Update: The following text is rough draft. The series has been substantially revised and abridged, and the section by the YouTube blogger Turd Flinging Monkey is available in a single PDF: here.
______ 卐 ______
The traditionalism cycle
“The worst form of tyranny the world has ever known is the tyranny of the weak over the strong. It is the only tyranny that lasts.”
—Oscar Wilde
The reason that I initiated this series with excerpts from John Spark’s book on the science of animal sexuality is that it is the basis to understand human sexuality. The blogger seems to agree: “In order to understand society one must understand reproduction and sexual dimorphism.” In both animals and humans patriarchy is a system in which the males have the power, not the females. Power here means which gender controls reproduction and the resources of the species.
We have seen in Sparks’ excerpts something that we may call Tournament mating. In tournament species the male skull is larger; males are bigger and stronger but have shorter life spans than females; males compete for or select the females (hence the word “tournament”) and after mating often abandon the family. On the other hand, in Pair-bonding species the skulls are of the same size and shape as well as the bodies of the two genders; they have about the same life spans and the females selects the male; sometimes the female abandons the family. In both forms of mating, the blogger says, “we are addicted to pussy because that’s how reproduction works. Without that pussy addiction humanity would have died a long time ago.” In his videos this blogger mentions other bloggers of the manosphere, and he often quotes them by their pennames. He devoted five videos to one of his favorite subjects, the first under the title “The traditionalism cycle.”
In this blog I have referred several times to The Course of Empire, the paintings that Thomas Cole painted in 1833-1836. The Course of Empire reflected popular sentiments of the times when many saw pastoralism as the ideal phase of human civilization, fearing that an American empire would lead to gluttony and inevitable decay. Cole’s paintings remind me the stages that the blogger tries to explain in his civilizational cycle. Let me rephrase his exposition and add a little input of my own.
Brutal patriarchy. Very harsh for women. In the most primitive or barbarous stage of human prehistory, little reds riding hoods are just the property of the wolves. They can be raped or even killed at the discretion of the lycanthrope in question. There is low child survival and early sexual maturity. Both males and resources are scarce and reproduction is prioritized. Endless tribal wars to obtain young females and resources. The male-female relationship is a master-slave one. Polygamy reigns and the way that males get access to the rather cute bodies of their little reds is through tournament mating (see my excerpts of Sparks’ first chapter).

The Arcadian or Pastoral State
Humane patriarchy. This is the point when civilization began thousands of years ago. Men stop killing each other in tribal wars and women have already some rights. Survival is prioritized and there is more male stability. Polygamy starts to be abandoned (cf. my excerpts of Starks’ last chapter). Soft patriarchy also marks the beginning of monogamy and a pair-bonding society. The master-slave relationship is replaced for an adult-child one, where men are the adults and treat women as grown-up children. In this society civilization starts to thrive. The economy of the tribe grows and the population develops patterns to work around the environment. There is still high fertility rate but late sexual maturity. Resource stability increases. Although the laws explicitly favor men over women, an embryonic form of feminism begins. Today’s feminists claim that they were oppressed during the humane or soft patriarchy. “They really weren’t,” says the blogger. “It was a very balanced society if you think about it.”
Feminism. High child survival. Low fertility rate and late sexual maturity. Resource stability increases but the welfare state starts to replace the male provider. Women are exempted from their former responsibilities—marriage, motherhood, submissiveness—but men are still obliged to provide resources even after their wives have applied for divorces. Women obtain authority that traditionally was a privilege for men but liberated women cannot be drafted—again, they enjoy authority without responsibilities while men are expected to have exactly the same responsibilities they had in the patriarchal society. The laws favor women and more laws are being issued at the expense of men. The welfare state cannot be reformed because of universal suffrage, and women consist of 51-52 percent of the population. “Once women can vote the slow death begins and cannot be stopped democratically.”
Feminism run amok. Harsh for men. The women have now completely betrayed us by claiming that they don’t need us anymore. Since egalitarianism cannot be enforced by laws in a dimorphic species like humans, it devolves into open misandry: an anti-male society, or more specifically an anti-white males society. Right now we are in this terminal stage. All those horror stories of the divorce courts we hear in the men’s rights movement describe this late stage. We can see it in Japan too, even though the Japanese don’t suffer a Jewish problem. If Third Reich Germany was destined to become an Empire of the Yang, what we might be calling the Empire of the yin reigns today throughout the West. According to the blogger this is our paradox: “The more peaceful or successful a society becomes the closer it becomes to collapse.” There are no matriarchal civilizations in recorded human history because it is men who carry civilization over our own shoulders.
Economic collapse. Marriage is abandoned. The welfare state becomes overburdened and finally crashes. The demographic winter of whites ends in societal collapse. Once civilization collapses “the whole system resets back to traditionalism.” According to the blogger the best way to keep women at bay is through poverty. More specifically, in order to reestablish patriarchy three factors must come together: a hostile environment, male scarcity and resource scarcity. The blogger believes that there cannot be a return to patriarchy without the three factors because, to use his crude words, women would still use their pussies to obtain what they want. In a non-collapsed milieu they won’t submit yet but trade sex for food and protection. But we represent survival for the weak sex. Once these factors come together women will beg us to protect them as in times of yore. If there are no men around women, the latter start dying like flies.
* * *
As I said, the blogger devoted five videos to explain the cycle that I am paraphrasing here, injecting bits of pro-white concerns absent in his YouTube channel.
In one of his videos he used the paradigm of Ancient Rome, when the father was the judge, jury and executioner of the family (pater familias). Roman history does not even register how many apprentices of feminists were executed by their husbands or fathers, as women are still executed today by husbands and fathers in the Muslim world. In our culture, decadence started after the Second Punic War, when a vital law was abolished. Lex Oppia restricted not only a woman’s wealth (it forbade any woman to possess more than half an ounce of gold) but also her display of wealth. Unsuccessfully, Cato the Elder opposed the abrogation of that law and Roman feminists harvested other triumphs, even in the Senate, and the trend smoothly continued up to the Christian era. By the time of the Byzantine Empire even mudblood women could inherit property.
The Roman Empire disintegrated but the Middle Ages rectified Rome’s mistake throughout Europe by getting back to patriarchy. After the Enlightenment the cycle that Cato opposed started again, with women “reclaiming their rights” and writing pamphlets. The eighteenth century influenced the nineteenth century, especially in England. In the United States the turning point occurred when women obtained the right to vote in 1920, although the women’s movement had started in 1848. The welfare state initiated in 1935 with Social Security and was expanded in 1965 to include Medicare. “No fault divorce” was another escalation of feminism, in addition to the 1967 initiative for affirmative action for women. From the 1990s feminism transformed itself into runaway feminism. In 2010 the welfare state was expanded again to include Obamacare. The beneficiaries of this state are women, especially single mothers, not men. Marginalizing the engine of society will end in economic collapse, something that I believe will happen under the watch of the next US president, whether Clinton or Trump.
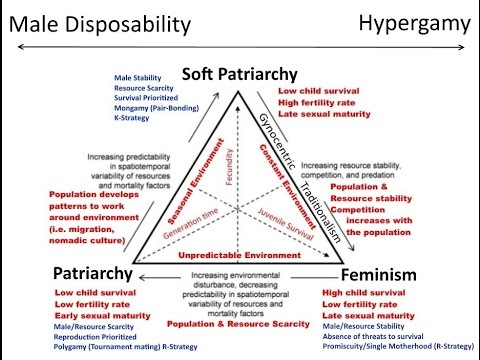
For the blogger, the most important question is exactly when we handed power over these creatures of long hair and short ideas. “We dropped the ball when we ceded authority to women.” He illustrates the cycle in an elaborate diagram:






 American white nationalists are pathetic. James Edwards for one is boasting his Christianity in today’s
American white nationalists are pathetic. James Edwards for one is boasting his Christianity in today’s 
