found in the Torah. All three recognize and revere the ancient patriarchs of the Old Testament. All three pay tribute to these stories as their foundational beliefs about monotheism. All three base their concepts of God upon the descriptions found in these stories. One only needs to compare these three religions with a religion like Buddhism or Hinduism to find the close relationship of mother Judaism and her two daughters.
Yet, while Western civilization has been profoundly influenced by these stories, the book in fact addresses the issues of the ancient Jews. The Bible was written by Jews, about Jews, for Jews. The information in the Torah was never intended to play any part outside Jewish culture for as it is written in the Babylonian Talmud, Sanhedrin 59a, (“Gemara… Johanan said: A heathen who studies the Torah deserves death, for it is written, Moses commanded us a law for an inheritance; it is our inheritance, not theirs”).
 It has been written that the worst reference source for information about water is a fish, for a fish is immersed in the fluid. The immersion of the fish is so complete that it does not even perceive that water exists. Thus, the fish’s immersion and dependence on water precludes any objective analysis of the fluid by the fish and so is the case with the Bible. Western civilization has been so profoundly influenced by its immersion in these stories that it can no longer see the original, objective truths behind them. The Bible is not a book about the history of the Jews: it is a book about the culture and beliefs of a people instrumental in shaping our world. Essentially, the Torah is a cookbook that might well be titled in the same manner as the one in Rod Serling’s play, To Serve Man.
It has been written that the worst reference source for information about water is a fish, for a fish is immersed in the fluid. The immersion of the fish is so complete that it does not even perceive that water exists. Thus, the fish’s immersion and dependence on water precludes any objective analysis of the fluid by the fish and so is the case with the Bible. Western civilization has been so profoundly influenced by its immersion in these stories that it can no longer see the original, objective truths behind them. The Bible is not a book about the history of the Jews: it is a book about the culture and beliefs of a people instrumental in shaping our world. Essentially, the Torah is a cookbook that might well be titled in the same manner as the one in Rod Serling’s play, To Serve Man.
Throughout their history, Jews have been renowned storytellers. Much of their superior verbal skills are undoubtedly derived from the history of their religion’s long oral tradition. Storytelling has long been the common method used by primitive cultures to pass down traditional beliefs and law, but the Jews elevated storytelling to the highest level possible. For Jews, storytelling goes well beyond even an art form, it is in fact the very thread from which they weave the fabric of their culture.
From the first millennia of their existence, Hebrew law and religious beliefs were passed down in the form of storytelling. Around the time of Yeshu, heated debate arose among the Sadducees and Pharisees over whether or not to continue adhering to the oral tradition. By the time of the second Temple period, a major point of friction between the Pharisees and the Sadducees was the validity of the oral law, since the Sadducees only adhered to the written law. Attempts were made to codify a collection of rulings, but the Sadducees rejected the Pharisees’ notion of abiding by the Oral tradition before it was later committed to ink.
There are some interesting considerations inherent to this disagreement. First and foremost, an oral tradition can be much more closely controlled as to who is allowed to receive the information. By this, one can see that had these stories not been committed to the written form, modern Christians would have no more idea of their content than they have of the Hebrew language. Secondly, oral traditions lend themselves to modification far more easily than written traditions. Orwell pointed out this difficulty in his book 1984, where an entire ministry is devoted exclusively to changing the written history of a culture. The Pharisees eventually won the argument as the modern Talmud teaches “God made a covenant with Israel only for the sake of that which was transmitted orally.” Yet, to this day, Jewish boys devote much of their time memorizing and reciting long, torturous, Talmudic tracts and arguing the legal precedence set by these laws, doing so in the very same manner as their ancestors.
Today, Hollywood’s writers, producers, and directors are predominantly Jewish; so it comes as no surprise to find the Torah’s influence clearly visible throughout most Hollywood productions. This marvelous ability to fantasize and tell tall tales can be visibly witnessed in numerous Hollywood and TV shows written and produced by these Jews. While names like Spielberg, Lear and Katzenberg have replaced Biblical names like Moses, Ezekiel, and Saul, the same form of story telling is still much in evidence. When one examines the fantastic and fanciful stories written and produced by those like Spielberg or Serling, or morality plays written by Norman Lear, one has a direct window into the mind of the Biblical storyteller.
_________
My two cents:
The author of the above foreword restricts his critique to animal sacrifice. More recent scholarship has established that those sacrifices, which would be condemned by any animal rights advocate today, were the sublimation of the ancient Hebrews’ filicidal impulses toward their own children: sublimation of actual child sacrifices in even more ancient Israelite history. See the pages of my book where I address this extremely disturbing subject: here.
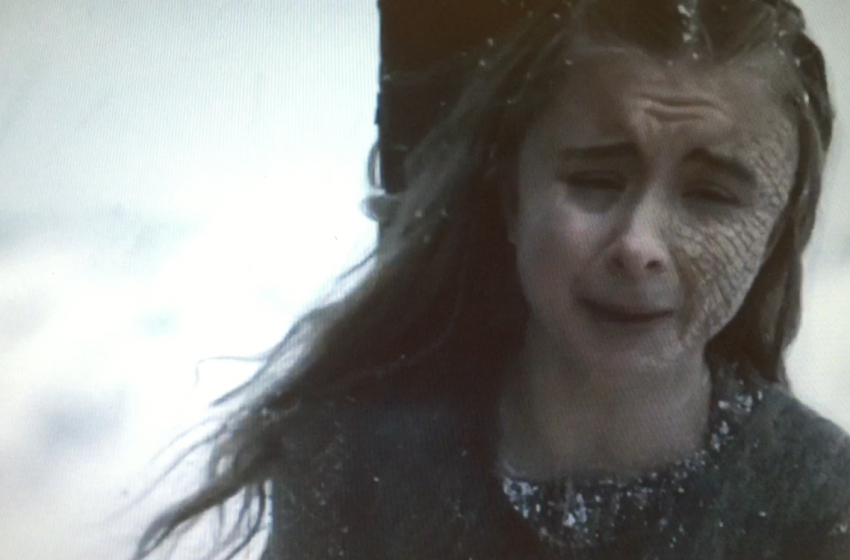 Was it really necessary to shock the audience with the ruthless decision of Stannis Baratheon to burn alive his daughter Shireen to death, as a sacrifice to the Lord of Light, in tonight’s episode of Game of Thrones (the scene doesn’t appear in the novels)?
Was it really necessary to shock the audience with the ruthless decision of Stannis Baratheon to burn alive his daughter Shireen to death, as a sacrifice to the Lord of Light, in tonight’s episode of Game of Thrones (the scene doesn’t appear in the novels)?