Sandro Botticelli:
La Nascita di Venere, 1482-1485
Category: Renaissance
I read ‘Nietzsche’s Der Antichrist: Looking Back From the Year 100’ in late 1993, in a hard copy issued in the winter of 1988/1989: one of the back copies of Free Inquiry that arrived in the mail when I discovered that organisation of freethinkers.
I met the author, Robert Sheaffer, at the 1994 CSICOP conference. If memory serves, he wore sandals, was dressed casually and had a beard. Last year I exchanged some correspondence with him.
Sheaffer is anything but a Hitlerite. However, the article that I abridge below is perfect for understanding a central part of esoteric Hitlerism. I mean that Uncle Adolf’s anti-Christianity, which wasn’t revealed to the masses of Germans (hence the epithet ‘esoteric’), already had antecedents in Germany.
Sheaffer’s complete article can be read here. Red emphasis is mine:
______ 卐 ______
Secular humanists have not infrequently criticized the beliefs and practices of the Christian religion, and its harmful effects on civilization and culture. Unfortunately, their voice is seldom heard. The proponents of the Christian world-view vastly outnumber secularists both in number and in activity. While humanists wonder what they they can do to more effectively convey their criticisms of religion, most of them have never read, and indeed have barely even heard of, a book written exactly a century ago containing the most devastating and complete philosophical attack on Christian psychology, Christian beliefs and Christian values ever written: Nietzsche’s Der Antichrist.
1888 was the final productive year of the life of Friedrich Nietzsche, but it was a year of incredible activity. He wrote five books during a six-month period in the latter part of that year. After that, he wrote nothing. Nietzsche’s works of 1888 have not received enough attention, especially given the inclination of many to concentrate primarily on the flamboyant and somewhat confusing Also Spracht Zarathustra, a book of intricate allegories and parables which requires that one already understand the principal elements of Nietzschean thought in order to decipher its hidden relationships and meanings. Zarathustra will be clearer if it is read at the end of a course of study of Nietzsche, not at the beginning.
The first book of 1888 was The Case of Wagner, in which Nietzsche set forth his aesthetic and philosophical objections to the music and the writings of his former close friend Richard Wagner… Next came The Twilight of the Idols (in German, Die Gotzen-dammerung, an obvious parody of Wagner’s Die Gotterdammerung, “The Twilight of the Gods”), in which he criticizes romanticism, Schopenhauer’s pessimism, German culture, Socrates’ acceptance of death as a “healing” of the disease of life, Christianity, and a good many other things. Then, in September of 1888, Nietzsche wrote Der Antichrist.
Unlike Zarathustra, there can be no mistaking the language or the intention of Der Antichrist, a work of exceedingly clear prose and seldom-equalled polemics. Even today, the depth of Nietzsche’s contempt for everything Christianity represents will surprise and shock many people, and not only devout Christians. Unlike other critics of religion, Nietzsche’s attack extends beyond religious theology to Christian-derived concepts that have spread out far beyond their ecclesiastical origins, to the very core of the value-system of Western, Christianized society.
Der Antichrist begins with a warning that “This book belongs to the very few,” perhaps to no one yet living. Nietzsche hints that only those who have already mastered the obscure symbolism of his Zarathustra could appreciate this work. Warnings aside, he begins by sketching the idea of declining vs. ascending life and culture. An animal, a species, or an individual is “depraved” or “decadent” when it loses its instincts for that which sustains its life, and “prefers what is harmful to it.” Life itself presupposes an instinct for growth, for sustinence, for “the will to power”, the striving for some degree of control and mastery of one’s surroundings. Christianity sets itself up in opposition to those instincts, and hence Christianity is an expression of decadence, a negation of the will to life [Antichrist, section 6].
“Pity”, says Nietzsche, is “practical nihilism”, the contagion of suffering. By elevating pity to a value—indeed, the highest value—its depressive effects thwart those instincts which preserve life, establishing the deformed or the sick as the standard of value. [A 7] To Nietzsche, the rejection of pity did not proscribe generosity, magnanimity, or benevolence—indeed, the latter are mandated for “higher” types—; what is rejected is to allow the ill-constituted to define what is good. Nietzsche was not hostile to the sick—Zarathustra bids the sick to “become convalescents”, and expresses sympathetic understanding of their unhappy frame of mind [Z I 3]—but what he opposed was the use of the existence of sickness and other afflications to thereby claim “life is refuted” [Z I 9].
No doubt Nietzsche’s attack on “pity” was triggered in part by his revulsion against Wagner’s blatantly irrational opera Parsifal, in which the formerly irreligious Wagner returned once again to pious Christian themes. In Parsifal, a series of calamities occur because a once-holy knight succumbs to “sins of the flesh,” and it is prophesied that the situation cannot be remedied by any act of self-directed effort, but only by one “through pity made wise, a pure fool.” Nietzsche’s contempt for the limp Christianity in Parsifal and for “the pure fool” knew no bounds. The already-strained bond between the two men, who were once extremely close, was irreparably broken.
Nietzsche explains that the pessimistic philosophy of Arthur Schopenhauer is, like Chrisitanity, decadent. Schopenhauer taught that since it is impossible to satisfy the desires of the will, one must ceaselessly renounce striving for what one wants, and become resigned to unhappiness. In the late 19th century Schopenhauer’s doctrines were extremely popular, especially among the Wagnerians. Wagner’s monumental Tristan and Isolde is an expression of Schopenhauerian nihilism, as the lovers sing of the impossibility of earthly happiness, and of their expected mystical union in the realm of “night” after their death. The opera closes with Isolde’s famous liebestod, or “love-death”, as she sings of a vision of her dead lover gloriously and mystically transfigured in the nether-regions, then dies to join him. Schopenhauer was hostile to life, says Nietzsche, “therefore pity became for him a virtue.” [A 7]
Nietzsche charges that Christianity denigrates the world around us as mere “appearance”, a position grounded in the philosophy of Plato and Kant, and hence invents a “completely fabricated” world of pure spirit. However, “pure spirit is pure lie,” and hence the theologian requires one to see the world falsely in order to remain a member in good standing in the religion. The Christian outlook was, he says, immensely bolstered against the attacks of the Enlightenment by Immanuel Kant, whose philosophy renders reality unknowable. (For Kant a virtue is something harmful to one’s life, a view Nietzsche could never accept. If you want to do something, Kant would say your action cannot possibly be virtuous; any action which contains an element of self-interest is by definition not virtuous.) Nietzsche summarizes, “anti-nature as instinct, German decadence as philosophy—that is Kant.” [A 8-11]
Nietzsche praises the skeptic (or “free spirit”) who rejects the priestly inversion of “true” and “untrue”. He says we skeptics no longer think of human life as having its origins in “spirit” or in “divinity”, but recognize the human race as a natural part of the animal kingdom… [A 12-14].
Returning to the theme of Christian doctrine as misrepresentation, Nietzsche charges that “in Christianity neither morality nor religion come into contact with reality at any point.” The religion deals with imaginary causes (such as God, soul, spirit) and imaginary effects (sin, grace, etc.), and the relationships between imaginary beings (God, souls, angels, etc.). It also has its own imaginary natural science (wholly anthropormorphic and non-naturalistic), an imaginary human psychology (based on repentance, temptation, etc.), as well as an imaginary teleology (apocalypse, the kingdom of God, etc.). Nietzsche concludes that this “entire fictional world has its roots in the hatred of the natural” world, a hatred which reveals its origin. For “who alone has reason to lie himself out of actuality? He who suffers from it” [A 15]. Here is the proof which convinced Nietzsche that Christianity is not only decadent in its origins, but rotten to its very core: no one reasonably satisfied with his own mind and abilities would wish to see the real world replaced with a lie.
 Comparing religions, Nietzsche came to the conclusion that in a healthy society, its gods represent the highest ideals, aspirations, and sense of competence of that people. For example, Zeus and Apollo were obviously powerful ideals for Greek society, an image of the mightiest mortals projected into the heavens. Such gods are fully human, and display human strengths and weaknesses alike. The Christian God, however, shows none of the normal human attributes and appetites. It is unthinkable for this God to desire sex, food, or even openly display revengefulness (as did the Greek gods). Such a God is clearly emaciated, sick, castrated, a reflection of the people who invented him. If a god symbolizes a people’s perceived sense of impotence, he will degenerate into being merely “good” (an idealized image of the kind master, as desired by all slaves), void of all genuinely human attributes. The Christian God represents the “divinity of decadence,” the reduction of the divine into a God who is the contradiction of life. Those impotent people who created such a God in their own image do not wish to call themselves “the weak,” so they call themselves “the good.” [A 16-19].
Comparing religions, Nietzsche came to the conclusion that in a healthy society, its gods represent the highest ideals, aspirations, and sense of competence of that people. For example, Zeus and Apollo were obviously powerful ideals for Greek society, an image of the mightiest mortals projected into the heavens. Such gods are fully human, and display human strengths and weaknesses alike. The Christian God, however, shows none of the normal human attributes and appetites. It is unthinkable for this God to desire sex, food, or even openly display revengefulness (as did the Greek gods). Such a God is clearly emaciated, sick, castrated, a reflection of the people who invented him. If a god symbolizes a people’s perceived sense of impotence, he will degenerate into being merely “good” (an idealized image of the kind master, as desired by all slaves), void of all genuinely human attributes. The Christian God represents the “divinity of decadence,” the reduction of the divine into a God who is the contradiction of life. Those impotent people who created such a God in their own image do not wish to call themselves “the weak,” so they call themselves “the good.” [A 16-19].
Nietzsche next compares Christianity to Buddhism. Both, he says, are religions of decadence, but Buddhism is a hundred times wiser and more realistic. Buddha does not demand prayer or aesceticism, demanding instead ideas which produce repose or cheerfulness. Buddhism, he says, is most at home in the higher and learned classes, while Christianity represents the revengeful instincts of the subjugated and the oppressed. Buddhism promotes hygiene, while Christianity repudiates hygiene as sensuality. Buddhism is a religion for mature, older cultures, for persons grown kindly and gentle—Europe is not nearly ripe for Buddhism. Christianity, however, tamed uncivilized barbarians, needing to subjugate wild “beasts of prey,” who cannot control their own “will to power.” The way it did so was to make them sick, making them thereby too weak to follow their destructive instincts. Thus Buddhism is a religion suited to the decadence and fatigue of an ancient civilization, while Christianity was useful in taming barbarians, where no civilization had existed at all. [A 20-22].
Nietzsche next emphasises Christianity’s origin in Judaism, and its continuity with Jewish theology. He was fond of pointing out the essential Jewishness of Christianity as a foil to the anti-Semites he so despised, effectively taunting them, “you who hate the Jews so, why did you adopt their religion?”. It was the Jews, he asserts, who first falsified the inner and outer world with a metaphysically complete anti-world, one in which natural causality plays no role. (One might of course object that such a concept considerably predates Old Testament times.) The Jews did this, however, not out of hatred or decadence, but for a good reason: to survive. The Jews’ will for survival is, he asserts, the most powerful “vital energy” in history, and Nietzsche admired those who struggle mightily to survive and prevail. As captives and slaves of more powerful civilizations—the Babylonians and the Egyptians—the Jews shrewdly allied themselves with every “decadence” movement, with everything that weakens a society, not because they were decadent themselves, but in order to weaken their oppressors. Thus, Nietzsche views the Jews as shrewdly inculcating guilt, resentment, and other values hostile to life among their oppressors as a form of ideological germ warfare, taking care not to become fully infected themselves. This technique was ultimately successful in defeating stronger parties—Babylonians, Egyptians, and Romans—by in essence making them “sick,” and hence less powerful. (The Romans, of course, succumbed to the Christian form of Judaism, in this view.) This parallels St. Augustine’s comment, quoting Seneca, that the Jews “have imposed their customs on their conquerors.” [A 23-26; De Civitate Dei VI 11]
“On a soil falsified in this way, where all nature, all natural value, all reality had the profoundest instincts of the ruling class against it, there arose Christianity, a form of mortal hostility to reality as yet unsurpassed.” The revolt led by Jesus was not primarily religious, says Nietzsche, but was instead a secular revolt against the power of the Jewish religious authorities. The very dregs of Jewish society rose up in “revolt against ‘the good and the just’, against ‘the saints of Israel’.” This was the political crime of Jesus, a crime of which he was surely guilty, and for which he was crucified. Nietzsche examines the psychology of Jesus, as is best possible from the Biblical accounts, and detects a profound sense of withdrawl: resist not evil, the kingdom of God is within you, etc. He sees parallels in the psychology of Christ not with some hero, but with Dostoyevsky’s The Idiot. (Dostoyevsky is not mentioned here by name, but we know from other sources that this is the “idiot” Nietzsche had in mind.)
Nietzsche deduces that the earliest Christians sought to retreat into a state of extreme withdrawl from “the world”, undisturbed by reality of any kind. They rejected all strong feelings, favorable or otherwise. Their fear of pain, even in infinitely small amounts, “cannot end otherwise than in a religion of love.” Thus Nietzsche sees early Christianity as promoting an extremely dysfunctional state resembling autism, a defense mechanism for those who cannot deal with reality. Noting Christianity’s claims to deny the world, and its stand in opposition to every active virtue, Nietzsche asks how can any person of dignity and accomplishment not feel ashamed to be called a Christian? [A 27-30; 38]…
By placing the center of life outside of life, in “the beyond”, Nietzsche says we deprive life of any focus or center whatsoever. The invention of the immortal soul automatically levels all rank in society: “‘immortality’ conceded to every Peter and Paul has so far been greatest, the most malignant attempt to assassinate noble humanity”. Thus “little prigs and three-quarter madmen may have the conceit that the laws of nature are constantly broken for their sakes,” thereby obiliterating all distinctions grounded in merit, knowledge or accomplishment. Christianity owes its success to this flattering of the vanity of “all the failures, all the rebellious-minded, all the less favored, the whole scum and refuse of humanity who were thus won over to it.” For Christianity is “a revolt of everything that crawls upon the ground directed against that which is elevated: the gospel of the ‘lowly’ makes low.” Here we clearly see Nietzsche’s repudiation of Christianity’s attitudes as well as its theology: as he pointedly noted in Ecce Homo, “no one hitherto has felt Christian morality beneath him”. All others saw it as an unattainable ideal. [A 43; EH 4 (“Why I Am a Fatality”) 8] Pre-Christian thinkers did not, of course, see poverty as suggestive of virtue, but rather of its absence. One point Nietzsche was unable to either forgive or forget was that the enemies of the early Christians were “the intelligent ones”, persons far more civilized, erudite, and accomplished than themselves, people who Nietzsche felt more fit to rule than the Christians.
Nietzsche sees the Gospels as proof that corruption of Christ’s ideals had already occurred in those early Christian communities. They say “Judge Not!”, then send to Hell anyone who stands in their way. Arrogance poses as modesty. He explains how the Gospel typifies the morality of ressentiment ( a French term Nietzsche used in his German texts), a spirit of vindictiveness and covert revengefulness common among those who are seething with a sense of their own impotence, and hence must hide their desire for vengeance. “Paul was the greatest of all apostles of revenge,” writes Nietzsche [A 44-45]…
At this point, Nietzsche advises the reader to “put on gloves” when reading the New Testament, because one is in proximity to “so much uncleanliness.” It is impossible, he says, to read the New Testament without feeling a partiality for everything it attacks. The Scribes and the Pharisees must have had considerable merit, to have been attacked by the rabble in such a manner. Everything the first Christians hate has value, for theirs is the unthinking hatred of the rabble for everyone who is not a wretched failure like themselves. Nietzsche sees Christianity’s origins in what Marxists would call “class warfare,” and sides with those possessing learning and self-discipline against those having neither. [A 46].
He next turns to a point essential for the understanding of Nietzschean thought: the inevitability of a “warfare” between Christianity and science. Because Christianity is a religion which has no contact with reality at any point, it “must naturally be a mortal enemy of ‘the wisdom of the world,’ that is to say, of science.” Here “science” is not to be understood as merely the physical sciences, but as any rigorous and disciplined field of human knowledge, all of which are potentially threats to Christian dogma. Hence Christianity must calumniate the “disciplining of the intellect” and intellectual freedom, bringing all organized secular knowledge into disrepute; for “Paul understood the need for the lie, for faith.” Nietzsche refers to the Genesis fable of Eve’s temptation, asking whether its significance has really been understood: “God’s mortal terror of science”? The priest perceives only one great danger: the human intellect unfettered. Continuing the metaphor of science as eating from the tree of knowledge:
Science makes godlike—it is all over with priests and gods when man becomes scientific. Moral: science is the forbidden as such—it alone is forbidden. Science is the first sin, the original sin. This alone is morality “Thou shalt not know”—the rest follows.
The priest invents and encourages every kind of suffering and distress so that man may not have the opportunity to become scientific, which requires a considerable degree of free time, health, and an outlook of confident positivism. Thus, the religious authorities work hard to make and keep people feeling sinful, unworthy, and unhappy. [A 47-49]
In previous works, Nietzsche had emphasised the necessity of struggling hard to uncover truth, of preferring an unpleasant truth to an agreeable delusion. [The Gay Science 344; Beyond Good and Evil 39] Consequently, he sees another reason for being suspicious of Christianity in its notion that “faith makes blessed,” that is, creates a state of pleasure in harmony with God. He re-iterates that whether or not a doctrine is comforting tells us nothing about its truth. Nor does the willingness of martyrs to suffer and die for a belief constitute any proof of veracity, suggesting that a visit to a madhouse will suffice to demonstrate the fallaciousness of such arguments. Martyrdoms have, in fact, been a great misfortune throughout history because “they have seduced” us into questionable doctrines. “Blood is the worst witness of truth”. [A 50-51, 53]
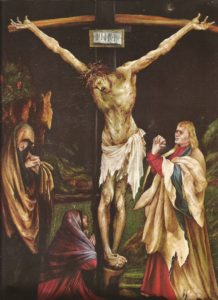 Christianity, says Nietzsche, needs sickness as much as Hellenism needed health. (To understand this point, compare a Greek statue of a tall, handsome, naked God with a Christian religious image of an unhygenic, slovenly figure suffering greatly.) One does not “convert” to Christianity, but rather one must be made “sick enough” for it. The Christian movement was, from its beginning, “a collective movement of outcast and refuse elements of every kind,” seeking to come to power through it. “In hoc signo decadence conquered.” Christianity also stands in opposition to intellectual, as well as physical, health. To doubt becomes sin. Nietzsche defines faith as “not wanting to know what is true,” a description which strikes me as stunning, and quite exact. [A 51-52]…
Christianity, says Nietzsche, needs sickness as much as Hellenism needed health. (To understand this point, compare a Greek statue of a tall, handsome, naked God with a Christian religious image of an unhygenic, slovenly figure suffering greatly.) One does not “convert” to Christianity, but rather one must be made “sick enough” for it. The Christian movement was, from its beginning, “a collective movement of outcast and refuse elements of every kind,” seeking to come to power through it. “In hoc signo decadence conquered.” Christianity also stands in opposition to intellectual, as well as physical, health. To doubt becomes sin. Nietzsche defines faith as “not wanting to know what is true,” a description which strikes me as stunning, and quite exact. [A 51-52]…
Nietzsche now turns to consider why the lie is told. Once again, Christian teachings are compared to those of another religion, that of Manu, “an incomparably spiritual and superior work.” Unlike the Bible, the Law-Book of Manu is a means for the “noble orders” to keep the mob under control. Here, human love, sensuality, and procreation are treated not with revulsion, but with reverence and respect. After a people acquires a certain experience and success in life, its most “enlightened,” most “reflective and far-sighted class” sets down a law summarizing its formula for success in life, which is represented as a revelation from a deity, for it to be accepted unquestioningly. Such a set of rules is a formula for obtaining “happiness, beauty, benevolence on earth.” This aristocratic group considers “the hard task a privilege… life becomes harder and harder as it approaches the heights—the coldness increases, the responsibility increases.” All ugly manners and pessimism are below such leaders: “indignation is the privilege of the Chandala” (Indian untouchable). What is bad? “Everything that proceeds from weakness, from revengefulness.” [A 57]
Thus Nietzsche holds that the purpose for the lie of “faith” makes a great difference in the effect it will have on society. Do the priests lie in order to preserve (as in the book of Manu, and presumably Greek myth), or to destroy (as in Christianity)? Thus Christians and socialist Anarchists are identical in their instincts: both seek solely to destroy. The Roman civilization was a magnificent edifice for the prosperity and advancement of life, “the most magnificent form of organization under difficult circumstances which has yet been achieved”, which Christianity sought to destroy because life prospered within it. These “holy anarchists” made it a religious duty to “destroy the world”, which actually meant, “destroy the Roman Empire”. They weakened the Empire so much that even “Teutons and other louts” could conquer it. Christianity was the “vampire” of the Roman Empire. These “stealthy vermin,” shrouded in night and fog, crept up and “sucked out” from everyone “the seriousness for true things and any instinct for reality.” Christianity moved truth into “the beyond”, and “with the beyond one kills life.”
Before charging Nietzsche with possibly irresponsible invective, compare the above with Gibbon’s summary of the role of Christianity in The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire:
The clergy successfully preached the doctrines of patience and pusillanimity; the active virtues of society were discouraged; and the last remains of a military spirit were buried in the cloister: a large portion of public and private wealth was consecrated to the specious demands of charity and devotion; and the soldiers’ pay was lavished on the useless multitudes of both sexes who could only plead the merits of abstinence and chastity.
On the positive side, Gibbon notes that even though Christianity clearly hastened the demise of Rome, it “mollified the ferocious temper of the conquerors”. This would seem to parallel Nietzsche’s view that Christianity seeks to control the uncivilized not by teaching them the self-discipline needed to control their own impulses, but by making them too “sick” to do a great deal of harm. [A 58; Gibbon, Chapter 38 ]
“The whole labor of the Ancient World in vain!”: thus does Nietzsche overstate the magnitude of the calamity. (Our civilization’s heritage from classical antiquity is obviously far from nothing!). Nonetheless, no one who prefers civilization to barbarism can be indifferent to the point here raised. Nietzsche emphasises that the foundations for a scholarly culture, for science, medicine, philosophy, and art, had all been magnificently laid in antiquity, only to be destroyed by the advent of Christianity. Today, he says, we have certainly made great progress, but each of us still retains bad Christian habits and instincts which we must work hard to overcome. Two thousand years ago, we had acquired that clear eye for reality, patience, attention to detail, seriousness in even small matters—and it was not obtained by “drill” or from habit, but flowed naturally from a civilized instinct. All this was lost! And it was not lost to some natural disaster or destroyed by “Teutons and other buffalos” (Nietzsche’s contempt for German nationalism and militarism knew no bounds!) but it was “ruined by cunning, stealthy, invisible, anemic vampires. Not vanquished-merely drained. Hidden vengefulness, petty envy become master.” Everything that was miserable and filled with bad feelings about itself came to the top at once. [A 59]…
The meaning and significance of the Renaissance is considered in this next-to-last section of Der Antichrist. “The Germans have cheated Europe out of the last great cultural harvest which Europe could still have brought home—that of the Renaissance.” Nietzsche views the Renaissance as “the revaluation of Christian values,” that is, the repudiation of life-denying Christian values and their replacement with secular values which emphasise art, culture, learning, and so on. With the Renaissance in Italy, Christianity was being repudiated at its very seat. “Christianity no longer sat on the Papal throne! Life sat there instead!”
 Nietzsche envisions the immortal roar of laughter that would have risen up from the gods on Mount Olympus had Cesare Borgia actually succeeded in his ruthless quest to become Pope. (The notorious murderer and poisoner Borgia, the son of Pope Alexander VI, spread his power ruthlessly across Italy. Father and son appointed or poisoned Cardinals as needed to position the son for election as the next Pope. However, the plan went awry when they accidentally tasted some wine that had been “prepared” to rid themselves of a wealthy cardinal! The father died, and the son became gravely ill, and was hence in no position to coerce the selection of his father’s successor.)
Nietzsche envisions the immortal roar of laughter that would have risen up from the gods on Mount Olympus had Cesare Borgia actually succeeded in his ruthless quest to become Pope. (The notorious murderer and poisoner Borgia, the son of Pope Alexander VI, spread his power ruthlessly across Italy. Father and son appointed or poisoned Cardinals as needed to position the son for election as the next Pope. However, the plan went awry when they accidentally tasted some wine that had been “prepared” to rid themselves of a wealthy cardinal! The father died, and the son became gravely ill, and was hence in no position to coerce the selection of his father’s successor.)
Nietzsche laments that this great world-historical event—life returning to Western culture—was ultimately undone by the work of “a German monk,” Martin Luther, who harbored the vengeful instincts of “a failed priest.” Through Luther’s Reformation, and Catholicism’s answer to it, the Counter-Reformation, Christianity was restored. [A 60] One might be tempted to dismiss Nietzsche’s dramatic interpretation of the Renaissance, except that his view meshes with that of Jacob Burckhardt, the single most influential historian of Renaissance civilization who ever lived. Burckhardt’s monumental work, The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy (1860), has influenced the study of that period as much as Gibbon’s Decline and Fall did that of ancient Rome. Neitzsche and Burckhardt were colleagues at the University of Basle, and friends as well. In the first section of his Civilization, Burchkardt writes that the greatest danger ever faced by the Papacy was its secularization during the Renaissance.
The danger that came from within, from the Popes themselves and their nipoti (relativies, “nepotism”), was set aside for centuries by the German Reformation… The moral salvation of the papacy was due to its mortal enemies… Without the Reformation—if indeed it is possible to think it away—the whole ecclesiastical state would have passed into secular hands long ago.
Pope Julius II, powerfully anti-Borgia, was “the savior of the Papacy,” who put an end to the practice of the buying and selling of Church positions. However, the Counter-Reformation “annihlated the higher spiritual life of the people,” according to Burckhardt. Nietzsche would have said this was because they had become Christian once again.
The final section of Der Antichrist contains “the most terrible charge” against the Christian Church that “any prosecutor has ever uttered… I call Christianity the one great curse, the one great intrinsic depravity, the one great instinct for revenge for which no expedient is sufficiently poisonous, secret, subterranean, petty—I call it the one immortal blemish of mankind.” Nietzsche suggests that instead of calculating time from the “unlucky day” on which this “fatality” arose, time should be measured instead from its last day: “from today.” [A 62].
Needless to say, Nietzsche’s Der Antichrist did not prove to be the dagger in the heart of Christianity he hoped it would. After finishing this work (which was not actually published until 1895), Nietzsche wrote Ecce Homo, a philosophical autobiography, in which we first see signs of the self-aggrandizing delusions which were to characterize his incipient mental collapse. The final major work of 1888 was Nietzsche Contra Wagner, containing more polemics against the “decadence” and anti-Semetism of Wagner’s followers, much of which was taken from his earlier published works. Nietzsche’s philosophical writings end there, in the closing weeks of 1888. No doubt the breakdown which followed was hastened by the frantic pace of work during that period. Living in Turin, Italy, alone as was his habit, he continued to send letters to his family and friends.
Early in January, 1889, Nietzsche collapsed on the street in Turin. Some local people helped him back to his room, and he was soon alone again. On January 6 he sent letters to Burckhardt and to Franz Overbeck, another friend and colleague at the University of Basle, displaying obvious signs of insanity. Burckhardt, quite concerned, consulted Overbeck, who was soon on a train headed for Turin to assist his friend. Overbeck brought Nietzsche back to his mother in Germany. He was placed in an institution for a few months, and was then released to the care of his family, where he lived another eleven years as an invalid. Nietzsche actually died twice: his mind died in 1889, while his body lived on helplessly until 1900…
If Nietzsche’s polemically effective suggestion had been adopted—to begin counting time from the start of Christianity’s presumed demise, the writing of Der Antichrist—then I would now be writing these words in the year 100 P.C., the hundredth year of the post-Christian era. It would obviously be premature to expect such a calendar to gain widespread acceptance today! Yet the failure of Nietzsche’s impossibly high expectations should not cause us to overlook the significance of this monumental work, with its searing insights into the psychology of Christian belief. All those who wish not to renounce life but to affirm it, all who seek to proclaim a triumphant “yes” to human prosperity, knowledge, and happiness, will find in Der Antichrist invaluable insights on how those goals can be achieved—and on what stands on the way of them.
Notes:
There are two excellent English translations of Der Antichrist readily available, one by R. J. Hollingdale (Penguin Classics, 1968), the other by Walter Kaufmann (in Kaufmann’s The Portable Nietzsche, Penguin Books, 1978).
by Evropa Soberana
Appendix to chapter 3:
Nietzsche on Christianity
On the Genealogy of Morality (1887), 1st treatise, § 8 [1]
But you fail to understand that? You have no eye for something that needed two millennia to emerge victorious…?
This Jesus of Nazareth, the personified evangelist of love, this ‘Saviour’ bringing holiness and victory to the poor, to the sick, to the sinners—was he not that very seduction in its most sinister and most irresistible form, the seduction and detour to exactly those Judaic values and innovations in ideals?
Didn’t Israel attain, precisely with the detour of this ‘Saviour’, of this apparent enemy against and dissolver of Israel, the final goal of its sublime thirst for vengeance?
Isn’t it part of the secret black art of a truly great politics of revenge, a farsighted, underground, slowly expropriating, and premeditated revenge, that Israel itself had to disown and nail to the cross, like some mortal enemy, the tool essential to its revenge before all the world, so that ‘all the world’, that is, all Israel’s enemies, could then take this particular bait without a second thought?…
At least it is certain that sub hoc signo Israel, with its vengeance and transvaluation of the worth of all other previous values, has triumphed again and again over all other ideals, over all nobler ideals.
§ 16
The two opposing values ‘good and bad’ and ‘good and evil’ have fought a fearful battle on earth for thousands of years… The symbol of this battle, written in a script which has remained legible through all human history up to the present, is called ‘Rome against Judea, Judea against Rome’. To this point there has been no greater event than this war, this posing of a question, this contradiction between deadly enemies.
Rome felt that the Jew was like something contrary to nature itself, its antipodal monstrum, as it were. In Rome the Jew was considered ‘convicted of hatred against the entire human race’. And that view was correct, to the extent that we are right to link the health and the future of the human race to the unconditional rule of aristocratic values—to Roman values…
By contrast, how did the Jews feel about Rome? We can guess that from a thousand signs, but it is sufficient to treat ourselves again to the Apocalypse of John, that wildest of all written outbursts which vengeance has on its conscience. (Incidentally, we must not underestimate the deep consistency of the Christian instinct when it ascribed this particular book of hate to the name of the disciple of love, the same man to whom it attributed that enthusiastic amorous gospel—there is some truth to this, no matter how much literary counterfeiting may have been necessary for this purpose.)
The Romans were indeed strong and noble men, stronger and nobler than any people who had lived on earth up until then or even than any people who had ever been dreamed up. Everything they left as remains, every inscription, is delightful, provided that we can guess what is doing the writing there.
By contrast, the Jews were par excellence that priestly people of resentment, who possessed an unparalleled genius for popular morality.
Which of them has proved victorious for the time being, Rome or Judea? Surely there’s not the slightest doubt. Just think of who it is people bow down to today in Rome itself as the personification of all the highest values (and not only in Rome, but in almost half the earth, all the places where people have become merely tame or want to become tame): in front of three Jews, as we know, and one Jewess—in front of Jesus of Nazareth, the fisherman Peter, the carpet maker Paul, and the mother of the first-mentioned Jesus, named Mary.
This is very remarkable: without doubt Rome has been conquered.
Tommaso Laureti, The Triumph of Christianity (also called The Triumph of the Cross, painted in 1585). The story of how an oriental messiah, with anorexic and masochistic air, came to replace the strong pagan gods.
The Anti-Christ: A Curse on Christianity (written in 1888)
§ 24
This is precisely why the Jews are the most disastrous people in world history: they have left such a falsified humanity in their wake that even today Christians can think of themselves as anti-Jewish without understanding that they are the ultimate conclusion of Judaism.
§ 58
The harvest is blighted overnight… That which stood there aere perennis, the imperium Romanum, the most magnificent form of organisation under difficult conditions that has ever been achieved, and compared to which everything before it and after it appears as patchwork, bungling, dilettantism—those holy anarchists made it a matter of ‘piety’ to destroy ‘the world’, which is to say, the imperium Romanum, so that in the end not a stone stood upon another.
The Christian and the anarchist: both are décadents; both are incapable of any act that is not disintegrating, poisonous, degenerating, blood-sucking; both have an instinct of mortal hatred of everything that stands up, and is great, and has durability, and promises life a future…
Christianity was the vampire of the imperium Romanum—overnight it destroyed the vast achievement of the Romans: the conquest of the soil for a great culture that could await its time. Can it be that this fact is not yet understood?
The imperium Romanum that we know, and that the history of the Roman provinces teaches us to know better and better—this most admirable of all works of art in the grand manner was merely the beginning, and the structure to follow was to prove its worth for thousands of years.
To this day, nothing on a like scale sub specie aeterni has been brought into being, or even dreamed of! This organisation was strong enough to withstand bad emperors: the accident of personality has nothing to do with such things—the first principle of all genuinely great architecture.
But it was not strong enough to stand up against the corruptest of all forms of corruption—against Christians… These stealthy worms, which under the cover of night, mist and duplicity, crept upon every individual, sucking him dry of all earnest interest in real things, of all instinct for reality—this cowardly, effeminate and sugar-coated gang gradually alienated all ‘souls’, step by step, from that colossal edifice, turning against it all the meritorious, manly and noble natures that had found in the cause of Rome their own cause, their own serious purpose, their own pride.
One has but to read Lucretius to know what Epicurus made war upon—not paganism, but ‘Christianity’, which is to say, the corruption of souls by means of the concepts of guilt, punishment and immortality. He combated the subterranean cults, the whole of latent Christianity—to deny immortality was already a form of genuine salvation. Epicurus had triumphed, and every respectable intellect in Rome was Epicurean—when Paul appeared…
Paul, the Chandala hatred of Rome, of ‘the world’, in the flesh and inspired by genius—the Jew, the eternal Jew par excellence…
What he saw was how, with the aid of the small sectarian Christian movement that stood apart from Judaism, a ‘world conflagration’ might be kindled; how, with the symbol of ‘God on the cross’, all secret seditions, all the fruits of anarchistic intrigues in the empire, might be amalgamated into one immense power.
‘Salvation is of the Jews’. Christianity is the formula for exceeding and summing up the subterranean cults of all varieties, that of Osiris, that of the Great Mother, that of Mithras, for instance: in his discernment of this fact the genius of Paul showed itself.
This was his revelation at Damascus: he grasped the fact that he needed the belief in immortality in order to rob ‘the world’ of its value, that the concept of ‘hell’ would master Rome—that the notion of a ‘beyond’ is the death of life… Nihilist and Christian: they rhyme in German, and they do more than rhyme…
§ 59
The whole labour of the ancient world gone for naught: I have no word to describe the feelings that such an enormity arouses in me!
And, considering the fact that its labour was merely preparatory, that with adamantine self-consciousness it laid only the foundations for a work to go on for thousands of years, the whole meaning of antiquity disappears…
To what end the Greeks? to what end the Romans? All the prerequisites to a learned culture, all the methods of science, were already there and had been there for two thousand years! All gone for naught! All overwhelmed in a night, but not by a convulsion of nature! But brought to shame by crafty, sneaking, invisible, anæmic vampires! Not conquered,—only sucked dry…!
Hidden vengefulness, petty envy, became master! Everything wretched, intrinsically ailing, and invaded by bad feelings, the whole ghetto-world of the soul was at once on top! One needs but read any of the Christian agitators, for example, St. Augustine, in order to realize, in order to smell, what filthy fellows came to the top.
§ 61
Here it becomes necessary to call up a memory that must be a hundred times more painful to Germans. The Germans have destroyed for Europe the last great harvest of civilisation that Europe was ever to reap—the Renaissance. Is it understood at last, will it ever be understood, what the Renaissance was? The transvaluation of Christian values: an attempt with all available means, all instincts and all the resources of genius to bring about a triumph of the opposite values, the more noble values…
To attack at the critical place, at the very seat of Christianity, and there enthrone the more noble values—that is to say, to insinuate them into the instincts, into the most fundamental needs and appetites of those sitting there…
I see before me the possibility of a perfectly heavenly enchantment and spectacle: it seems to me to scintillate with all the vibrations of a fine and delicate beauty, and within it there is an art so divine, so infernally divine, that one might search in vain for thousands of years for another such possibility; I see a spectacle so rich in significance and at the same time so wonderfully full of paradox that it should arouse all the gods on Olympus to immortal laughter: Cæsar Borgia as pope!… Am I understood?… Well then, that would have been the sort of triumph that I alone am longing for today: by it Christianity would have been swept away!
What happened? A German monk, Luther, came to Rome. This monk, with all the vengeful instincts of an unsuccessful priest in him, raised a rebellion against the Renaissance in Rome…
Instead of grasping, with profound thanksgiving, the miracle that had taken place: the conquest of Christianity at its capital—instead of this, his hatred was stimulated by the spectacle. A religious man thinks only of himself. Luther saw only the depravity of the papacy at the very moment when the opposite was becoming apparent: the old corruption, the peccatum originale, Christianity itself, no longer occupied the papal chair! Instead there was life! Instead there was the triumph of life! Instead there was a great yea to all lofty, beautiful and daring things!…
And Luther restored the church.
§ 62
With this I come to a conclusion and pronounce my judgment. I condemn Christianity; I bring against the Christian church the most terrible of all the accusations that an accuser has ever had in his mouth. It is, to me, the greatest of all imaginable corruptions; it seeks to work the ultimate corruption, the worst possible corruption. The Christian church has left nothing untouched by its depravity; it has turned every value into worthlessness, and every truth into a lie, and every integrity into baseness of soul.
This eternal accusation against Christianity I shall write upon all walls, wherever walls are to be found—I have letters that even the blind will be able to see… I call Christianity the one great curse, the one great intrinsic depravity, the one great instinct of revenge, for which no means are venomous enough, or secret, subterranean and small enough, —I call it the one immortal blemish upon the human race…
And mankind reckons time from the dies nefastus when this fatality befell—from the first day of Christianity!—Why not rather from its last?—From today?—
Transvaluation of all values!
__________________
[1] Note of the Ed.: While I follow Evropa Soberana’s quotes of On the Genealogy of Morality, in the case of The Antichrist I added other paragraphs to the author’s quotes from the last pages Nietzsche’s book (included the final page that will appear in the next entry).
Night of 21st-22nd July 1941
Similarities between Germany and Italy—Dante and Luther—Delightful Italian towns—Rome and Paris.
Luther had the merit of rising against the Pope and the organisation of the Church. It was the first of the great revolutions.
And thanks to his translation of the Bible, Luther replaced our dialects by the great German language! It’s remarkable to observe the resemblances between the evolution of Germany and that of Italy. The creators of the language, Dante and Luther, rose against the oecumenical desires of the papacy. Each of the two nations was led to unity, against the dynastic interests, by one man. They achieved their unity against the will of the Pope.
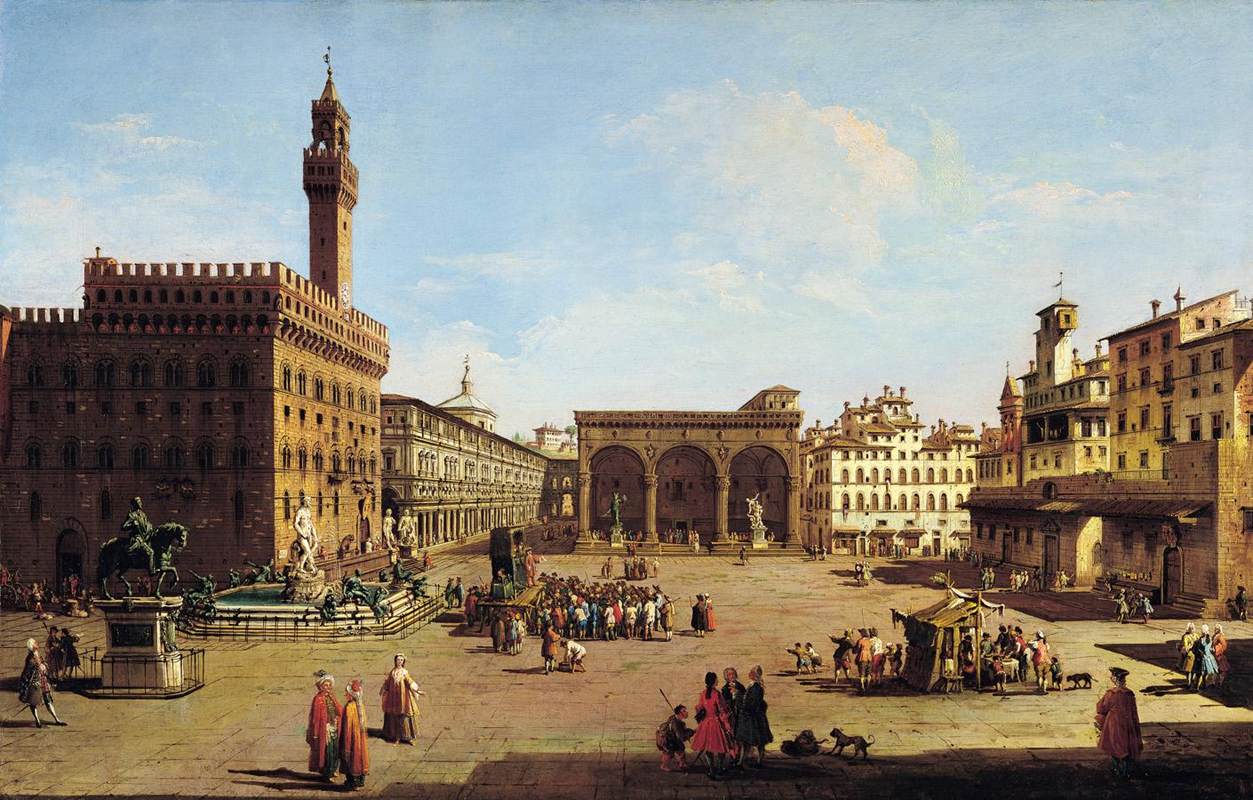
The Italian people’s musical sense, its liking for harmonious proportions, the beauty of its race! The Renaissance was the dawn of a new era, in which Aryan man found himself anew. There’s also our own past on Italian soil. A man who is indifferent to history is a man without hearing, without sight.
Such a man can live, of course—but what a life? The magic of Florence and Rome, of Ravenna, Siena, Perugia! Tuscany and Umbria, how lovely they are! The smallest palazzo in Florence or Rome is worth more than all Windsor Castle. If the English destroy anything in Florence or Rome, it will be a crime.
I’ve seen Rome and Paris, and I must say that Paris, with the exception of the Arc de Triomphe, has nothing on the scale of the Coliseum, or the Castle of San Angelo, or St. Peter’s. These monuments, which are the product of a collective effort, have ceased to be on the scale of the individual. There’s something queer about the Paris buildings, whether it’s those bull’s-eye windows, so badly proportioned, or those gables that obliterate whole façades. If I compare the Pantheon in Rome with the Pantheon in Paris, what a poor building—and what sculptures! What I saw in Paris has disappeared from my memory: Rome really seized hold of me.
Naples, apart from the castle, might be anywhere in South America. But there’s always the courtyard of the royal palace. What nobility of proportions!
My dearest wish would be to be able to wander about in Italy as an unknown painter.
For an introduction to these series, see here.
Below, some indented excerpts of “The Hero as Artist,” the fifth chapter of Civilisation by Kenneth Clark, after which I offer my comments.
Ellipsis omitted between unquoted passages:
In the Middle Ages men had been crushed by this [ancient Roman] gigantic scale. They said that these buildings must be the work of demons, or at best they treated them simply as natural phenomena—like mountains—and built their huts in them.
But by 1500 the Romans had begun to realise that they had been built by men. The lively and intelligent individuals who created the Renaissance, bursting with vitality and confidence, were not in a mood to be crushed by antiquity. They meant to absorb it, to equal it, to master it. They were going to produce their own race of giants and heroes.
In what is commonly described as the decadence of the papacy, the Popes were men of unusual ability who used their international contacts, their great civil service and their increasing wealth in the interests of civilisation. Nicholas V, the friend of Alberti and the humanists, was the first man who saw that papal Rome could revive the grandeurs of pagan Rome.
Pius II, a poet, a lover of nature and of beauty in all its forms, yet gave up his life in an attempt to save Christendom from the Turks. Even Sixtus IV, who was as brutal and cunning as he looks in the wall-painting by Melozzo da Forlo, founded the Vatican library and made the great humanist, Platina, its first prefect. Pope Julius II was able by magnanimity and strength of will to inspire and bully three men of genius—Bramante, Michelangelo and Raphael. Without him Michelangelo would not have painted the Sistine Ceiling, nor Raphael decorated the papal apartments, and so we should have been without two of the greatest visible expressions of spiritual power and humanist philosophy.
The above paragraphs remind me what Nietzsche said almost at the end of his Antichrist: that without the Reformation and Counter-Reformation these rather pagan popes would have brought Christianity down. Clark continues:
The old St Peter’s was one of the largest and most ancient churches in the western world, and certainly the most venerable. Julius decided to pull it down and put something far more splendid in its place. The first step in this visible alliance between Christianity and antiquity was taken when Julius decided to pull down the old basilica.
The men of fifteenth-century Florence had looked back eagerly to the civilisation of Greece and Rome. They sought for ancient authors and read them with passion, and wrote to each other in Latin. Their greatest source of pride was to write prose like Cicero. But the man who really assimilated antique art and recreated it, with all its expressive power made more vital and more intense, was Michelangelo.
Seen by itself the David’s body might be some unusually taut and vivid work of antiquity; it is only when we come to the head that we are aware of a spiritual force that the ancient world never knew. I suppose that this quality, which I may call heroic, is not part of most people’s idea of civilisation. It involves a contempt for convenience and a sacrifice of all those pleasures that contribute to what we call civilised life. It is the enemy of happiness.
And this of course can only remind me of Harold Covington’s extreme contempt for those so-called “nationalists” who watch TV while eating so tasty Nachos that only grow their bellies; always reluctant to come home and fight for the creation of a new nation. Clark continues:
And yet we recognise that to despise material obstacles, and even to defy the blind forces of fate, is man’s supreme achievement; and since, in the end, civilisation depends of man extending his powers of mind and spirit to the utmost, we must reckon the emergence of Michelangelo as one of the great events in the history of western man.
[His drawing of Battle of Cascina] was the first authoritative statement that the human body—that body which, in Gothic times, had been the subject of shame and concealment, that body which Alberti has praised so extravagantly—could be made the means of expressing noble sentiments, life-giving energy and God-like perfection. It was an idea that was to have an incalculable influence on the human mind for four hundred years.
And this brings us back to Rome, and to the terrible Pope. Julius II was not only ambitious for the Catholic Church: he was ambitious for Julius II, and in his new temple he planned to erect the greatest tomb of any ruler since the time of Hadrian. It was a staggering example of superbia; and Michelangelo at that time was not without the same characteristic. I need not go into the question of why the tomb was never built. There was a quarrel—heroes do not easily tolerate the company of other heroes. Nor does it matter to us what the tomb was going to look like. All that matters is that some of the figures made for it survive, and they add something new to the European spirit—something that neither antiquity nor the great civilisations of India and China had ever dreamed of. As a matter of fact the two most finished of them were derived from antiques, but Michelangelo has turned them from athletes to captives, one of them struggling to be free—freedom from mortality?—and the other sensuously resigned.
People sometimes wonder why the Renaissance Italians, with their intelligent curiosity, didn’t make more of a contribution to the history of thought. The reason is that the most profound thought of the time was not expressed in words, but in visual imagery.
For centuries writers on Michelangelo have criticised Julius for taking him off the tomb, on which he had set his heart, and putting him to work on the painting of the Sistine Ceiling, although he always said he hated the act of painting.
Michelangelo’s power of prophetic insight gives one the feeling that he belongs to every epoch, and most of all, perhaps, to the epoch of the great Romantics, of which we are still the most bankrupt heirs. It is the attribute that distinguishes him most sharply from his brilliant rival, Raphael. Michelangelo took no interest in the opposite sex; Leonardo thought of women solely as reproductive mechanisms. But Raphael loved girls as much as any Venetian.
The convention by which great events in biblical or secular history could be enacted only by magnificent physical specimens, handsome and well-groomed, went on for a long time—till the middle of the nineteenth century. Only a very few artists—perhaps only Rembrandt and Caravaggio in the first rank—were independent enough to stand against it. And I think that this convention, which was an element in the so-called grand manner, became a deadening influence on the European mind. It deadened our sense of truth, even our sense of moral responsibility; and led, as we now see, to a hideous reaction.
For an introduction to these series, see here.
Below, some indented excerpts of “Man—the Measure of all Things,” the fourth chapter of Civilisation by Kenneth Clark, after which I offer my comments.
Ellipsis omitted between unquoted passages:
The Pazzi Chapel, built by the great Florentine Brunellesco in about 1430, is in a style that has been called the architecture of humanism. His friend and fellow-architect, Leon Battista Alberti, addressed man in these words: ‘To you is given a body more graceful than other animals.’
There is no better instance of how a burst of civilisation depends on confidence than the Florentine state of mind in the early fifteenth century. For fifty years the fortunes of the republic, which in a material sense had declined, were directed by a group of the most intelligent individuals who have ever been elected to power by a democratic government. From Salutati onwards the Florentine chancellors were scholars, believers in the studia humanitatis, in which learning could be used to achieve a happy life.
In Florence the first thirty years of the fifteenth century were the heroic age of scholarship when new texts were discovered and old texts edited. It was to house these precious texts, any one of which might contain some new revelation that might alter the course of human thought, that Cosimo de Medici built the library of San Marco. It looks to us peaceful and remote—but the first studies that took place there were not remote from life at all. It was the humanist equivalent of the Cavendish Laboratory. The manuscripts unpacked and studied under these harmonious vaults could alter the course of history with an explosion, not of matter, but of mind.
The discipline of trade and banking, in its most austere form, was beginning to be relaxed, and life—a full use of the human faculties—became more important than making money.
The dignity of man. Today these words die on our lips. But in the fifteenth century Florence their meaning was still a fresh and invigorating belief. Gianozzo Manetti, a humanist man of affection, who had seen the seamy side of politics, nevertheless wrote a book entitled On the Dignity and Excellence of Man. And this is the concept that Brunellesco’s friends were making visible.
Gravitas, the heavy tread of moral earnestness, becomes a bore if it is not accompanied by the light step of intelligence. Next to the Pazzi Chapel are the cloisters of Santa Croce, also built by Brunellesco. I said that the Gothic cathedrals were hymns to the divine light. These cloisters happily celebrate the light of human intelligence, and sitting in them I find it quite easy to believe in man. They have the qualities that give distinction to a mathematical theorem: clarity, economy, elegance.
Alberti, in his great book on building, describes the necessity of a public square ‘where young men may be diverted from the mischievousness and folly natural to their age.’ The early Florentine Renaissance was an urban culture, bourgeois properly so-called. Men spent their time in the streets and squares, and in the shops.
Elsewhere I’ve talked about how the modern world of money is inimical to racial interests. As to date, no white nationalist that I know has criticized the barbarous architecture, symptomatic in the worshiping of the new god of capitalism, so well epitomized in both London and New York: the subject of the last episode of Civilisation.
Together with the degenerate music, TV and Hollywood tastes and sexual lifestyles of some nationalists, architecture is another facet where the uncorrupted individual can read the signs of a decadent society; and why he cannot blame non-gentiles for all our problems when even the nationalists themselves are part of this problem.
Remember Clark’s words in the first episode? “If I had to say which was telling the truth about society, a speech by a Minister of Housing or the actual buildings put up in his time, I should believe the buildings.” One only has to contrast the completely soulless edifices we see everyday going to work with Raphael’s town square and see how extremely degraded, Mammonesque in fact our large cities have become.
In the popular imagination, the extreme examples of this degeneracy are the Foundation novels of Asimov and the latest Star Wars films, where a whole planet has become metropolis: the exact opposite of the most humane sci-fi novels by Arthur C. Clarke where, like the Florentines, the white people lived in small Elysian towns. Architecture today is so degenerate that even Roger Scruton in Why Beauty Matters—a 2009 BBC documentary that, unlike Clark’s Civilisation, is marred by the constant presence of non-whites—pays special attention to the sterile architectural forms of today’s world.
I wish young nationalists became believers in the studia humanitatis and familiarise themselves with those intellectuals in the movement that (like Clark) have a much broader sense of European culture than the common white nationalist blogger. I refer to people like Tom Sunic in Europe and Michael O’Meara in America. Both could help us to leave behind the provincial scene so common in the nationalist sphere as well as the simplistic single-cause hypothesis.
It is true that, unlike the Athenians, fifteenth century Florentines were chiefly interested, like contemporary western man, in making money. But like the Athenians the Florentines… loved beauty. Of the landscapes whose beauty mostly caught my attention during a trip through Europe by train, I still remember the Italian, about which Clark said:
Looking at the Tuscan landscape with its terraces of vines and olives and the dark vertical accents of the cypresses, one has the impression of timeless order. There must have been a time when it was all forest and swamp—shapeless, formless; and to bring order out of chaos is a process of civilisation.
Then, in the first years of the sixteenth century, the Venetian painter Giorgione transformed this happy contact with nature into something openly sensual. The ladies who, in the Gothic gardens, had been protected by voluminous draperies, are now naked; and, as a result, his Fête Champêtre opens a new chapter in European art. Giorgione was, indeed, one of the inspired, unpredictable innovators who disturb the course of history; and in this picture he has illustrated one of the comforting illusions of civilised man, the myth of Arcadia, which had been popularised some twenty years earlier by the poet Sannazaro. Of course, it is only a myth. Country life isn’t at all like this, and even on a picnic ants attack the sandwiches and wasps buzz round the wine glasses. But the pastoral fallacy had inspired Theocritus and Virgil, and had not been unknown in the Middle Ages. Giorgione has seen how fundamentally pagan it is.
True, but I don’t believe that the pastoral fallacy is childish. Pace Arthur Clarke, achieving Arcadia is an essentially psychogenic endeavour rather than a technological one. And I sincerely believe that utopia is feasible: only human primitivism, and especially the “monsters from the Id” currently affecting the white peoples, prevent it.
It has long seemed to me wise thinking about an ideal to direct our efforts toward it. It doesn’t matter if the ideal encounters numerous pitfalls: our will should incessantly be directional toward the worlds of the Florentine Fête. If the will of a sufficiently massive amount of white people is noble, the outside world can and will only represent the nobility of that will. Clark said:
With Giorgione’s picnic the balance and enjoyment of our human faculties seems to achieve perfection. But in history all points of supposed perfection have a hint of menace; and Giorgione himself discovers it in that mysterious picture known as the Tempesta.
What on earth is going on? What is the meaning of this half-naked woman suckling a baby, this flash of lightening, this broken column? Nobody knows; nobody has ever known.
To me the meaning is obvious. Even since the Renaissance artists started to see that the cities, more inclined to Mammon than to Raphael’s square, were places of tribulation in contrast to the madonna and her child with the man standing in contrapposto. Broken pillars often symbolize death (that bucolic world was about to die), and the painting’s storm in the background could be interpreted to symbolize urban turmoil.
From David Irving’s web page:
The Table Talks’ content [originally written in shorthand] is more important in my view than Hitler’s Mein Kampf, and possibly even more than his Zweites Buch (1928). It is unadulterated Hitler. He expatiates on virtually every subject under the sun, while his generals and private staff sit patiently and listen, or pretend to listen, to the monologues.
The first excerpt is taken from what Hitler said in a night of July of 1941 (ellipsis omitted between unquoted passages):
Hitler’s Table Talk, 1941-1944
His Private Conversations
Part I
1941
When National Socialism has ruled long enough, it will no longer be possible to conceive of a form of life different from ours. In the long run, National Socialism and religion will no longer be able to exist together.
(On a question from C. S., whether this antagonism might mean a war, the Führer continued:)
No, it does not mean a war. The ideal solution would be to leave the religions to devour themselves, without persecutions. But in that case we must not replace the Church by something equivalent. That would be terrifying! It goes without saying that the whole thing needs a lot of thought. Everything will occur in due time. It is a simple question of honesty, that’s what it will finally boil down to.
The German people’s especial quality is patience; and it’s the only one of the peoples capable of undertaking a revolution in this sphere. It could do it, if only for the reason that only the German people have made moral law the governing principle of action.
The heaviest blow that ever struck humanity was the coming of Christianity. Bolshevism is Christianity’s illegitimate child. Both are inventions of the Jew. The deliberate lie in the matter of religion was introduced into the world by Christianity. Bolshevism practises a lie of the same nature, when it claims to bring liberty to men, whereas in reality it seeks only to enslave them. In the ancient world, the relations between men and gods were founded on an instinctive respect. It was a world enlightened by the idea of tolerance. Christianity was the first creed in the world to exterminate its adversaries in the name of love. Its key-note is intolerance.
Without Christianity, we should not have had Islam. The Roman Empire, under Germanic influence, would have developed in the direction of world-domination, and humanity would not have extinguished fifteen centuries of civilisation at a single stroke.
Let it not be said that Christianity brought man the life of the soul, for that evolution was in the natural order of things. The result of the collapse of the Roman Empire was a night that lasted for centuries.
The Romans had no dislike of the Germans. This is shown by the mere fact that blond hair was fashionable with them. Amongst the Goths there were many men with dark hair.
23rd September 1941, evening
To make death easier for people, the Church holds out to them the bait of a better world. We, for our part, confine ourselves to asking man to fashion his life worthily. For this, it is sufficient for him to conform to the laws of nature. Let’s seek inspiration in these principles, and in the long run we’ll triumph over religion.
10th October 1941, midday
Christianity is a rebellion against natural law, a protest against nature. Taken to its logical extreme, Christianity would mean the systematic cultivation of the human failure.
14th October 1941, midday
Special Guest: Reichsfuehrer Himmler
It may be asked whether concluding a concordat with the churches wouldn’t facilitate our exercise of power.
On this subject one may make the following remarks: Firstly, in this way the authority of the State would be vitiated by the fact of the intervention of a third power concerning which it is impossible to say how long it would remain reliable. In the case of the Anglican Church, this objection does not arise, for England knows she can depend on her Church. But what about the Catholic Church?
I’m convinced that any pact with the Church can offer only a provisional benefit, for sooner or later the scientific spirit will disclose the harmful character of such a compromise. Thus the State will have based its existence on a foundation that one day will collapse.
An educated man retains the sense of the mysteries of nature and bows before the unknowable. An uneducated man, on the other hand, runs the risk of going over to atheism (which is a return to the state of the animal) as soon as he perceives that the State, in sheer opportunism, is making use of false ideas in the matter of religion, whilst in other fields it bases everything on pure science.
That’s why I’ve always kept the Party aloof from religious questions. I’ve thus prevented my Catholic and Protestant supporters from forming groups against one another, and inadvertently knocking each other out with the Bible and the sprinkler. So we never became involved with these Churches’ forms of worship. And if that has momentarily made my task a little more difficult, at least I’ve never run the risk of carrying grist to my opponents’ mill. The help we would have provisionally obtained from a concordat would have quickly become a burden on us. In any case, the main thing is to be clever in this matter and not to look for a struggle where it can be avoided.
Being weighed down by a superstitious past, men are afraid of things that can’t, or can’t yet, be explained—that is to say, of the unknown. If anyone has needs of a metaphysical nature, I can’t satisfy them with the Party’s programme. Time will go by until the moment when science can answer all the questions.
So it’s not opportune to hurl ourselves now into a struggle with the Churches. The best thing is to let Christianity die a natural death. A slow death has something comforting about it. The dogma of Christianity gets worn away before the advances of science. Religion will have to make more and more concessions. Gradually the myths crumble.
Nobody has the right to deprive simple people of their childish certainties until they’ve acquired others that are more reasonable. Indeed, it’s most important that the higher belief should be well established in them before the lower belief has been removed. We must finally achieve this. But it would serve no purpose to replace an old belief by a new one that would merely fill the place left vacant by its predecessor.
♣
It seems to me that nothing would be more foolish than to re-establish the worship of Wotan. Our old mythology had ceased to be viable when Christianity implanted itself. Nothing dies unless it is moribund. At that period the ancient world was divided between the systems of philosophy and the worship of idols. It’s not desirable that the whole of humanity should be stultified—and the only way of getting rid of Christianity is to allow it to die little by little.
Science cannot lie, for it’s always striving, according to the momentary state of knowledge, to deduce what is true. When it makes a mistake, it does so in good faith. It’s Christianity that’s the liar. It’s in perpetual conflict with itself.
One may ask whether the disappearance of Christianity would entail the disappearance of belief in God. That’s not to be desired. The notion of divinity gives most men the opportunity to concretise the feeling they have of supernatural realities. Why should we destroy this wonderful power they have of incarnating the feeling for the divine that is within them?
I envisage the future, therefore, as follows: First of all, to each man his private creed. Superstition shall not lose its rights. We’ll see to it that the Churches cannot spread abroad teachings in conflict with the interests of the State. We shall continue to preach the doctrine of National Socialism, and the young will no longer be taught anything but the truth.
19th October 1941, night
The reason why the ancient world was so pure, light and serene was that it knew nothing of the two great scourges: the pox and Christianity.
Christianity is a prototype of Bolshevism: the mobilisation by the Jew of the masses of slaves with the object of undermining society. Thus one understands that the healthy elements of the Roman world were proof against this doctrine.
Yet Rome to-day allows itself to reproach Bolshevism with having destroyed the Christian churches. As if Christianity hadn’t behaved in the same way towards the pagan temples!
21st October 1941, midday
When one thinks of the opinions held concerning Christianity by our best minds a hundred, two hundred years ago, one is ashamed to realise how little we have since evolved. I didn’t know that Julian the Apostate had passed judgment with such clear-sightedness on Christianity and Christians. You should read what he says on the subject.
Originally, Christianity was merely an incarnation of Bolshevism the destroyer. Nevertheless, the Galilean, who later was called the Christ, intended something quite different. He must be regarded as a popular leader who took up his position against Jewry. Galilee was a colony where the Romans had probably installed Gallic legionaries, and it’s certain that Jesus was not a Jew. The Jews, by the way, regarded Him as the son of a whore—of a whore and a Roman soldier.
The decisive falsification of Jesus’ doctrine was the work of St. Paul. He gave himself to this work with subtlety and for purposes of personal exploitation. For the Galilean’s object was to liberate his country from Jewish oppression.
On the road to Damascus, St. Paul discovered that he could succeed in ruining the Roman State by causing the principle to triumph of the equality of all men before a single God—and by putting beyond the reach of the laws his private notions, which he alleged to be divinely inspired. If, into the bargain, one succeeded in imposing one man as the representative on earth of the only God, that man would possess boundless power.
Nobody was more tolerant than the Romans. Every man could pray to the god of his choice, and a place was even reserved in the temples for the unknown god. Moreover, every man prayed as he chose, and had the right to proclaim his preferences.
St. Paul knew how to exploit this state of affairs in order to conduct his struggle against the Roman State. Nothing has changed; the method has remained sound.
The religious ideas of the Romans are common to all Aryan peoples. The Jew, on the other hand, worshipped and continues to worship, then and now, nothing but the golden calf. The Jewish religion is devoid of all metaphysics and has no foundation but the most repulsive materialism.
It’s since St. Paul’s time that the Jews have manifested themselves as a religious community, for until then they were only a racial community. St. Paul was the first man to take account of the possible advantages of using a religion as a means of propaganda. If the Jew has succeeded in destroying the Roman Empire, that’s because St. Paul transformed a local movement of Aryan opposition to Jewry into a supra-temporal religion, which postulates the equality of all men amongst themselves, and their obedience to an only god. This is what caused the death of the Roman Empire.
It’s striking to observe that Christian ideas, despite all St. Paul’s efforts, had no success in Athens. The philosophy of the Greeks was so much superior to this poverty-stricken rubbish that the Athenians burst out laughing when they listened to the apostle’s teaching. But in Rome St. Paul found the ground prepared for him. His egalitarian theories had what was needed to win over a mass composed of innumerable uprooted people.
Whilst Roman society proved hostile to the new doctrine, Christianity in its pure state stirred the population to revolt. Rome was Bolshevised, and Bolshevism produced exactly the same results in Rome as later in Russia.
Yesterday, the instigator was Saul: the instigator to-day, Mardochai. Saul has changed into St. Paul, and Mardochai into Karl Marx. By exterminating this pest, we shall do humanity a service of which our soldiers can have no idea.
25th October 1941, evening
Special Guests: Reichsfuehrer SS Himmler and SS General (Obergruppenfuehrer) Heydrich
From the rostrum of the Reichstag I prophesied to Jewry that, in the event of war’s proving inevitable, the Jew would disappear from Europe. That race of criminals has on its conscience the two million dead of the First World War, and now already hundreds of thousands more. Let nobody tell me that all the same we can’t park them in the marshy parts of Russia! Who’s worrying about our troops? It’s not a bad idea, by the way, that public rumour attributes to us a plan to exterminate the Jews. Terror is a salutary thing. The attempt to create a Jewish State will be a failure.
The book that contains the reflections of the Emperor Julian should be circulated in millions. What wonderful intelligence, what discernment, all the wisdom of antiquity! It’s extraordinary.
With what clairvoyance the authors of the eighteenth, and especially those of the past, century criticised Christianity and passed judgment on the evolution of the Churches!
People only retain from the past what they want to find there. As seen by the Bolshevik, the history of the Tsars seems like a blood-bath. But what is that, compared with the crimes of Bolshevism?
There exists a history of the world, compiled by Rotteck, a liberal of the ’forties, in which facts are considered from the point of view of the period; antiquity is resolutely neglected. We, too, shall re-write history, from the racial point of view. Starting with isolated examples, we shall proceed to a complete revision. It will be a question, not only of studying the sources, but of giving facts a logical link. There are certain facts that can’t be satisfactorily explained by the usual methods. So we must take another attitude as our point of departure. As long as students of biology believed in spontaneous generation, it was impossible to explain the presence of microbes.
What a certificate of mental poverty it was for Christianity that it destroyed the libraries of the ancient world! Graeco-Roman thought was made to seem like the teachings of the Devil.
Christianity set itself systematically to destroy ancient culture. What came to us was passed down by chance, or else it was a product of Roman liberal writers. Perhaps we are entirely ignorant of humanity’s most precious spiritual treasures. Who can know what was there?
The Papacy was faithful to these tactics even during recorded history. How did people behave, during the age of the great explorations, towards the spiritual riches of Central America?
In our parts of the world, the Jews would have immediately eliminated Schopenhauer, Nietzsche and Kant. If the Bolsheviks had dominion over us for two hundred years, what works of our past would be handed on to posterity? Our great men would fall into oblivion, or else they’d be presented to future generations as criminals and bandits.
I don’t believe at all in the truth of certain mental pictures that many people have of the Roman emperors. I’m sure that Nero didn’t set fire to Rome. It was the Christian-Bolsheviks who did that, just as the Commune set fire to Paris in 1871 and the Communists set fire to the Reichstag in 1932.
5th November 1941, evening
Special Guests: SS Colonel (Standartenfuehrer) Blaschkeand Dr. Richter
The great trick of Jewry was to insinuate itself fraudulently amongst the religions with a religion like Judaism, which in reality is not a religion. Simply, the Jew has put a religious camouflage over his racial doctrine. Everything he undertakes is built on this lie.
The Jew can take the credit for having corrupted the Graeco-Roman world. We can live without the Jews, but they couldn’t live without us. When the Europeans realise that, they’ll all become simultaneously aware of the solidarity that binds them together. The Jew prevents this solidarity. He owes his livelihood to the fact that this solidarity does not exist.
Night of 1st December 1941
I’m convinced that there are Jews in Germany who’ve behaved correctly—in the sense that they’ve invariably refrained from doing injury to the German idea. It’s difficult to estimate how many of them there are, but what I also know is that none of them has entered into conflict with his co-racialists in order to defend the German idea against them.
Probably many Jews are not aware of the destructive power they represent. Now, he who destroys life is himself risking death. That’s the secret of what is happening to the Jews. Whose fault is it when a cat devours a mouse? The fault of the mouse, who has never done any harm to a cat?
This destructive rôle of the Jew has in a way a providential explanation. If nature wanted the Jew to be the ferment that causes peoples to decay, thus providing these peoples with an opportunity for a healthy reaction, in that case people like St. Paul and Trotsky are, from our point of view, the most valuable. By the fact of their presence, they provoke the defensive reaction of the attacked organism. Dietrich Eckart once told me that in all his life he had known just one good Jew: Otto Weininger, who killed himself on the day when he realised that the Jew lives upon the decay of peoples.
It is remarkable that the half-caste Jew, to the second or third generation, has a tendency to start flirting again with pure Jews. But from the seventh generation onwards, it seems the purity of the Aryan blood is restored. In the long run nature eliminates the noxious elements.
13th December 1941, midday
Special Guests: Ribbentrop, Rosenberg, Goebbels, Terboven and Reichsleiter Bouhler
The war will be over one day. I shall then consider that my life’s final task will be to solve the religious problem. Only then will the life of the German native be guaranteed once and for all. I don’t interfere in matters of belief. Therefore I can’t allow churchmen to interfere with temporal affairs. The organised lie must be smashed. The State must remain the absolute master.
But Christianity is an invention of sick brains: one could imagine nothing more senseless, nor any more indecent way of turning the idea of the Godhead into a mockery.
When all is said, we have no reason to wish that the Italians and Spaniards should free themselves from the drug of Christianity. Let’s be the only people who are immunised against the disease.
14th December 1941, midday
Special Guests: Rosenberg, Bouhler, Himmler
Kerrl, with the noblest of intentions, wanted to attempt a synthesis between National Socialism and Christianity. I don’t believe the thing’s possible, and I see the obstacle in Christianity itself.
I think I could have come to an understanding with the Popes of the Renaissance. Obviously, their Christianity was a danger on the practical level—and, on the propaganda level, it continued to be a lie. But a Pope, even a criminal one, who protects great artists and spreads beauty around him, is nevertheless more sympathetic to me than the Protestant minister who drinks from the poisoned spring.
Pure Christianity—the Christianity of the catacombs—is concerned with translating the Christian doctrine into facts. It leads quite simply to the annihilation of mankind. It is merely whole-hearted Bolshevism, under a tinsel of metaphysics.
End of 1941










