Category: Ancient Rome
Excerpted from the 18th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Christian ethics—the slave morality preached in the Roman catacombs—was like a time bomb ticking away in Europe—a Trojan horse brought inside the fortress, waiting for its season. That season came, and the damage was done. Today Christianity is one of the most active forces working from within to destroy the White race.
From the Christian churches came the notion of “the White man’s burden,” along with the missionaries who saw in every African cannibal or Chinese coolie a soul to be saved, of equal value in the eyes of Jehovah to any White soul. It is entirely a Christian impulse—at least, on the part of the average American voter, if not the government—which sends American food and medical supplies to keep alive swarming millions of Asiatics, Africans, and Latins every time they have a famine, so that they can continue to outbreed Whites.
The otherworldly emphasis on individual salvation, on an individual relationship between Creator and creature which relegates the relationship between individual and race, tribe, and community to insignificance; the inversion of natural values inherent in the exalting of the botched, the unclean, and the poor in spirit in the Sermon on the Mount, the injunction to “resist not evil” — all are prescriptions for racial suicide. Indeed, had a fiendishly clever enemy set out to concoct a set of doctrines intended to lead the White race to its destruction, he could hardly have done better.
The “White guilt” syndrome exploited so assiduously by America’s non-White minorities is a product of Christian teachings, as is the perverse reverence for “God’s chosen people” which has paralyzed so many Christians’ wills to resist Jewish depredations.
Moses Replaces Hermann
Not the least of the damage done by the Christianization of Europe was the gradual replacement of White tradition, legend, and imagery by that of the Jews. Instead of specifically Celtic or German or Slavic heroes, the Church’s saints, many of them Levantines, were held up to the young for emulation; instead of the feats of Hermann or Vercingetorix, children were taught of the doings of Moses and David.
 Europeans’ artistic inspiration was turned away from the depiction of their own rich heritage and used to glorify that of an alien race; Semitic proverbs and figures of speech took precedence over those of Indo-European provenance; Europeans even abandoned the names of their ancestors and began giving Jewish names to their children: Samuel and Sarah, John and Joan, Michael and Mary, Daniel and Deborah.
Europeans’ artistic inspiration was turned away from the depiction of their own rich heritage and used to glorify that of an alien race; Semitic proverbs and figures of speech took precedence over those of Indo-European provenance; Europeans even abandoned the names of their ancestors and began giving Jewish names to their children: Samuel and Sarah, John and Joan, Michael and Mary, Daniel and Deborah.
Despite all these long-term consequences of Christianity, however, the immediate symptoms of the infection which the conquering Germans picked up from the defeated Romans were hardly noticeable. White morals and manners, motivations and behavior remained much as they had been, for they were rooted in the genes—but now they had a new rationale.
Today’s Christian Patriots
And it is only fair to note that even today a fairly substantial minority of White men and women who still think of themselves as Christians have not allowed their sounder instincts to be corrupted by doctrines suited to a following of mongrelized slaves. They ignore the Jewish origins of Christianity and justify their instinctive dislike and distrust of Jews with the fact that the Jews, in demanding that Jesus be killed, became a race forever accursed (“His blood be on us and on our children”).
They interpret the divine injunction of brotherhood as applying only to Whites. Like the Franks of the Middle Ages, they believe what suits them and conveniently forget or invent their own interpretation for the rest. Were they the Christian mainstream today, the religion would not be the racial menace that it is.
Unfortunately, however, they are not: virtually none are actively affiliated with any of the larger, established Christian churches.
♣
Pierce’s book continues for other eight chapters.
I am convinced that the white race won’t be saved
unless whites—agnostics and atheists included—
give up Christian axiology (see: here).
Christianity Spreads
Excerpted from the 18th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
During the turbulent and eventful fifth century the Germans largely completed their conquest of the West. In the early years of that century German tribesmen, who had been raiding the coast of Roman Britain for many years, began a permanent invasion of the southeastern portion of the island, a development which was eventually to lead to a Germanic Britain.
Oriental Infection
But the Germans did not make their conquest of the Roman world without becoming infected by some of the diseases which flourished so unwholesomely in Rome during her last days. Foremost among these was an infection which the Romans themselves had caught during the first century, a consequence of their own conquest of the Levant. It had begun as an offshoot of Judaism, had established itself in Jerusalem and a few other spots in the eastern Mediterranean area, and had traveled to Rome with Jewish merchants and speculators, who had long found that city an attractive center of operations.
It eventually became known to the world as Christianity, but for more than two centuries it festered in the sewers and catacombs of Rome, along with dozens of other alien religious sects from the Levant; its first adherents were Rome’s slaves, a cosmopolitan lot from all the lands conquered by the Romans. It was a religion designed to appeal to slaves: blessed are the poor, the meek, the wretched, the despised, it told them, for you shall inherit the earth from the strong, the brave, the proud, and the mighty; there will be pie in the sky for all believers, and the rest will suffer eternal torment. It appealed directly to a sense of envy and resentment of the weak against the strong.
The new religion spread from the slaves to the freedmen, that motley conglomeration of Syrians, Egyptians, Jews, Armenians, and members of a dozen other nations who made up Rome’s mercantile, petty entrepreneur, and free worker class. It even began to catch on in some of Rome’s legions.
By the end of the third century Christianity had become the most popular as well as the most militant of the Oriental sects flourishing among the largely non-Roman inhabitants of the decaying Roman Empire. Even as late as the first years of the fourth century, under Emperor Diocletian, the Roman government was still making efforts to keep the Christians under control, but in 313 a new emperor, Constantine, decided that, if you can’t lick ’em, join ’em, and he issued an imperial edict legitimizing Christianity.
Although one of Constantine’s successors, Julian, attempted to reverse the continuing Christianization of the Roman Empire a few years later, it was already too late: the Goths, who made up the bulk of Rome’s armies by this time, had caught the infection from one of their own slaves, a Christian captive whom they called Wulfila. Wulfila was a tireless and effective missionary, and the Goths were an uprooted and unsettled people, among whom the new religion took hold easily. Wulfila’s translation of the Bible into Gothic greatly speeded up the process.
Conversion of the Franks
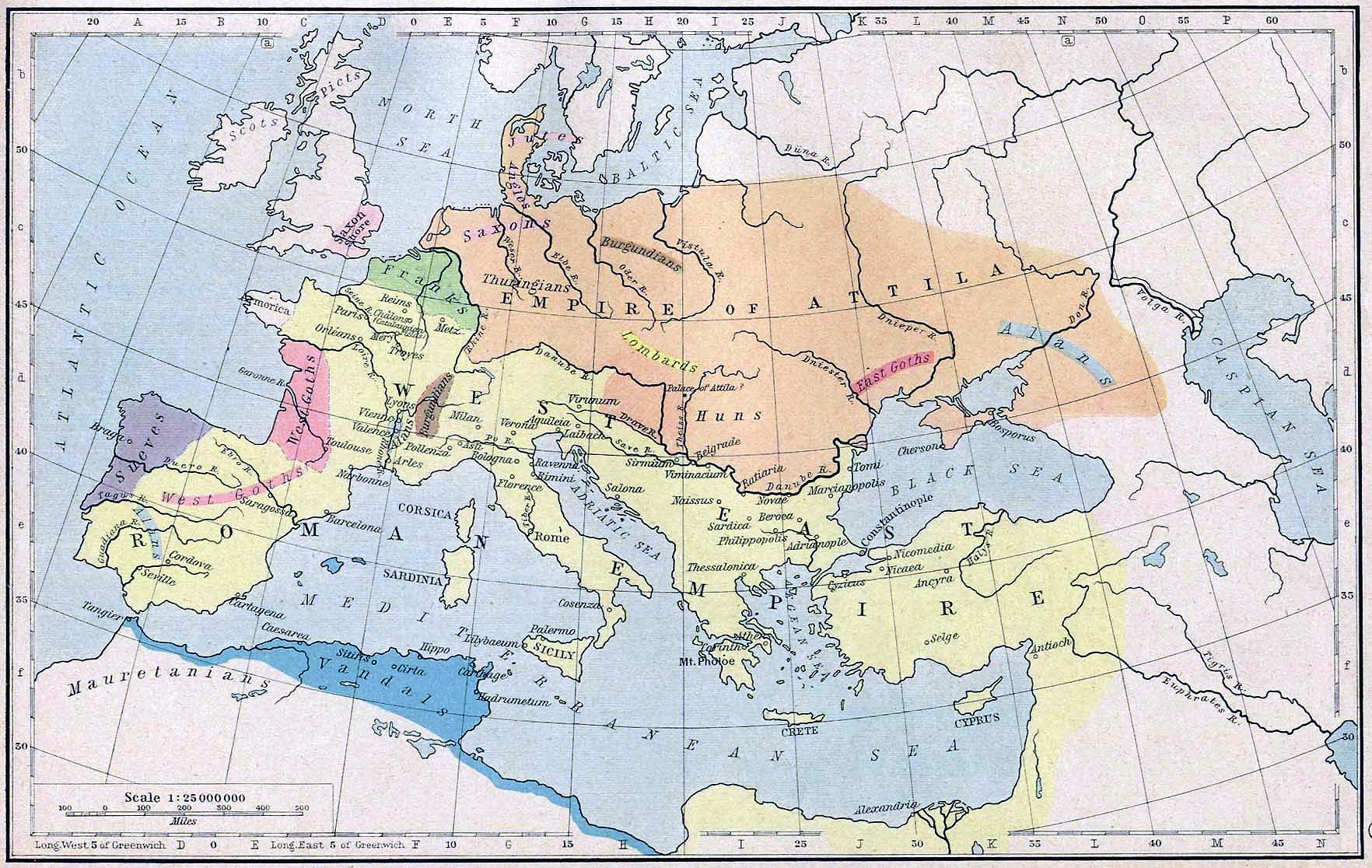
Before the end of the fourth century Christianity had also spread to the Vandals, Burgundians, Lombards, Gepids, and several other German tribes. A little over a century later the powerful nation of the Franks was converted. By the beginning of the second quarter of the sixth century, the only non-Christian Whites left were the Bavarians, Thuringians, Saxons, Frisians, Danes, Swedes, and Norse among the Germans—and virtually all the Balts and Slavs.
Athanaric the Goth
The Christians had many individual opponents, of course: among the Romans several of the more responsible and civic-minded emperors, such as Diocletian, as well as what was left of the tradition-minded aristocracy; and among the Germans many farsighted leaders who resisted the imposition of an alien creed on their people and the abandonment of their ancient traditions. Athanaric, the great Gothic chieftain who led his people across the Danube in 376 to save them from the invading Huns, was notable in this regard.
Athanaric and the other traditionalists failed to halt the spread of Christianity, because they were only individuals. Although there were pagan priests, the traditional German religion never really had a church associated with it. It consisted in a body of beliefs, tales, and practices passed from generation to generation, but it had no centralized organization like Christianity.
Early Christianity, in contrast to German religion, was as utterly intolerant as the Judaism from which it sprang. Even Roman religion, which, as an official state religion, equated religious observance with patriotism, tolerated the existence of other sects, so long as they did not threaten the state. But the early Christians were inspired by a fanatical hatred of all opposing creeds.
Also in contrast to German and Roman religion, Christianity, despite its specifically Jewish roots, claimed to be a universal (i.e., “catholic”) creed, equally applicable to Germans, Romans, Jews, Huns, and Negroes.
As for the brotherhood of man and equality in the eyes of the Lord, the Germans had no time for such nonsense; when confronted with non-Whites, they instinctively reached for the nearest lethal weapon. They made mincemeat out of the Avars, who were cousins to the Huns, in the seventh century, and the Christianized Franks or Goths of that era would know exactly what to do with a few hundred thousand rioting American Blacks; they would, in fact, positively relish the opportunity to do what needed doing.
It could not have been expected to be otherwise. In the first place, a totally alien religion cannot be imposed on a spiritually healthy people—and the Germans were still essentially healthy, despite the dislocations caused by the Voelkerwanderung.
Excerpted from the 17th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
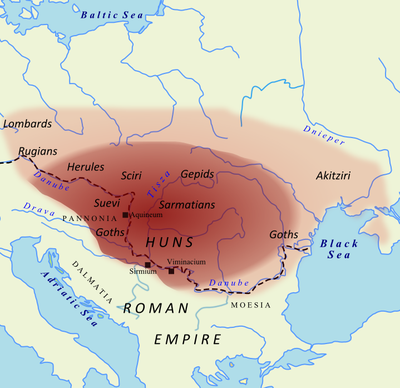
The Huns halted their westward push for more than 40 years while they consolidated their hold on all of central and eastern Europe, and on much of northern Europe as well. In 433 they gained a new king, whose name was Attila. In 445, when Attila established his new capital at Buda, in what is now Hungary, the empire of the Huns stretched from the Caspian Sea to the North Sea.
In 451 Attila began moving west again, with the intention of seizing Gaul and then the rest of the Western Empire. His army consisted not only of Huns but also of contingents from all the conquered peoples of Europe: Ostrogoths, Gepids, Rugians, Scirians, Heruls, Thuringians, and others, including Slavs.
One contingent was made up of Burgundians, half of whom the Huns had subjugated (and nearly annihilated) in 436. The struggle between the Burgundians and the Huns forms the background for the German heroic epic, the Nibelungenlied.
Scourge of God
Attila’s mixed army threw western Europe into a state of terror as it advanced. So great was the devastation wrought on the countryside that Attila was given the nickname “the Scourge of God,” and it was said that grass never again grew where his horse had trod.
Two armies, one commanded by Aëtius, the last of the Western Empire’s Roman generals, and the other by Theodoric, King of the Visigoths, rode against Attila. Aëtius and Theodoric united their armies south of the Loire, in central Gaul, and compelled Attila to withdraw to the north-east.
Attila carefully chose the spot to halt his horde and make his stand. It was in a vast, open, and nearly level expanse of ground in northeastern France between the Marne and the Seine, where his cavalry would have ideal conditions for maneuvering. The region was known as the Catalaunian Plains, after the Catalauni, a Celtic people. The name of Chalons (ancient Catalaunum), is most often associated with the battle which took place on the Catalaunian Plains, although the actual site is much closer to the city of Troyes.
White Victory
In a furious, day-long battle frightful losses were inflicted on both sides, but the Visigoths, Franks, free Burgundians, and Alans of Aëtius and Theodoric had gained a decisive advantage over the Huns and their allies by nightfall. Attila retreated behind his wagons and in despair ordered a huge funeral pyre built for himself. He intended neither to be taken alive by his foes nor to have his corpse fall into their hands.
King Theodoric had fallen during the day’s fighting, and the command of the Visigothic army had passed to his son, Thorismund. The latter was eager to press his advantage and avenge his father’s death by annihilating the Hunnic horde.
Empire of Attila (orange) by 450 A.D.
The wily Roman Aëtius, however, putting the interests of his dying Empire first, persuaded Thorismund to allow Attila to withdraw his horde from Gaul. Aëtius was afraid that if Thorismund completely destroyed the power of the Huns, then the Visigoths would again be a menace to the Empire; he preferred that the Huns and the Visigoths keep one another in check.
Battle of the Nedao
Attila and his army ravaged the countryside again, as they made their way back to Hungary. The following year they invaded northern Italy and razed the city of Aquileia to the ground; those of its inhabitants who were not killed fled into the nearby marshes, later to found the city of Venice.
But in 453 Attila died. The 60-year-old Hun burst a blood vessel during his wedding-night exertions, following his marriage to a blonde German maiden, Hildico (called Kriernhild in the Nibelungenlied). The Huns had already been stripped of their aura of invincibility by Theodoric, and the death of their leader diminished them still further in the eyes of their German vassals.
The latter, under the leadership of Ardaric the Gepid, rose up in 454. At the battle of the Nedao River in that year it was strictly German against Hun, and the Germans won a total victory, completely destroying the power of the Huns in Europe.
Slavic Opportunity
The vanquished Huns fled eastward, settling finally around the shores of the Sea of Azov in a vastly diminished realm. They left behind them only their name, in Hungary. Unfortunately, they also left some of their genes in those parts of Europe they had overrun. But in 80 years they had turned Europe upside down. Entire regions were depopulated, and the old status quo had vanished.
This provided an opportunity for the Slavs to expand, and they took advantage of it, as mentioned earlier. Unfortunately for them—and for our entire race—the area into which the Slavs expanded corresponded largely to the area invaded repeatedly in later centuries by Asiatic hordes from the east, and the Slavic peoples suffered grievously. We will examine these Asiatic invasions in later installments.
Excerpted from the 17th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
The Gothic nation, as was mentioned in the previous installment, had established itself on the southern shore of the Baltic, around the mouth of the Vistula, before 300 B.C. Prior to that the Goths had lived in southern Sweden.
Conquest of the Steppe
The Goths west of the Dniester—the Visigoths—moved down into the Danubian lands west of the Black Sea, where they inevitably came into conflict with the Romans. They conquered the Roman province of Dacia for themselves, after defeating a Roman army and killing a Roman emperor (Decius) in the year 251.
For the next century and a quarter both the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths prospered, while the fortunes of the Roman Empire continued to decline. The Goths, who were excellent seamen, raided the Black Sea coastal cities of Asia Minor at will, and Rome was also hard pressed to defend other portions of her long border with the Germans.
Peaceful Coexistence
Toward the end of the third century, during the reign of Diocletian, the Empire was divided into eastern and western halves, for administrative and military purposes. The progressive breakdown of communications led eventually to separate de facto powers, one centered in Rome and the other in Byzantium (later renamed Constantinople).
During the first three-quarters of the fourth century, despite occasional raids, a state of relatively peaceful coexistence between Goths and Romans pervaded. Especially in the eastern half of the Empire, diplomacy and bribery were used to hold the Goths at bay. During the reign of Constantine (306-337) 40,000 Goths were recruited into the Roman army, and they thenceforth were the bulwark of the Eastern Empire.
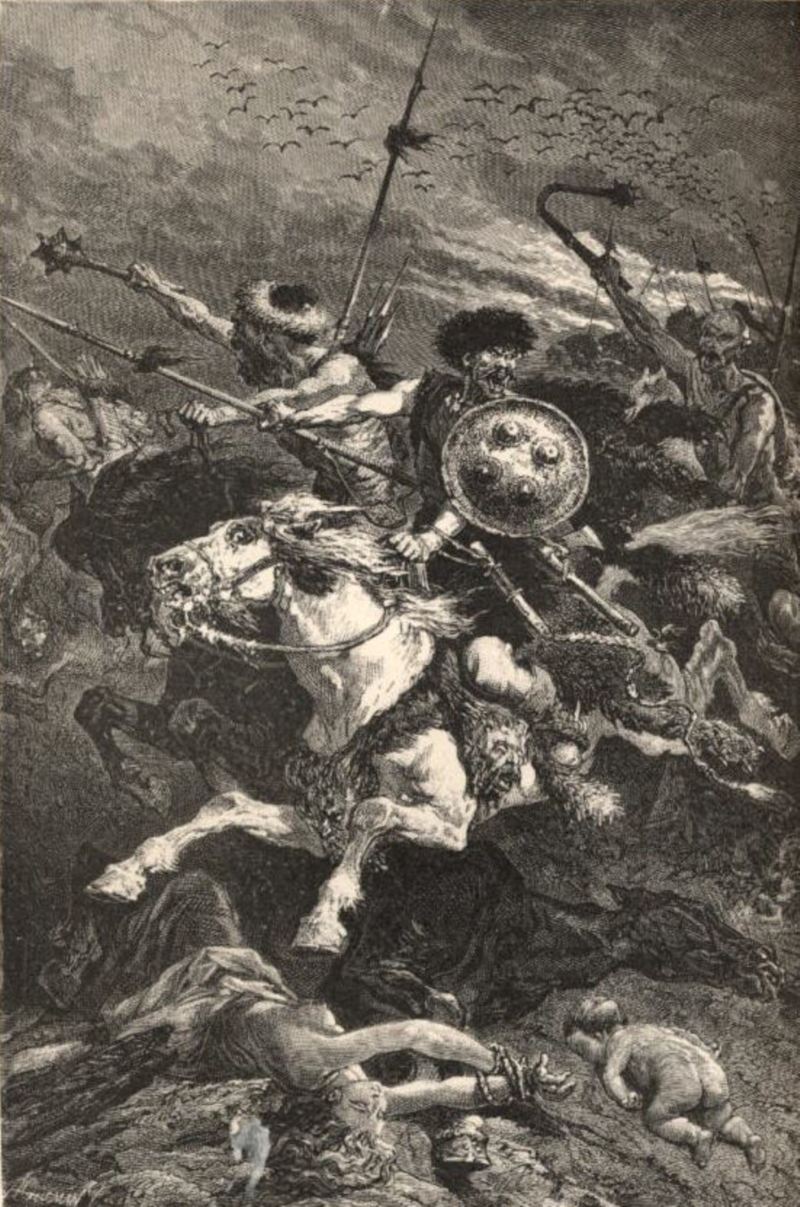
It was in the reign of Emperor Valens, in the year 372, that the greatest menace to the White race, both Germans and Romans, since the beginning of recorded history suddenly appeared on the eastern horizon. From the depths of Central Asia a vast horde of brown- skinned, flat-nosed, slant-eyed little horsemen—fast, fierce, hardy, bloodthirsty, and apparently inexhaustible in numbers—came swarming across the steppe around the north end of the Caspian Sea. They were the Huns.
The first to feel their impact were the Alans, living south of the Don between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. The Hunnic horde utterly crushed the Alans, some of whose remnants retreated southward into the Caucasus Mountains, while others fled westward in confusion, seeking refuge among the Goths. In the Caucasus today traces of the Nordic Alans are found in the Ossetes, whose language is Indo-European and who are taller and lighter than the Caucasic-speaking peoples around them.
End of the Ostrogoths
Next the Huns fell upon the Ostrogoths and routed them. The aged Ostrogothic king, Hermanric, slew himself in despair, and his successor, Vitimer, was killed in a vain effort to hold back the Brown flood. The Ostrogothic kingdom disintegrated, and its people streamed westward in terror, with the Huns at their heels. Athanaric, king of the Visigoths, posted himself at the Dniester with a large army, but the Huns crossed the river and defeated him, inflicting great slaughter on his army.
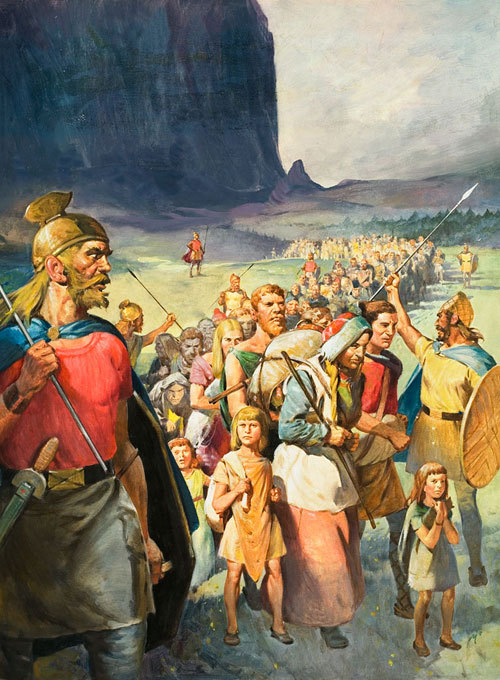
Thus, the Visigoths too were forced to retreat westward. Athanaric petitioned Valens for permission for his people to cross the Danube and settle in Roman lands to the south. Valens consented, but he attached very hard conditions, which the Goths, in their desperation, were forced to accept: they were required to surrender all their weapons and to give up their women and children as hostages to the Romans.
Oppression and Rebellion
The Goths crossed the Danube in 376 and settled in the Roman province of Lower Moesia, which corresponds roughly to modern Bulgaria. There the Romans took shameful advantage of them. Roman-Jewish merchants, in return for grain and other staples, took the hostage children of the Goths as slaves.
The Goths secretly rearmed themselves and rose up. For two years they waged a war of revenge, ravaging Thrace, Macedonia, and Thessaly. Finally, on August 9, 378, in the great battle of Hadrianople, the Gothic cavalry, commanded now by Fritigern, annihilated Valens’ infantry (most of whom were also Goths), and the emperor himself was killed. This was the worst defeat Rome had suffered since the Goths defeated and killed Decius 127 years earlier, and the battle decisively changed the conduct of future wars. Heretofore, Roman infantry tactics had been considered unbeatable, but Fritigern’s Goths had shown what heavy cavalry could do to infantry unprotected by its own cavalry.
The emperor of the eastern half of the Empire who succeeded Valens took a much more conciliatory stance toward the Goths, and they were confirmed in their possession of much of the territory south of the Danube which they had seized between 376 and 378. The Huns, meanwhile, had occupied Gothic Dacia (present-day Romania), as well as all the lands to the east.
Loss of a Homeland
The ancient homeland of the Nordic race was now in the hands of non-Whites. For more than four millennia wave after wave of White warriors had come out of the eastern steppe to conquer and colonize Europe: Achaeans, Dorians, Latins, Celts, Germans, Balts, Slavs, Cimmerians, Scythians, Sarmatians, and uncounted and unnamed peoples before all these. But the Sarmatians were the last; after the Huns drove them and the Goths out, no other White barbarians were to come riding out of the east.
For the next thousand years the eastern steppe which had been the breeding ground of the Nordic race became the invasion route into Europe for periodic waves of non-White hordes from Asia: Huns, Avars, Turks, Magyars, Mongols.
German vs. German
The Huns contented themselves, for the time being, with that portion of Europe between the Carpathians and the Danube, leaving the Romans and the Germans elsewhere to their own devices. Rome, a hollow shelf peopled largely by Levantines and ruled in effect by a gaggle of filthy-rich Middle Eastern moneylenders, speculators, and merchants, depended for her continued existence upon cleverness and money rather than real strength. Germans menaced her and Germans defended her, and the Romans concentrated their energies on playing German off against German.
The game succeeded in the Eastern Empire, more or less, but not in the Western Empire. A Frank, Arbogast, was the chief adviser—and effective master—of Western Emperor Eugenius in the year 394, having assassinated Eugenius’ predecessor. The emperor of the East, Theodosius, sent his Gothic army against Arbogast, and Arbogast called on his fellow Franks for support. The two German armies fought at Aquileia, near modern Venice, and the Goths defeated the Franks.
Alaric the Bold
Two of the leaders of Theodosius’ army were Alaric the Bold, a Gothic prince, and Stilicho, a Vandal. After the battle of Aquileia Stilicho, nominally subordinate to Theodosius, became the effective master of the Western Empire. Alaric was chosen king of the Visigoths by his tribe and decided to challenge Stilicho, but as long as Stilicho lived he was able to hold Alaric at bay.
The emasculated and Levantinized Romans, unable to face the Germans man to man, bitterly resented their German allies as much as they did their German enemies. This resentment, born of weakness and cowardice, finally got the better of the Romans in 408, and they conspired to have their protector, Stilicho, murdered. Then the Romans in all the Italian cities butchered the wives and children of their German allies—60,000 of them.
This foolish and brutal move sent Stilicho’s German soldiers into Alaric’s arms, and Italy was then at the Goth’s mercy. Alaric’s army ravaged large areas of the peninsula for two years in revenge for the massacre of the German families. Alaric demanded a large ransom from the Romans and forced them to release some 40,000 German slaves.
Fall of Rome
Then, on the night of August 24, 410, Alaric’s Goths took Rome and sacked the city. This date marked, for all practical purposes, the end of the capital of the world. Rome had endured for 1,163 years and had ruled for a large portion of that time, but it would never again be a seat of power. For a few more decades the moribund Empire of the West issued its commands from the fortress city of Ravenna, 200 miles north of Rome, until the whole charade was finally ended in 476. The Empire of the East, on the other hand, would last another thousand years.
Excerpted from the 15th and 16th articles of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
The philosopher Lucius Annaeus Seneca, also writing in the first century, shared Tacitus’ respect for the Germans’ martial qualities: “Who are braver than the Germans? Who more impetuous in the charge? Who fonder of arms, in the use of which they are born and nourished, which are their only care?”
Caesar, Tacitus, and other writers also described other attributes of the Germans and various aspects of their lives: their shrines, like those of the Celts and the Balts, were in sacred groves, open to the sky; their family life (in Roman eyes) was remarkably virtuous, although the German predilection for strong drink and games of chance must have been sorely trying to wives; they were extraordinarily hospitable to strangers and fiercely resentful of any infringements on their own rights and freedoms; each man jealously guarded his honor, and a liar was held in worse repute than a murderer; usury and prostitution were unknown among them.
[Here Pierce recounts the clash between the Germanics and the Romans under Caesar, Augustus and Tiberius. Then he adds:]
Five Decisive Things
During the 401 years between Hermann’s victory in the Teutoburger Forest and the sacking of the city of Rome by a German army in August 410, a great many things of historical importance occurred. We will be able to look at only a few of them in detail, however; we do not want to be distracted from our history of the race by the minutiae of political history, no matter how important.
Five things which happened or were ongoing during this period stand out as decisive, from a racial viewpoint. First, there was the continued decadence of the Romans, a matter we have already treated. Second, there was the growing Germanization of the Roman army. Third, there was the migration of the Goths from their home in Scandinavia back to the ancient Indo-European homeland in southern Russia. Fourth, there was the invasion of Europe by a non-White horde from the Far East: the Huns. And fifth, there was the final undermining of Roman strength by the spread of a new religion from the Levant—an Oriental religion of pacifism and egalitarianism which also began to have an effect on the Germans.
 When Marcus Aurelius, the last Roman emperor able to inspire any real fear or respect in the Germans, tried to recruit troops to defend Rome’s Danubian border in 168, not even the threat of death induced Italians to enlist in the legions. The emperor finally resorted to conscripting all of Rome’s gladiators, most of whom were Celtic or German prisoners of war, into the army, whereupon the Roman masses, as addicted to their spectator sports as America’s masses are to their TV, threatened insurrection. “He deprives us of our amusements,” the populace cried out in anger against the emperor, “in order to make us philosophers like himself.” As they had become less martial, the Romans—or, rather, the Jews, Syrians, Egyptians and debased Greeks of the Empire who unworthily bore that once-honorable name—had grown ever more fond of the cruel blood sports of the Colosseum.
When Marcus Aurelius, the last Roman emperor able to inspire any real fear or respect in the Germans, tried to recruit troops to defend Rome’s Danubian border in 168, not even the threat of death induced Italians to enlist in the legions. The emperor finally resorted to conscripting all of Rome’s gladiators, most of whom were Celtic or German prisoners of war, into the army, whereupon the Roman masses, as addicted to their spectator sports as America’s masses are to their TV, threatened insurrection. “He deprives us of our amusements,” the populace cried out in anger against the emperor, “in order to make us philosophers like himself.” As they had become less martial, the Romans—or, rather, the Jews, Syrians, Egyptians and debased Greeks of the Empire who unworthily bore that once-honorable name—had grown ever more fond of the cruel blood sports of the Colosseum.
All-Volunteer Army
Until the end of the third century law prohibited the enlistment of foreigners in the Roman army. Although the law was often violated, it resulted in most of Rome’s soldiers being recruited from among the Celts and Germans of the conquered provinces during a period of about 150 years. By the time of Constantine not even the provinces could provide enough soldiers to defend the degenerate Roman Empire, and the greatest source of military manpower became the free Germans, who enlisted for purely mercenary motives.
By the middle of the fourth century, the Roman army was Roman in name only. Germans not only filled the ranks, but most of the officers, up to the highest levels of command, were Germans as well. Thus, the more or less continual state of war which existed between the free Germans and the Roman Empire during the third, fourth, and fifth centuries—up until 476, when the last Roman emperor was deposed and banished and a German leader ruled Italy as king—was not fought between Germans and Romans, but between Germans on the one side and Germans on the other.
Gold for Blood
The Romans bought their protection instead of fighting for it. Gold paid for blood for more than 200 years, but in the end all their money and their civilized cleverness were not enough.
If the Germans could have added a stronger sense of racial solidarity to their other virtues, they could have put an end to the sewer that was Rome 200 or even 300 years sooner than they did. They would not only have avoided spilling torrents of their own blood, but they could have stamped out a source of poison that, allowed to continue festering, ultimately would infect them.
Declining Rome’s many wars with the Germans involved a number of tribes. The incursions across the Danube into Pannonia that Marcus Aurelius bloodily repulsed in the second century were by tribes confederated with the Marcomanni, for example. During the third and fourth centuries the Franks raided across the Rhine into Gaul, and the Saxons harassed the coasts of that country and Britain. But it was the Goths above all the others who wrote the final chapters of the struggle between Germany and Rome.
Gothic Victory
After several skirmishes between Goths and Romans along the lower Danube, in the year 251 the Goths inflicted the worst defeat on the Romans they had suffered since the Hermannschlacht, annihilating a Roman army and killing its commander, the emperor Decius.
Within two more decades Rome had abandoned all claim to Dacia, and the province which Trajan had conquered 150 years earlier was thenceforth firmly in German hands, with the Danube once again the border between Rome and Germany.
Excerpted from the 15th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Closely related to the Celts, whose fortunes we traced in the previous installment, and settled into the area of Europe directly north of them, were the Germans. Like the Celts, they immigrated into northern Europe over a period of many centuries. It would be incorrect, of course, to refer to these earliest Nordic immigrants as “Germans.” All that can be said of them, just as of those immigrants south of them who later gave birth to the Celts, is that they were Indo-Europeans.
Celtic Buffer
Was there some quality which distinguished the Germans from the Celts, so that the former were able to prevail over the decaying civilization to the south and the latter were not? Certainly not initially, for the two were of the same stock. Nevertheless, the Germans had two enormous advantages over the Celts.
First, the proto-German homeland was buffered from the imperialistic designs of the Romans by the Celts; the latter took the full brunt of the Roman armies, while the German homeland remained relatively inviolate. And yet the Germans, unlike the Balts and the Slavs, had just enough contact with the Romans to serve as a stimulus for their later invasions and conquest of the Roman Empire.
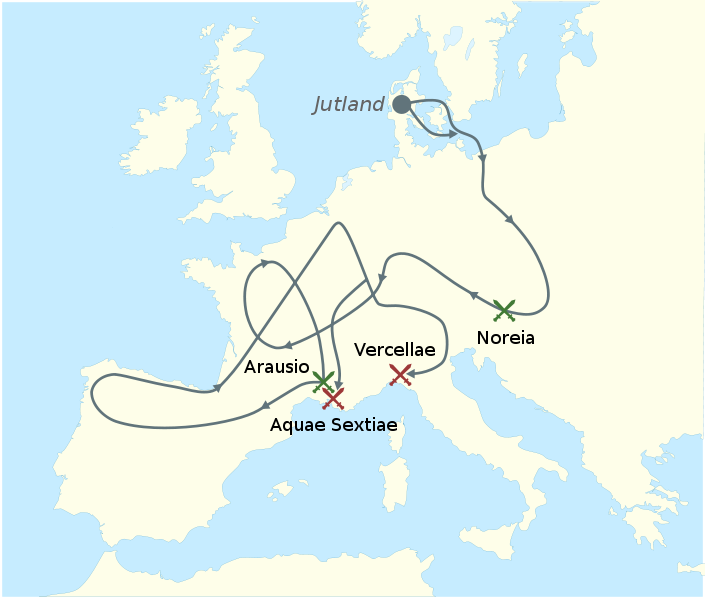
The death struggle between Latins and Germans began even before Caesar’s subjection of Gaul. Late in the second century two neighboring German tribes, the Cimbrians and the Teutons, left their homes in the Danish peninsula because, they said, of the sinking of much of their low-lying land into the sea. Some 300,000 in number, they headed south, crossing the Tyrolese Alps into northern Italy in 113 B.C., where they asked the Romans for permission either to settle or to cross Roman territory into the Celtic lands to the west.
A Tragic End
The Roman consul, Papirius Carbo, attempted to halt them, and they defeated his army. The Germans then proceeded westward into Gaul and went as far as Spain, where they raised havoc. Ten years later, however, they returned to northern Italy.
(Part of the Cimbrian War)
This time they were met by a more competent Roman general, the consul Gaius Marius. In two horrendous battles, in 102 and 101 B.C., Marius virtually exterminated the Teutons and the Cimbrians. So many Teutons were massacred at Aquae Sextiae in 102 that, according to a contemporary Roman historian, their blood so fertilized the earth that the orchards there were especially fruitful for years afterward, and German bones were used to build fences around the vineyards.
More Conflict
At Vercelli the Cimbrians met a similar fate the following year; more than 100,000 were slaughtered. When the German women saw their men being defeated, they first slew their children and then killed themselves in order to avoid the shame of slavery.
The annihilation of these two German nations was followed by a few decades in which Italy remained relatively safe from further incursions from the north. The Germans’ territory was bounded, roughly, on the east by the Vistula and on the south by the Danube. In the west the boundary was less definite, and the Germans west of the Rhine came into repeated conflict with Roman armies in Gaul.
Tacitus on the Germans
The Romans were naturally curious about the teeming tribes of fierce, warlike people beyond the Rhine who dared contest their conquest of the lands in northern Gaul, and several Roman writers enumerated them and described their way of life, most notably the historian Gaius Cornelius Tacitus. Writing in a first-century Rome which was thoroughly mongrelized, Tacitus was strongly impressed by the Germans’ apparent racial homogeneity:
I concur in opinion with those who deem the Germans never to have intermarried with other nations but to be a pure and unmixed race, stamped with a distinct character. Hence, a family likeness pervades the whole, though their numbers are so great. Their eyes are stern and blue, their hair ruddy, and their bodies large, powerful in sudden exertion, but impatient of toil and not at all capable of sustaining thirst and heat. They are accustomed by their climate to endure cold and hunger.
Tacitus added: “Traitors and deserters are hanged; cowards and those guilty of unnatural practices are suffocated in mud under a hurdle.” Subject to the same punishment as cowards and homosexuals were draft dodgers: those who failed to present themselves for military service when summoned.
The education of the German youth stressed not only bravery and skill in arms, but loyalty in the highest degree. Tacitus gives an interesting description of the mutual obligations between a German leader and his companions in arms:
The Germans transact no business, public or private, without being armed, but it is not customary for any person to assume arms until the state has approved his ability to use them. Then, in the midst of the assembly, either one of the chiefs, or the father, or a relative, equips the youth with a shield and a spear. These are to them the manly gown (toga virilis); this is the first honor conferred on youth. Before, they are considered as part of a household; afterwards, of the state.
Excerpted from the 14th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Celtic bands continued to whip Roman armies, even to the end of the second century B.C., but then Roman military organization and discipline turned the tide. The first century B.C. was a time of unmitigated disaster for the Celts. Caesar’s conquest of Gaul was savage and bloody, with whole tribes, including women and children, being slaughtered by the Romans.
By the autumn of 54 B.C, Caesar had subdued Gaul, having destroyed 800 towns and villages and killed or enslaved more than three million Celts. And behind his armies came a horde of Roman-Jewish merchants and speculators, to batten on what was left of Gallic trade, industry, and agriculture like a swarm of locusts. Hundreds of thousands of blond, blue-eyed Celtic girls were marched south in chains, to be pawed over by greasy, Semitic flesh-merchants in Rome’s slave markets before being shipped out to fill the bordellos of the Levant.
Last Effort
Then began one, last, heroic effort by the Celts of Gaul to throw off the yoke of Rome, thereby regaining their honor and their freedom, and—whether consciously or not—reestablishing the superiority of Nordic mankind over the mongrel races of the south. The ancestors of the Romans had themselves established this superiority in centuries past, but by Caesar’s time Rome had sunk irretrievably into the quagmire of miscegenation and had become the enemy of the race which founded it.
The rebellion began with an attack by Ambiorix, king of the Celtic tribe of the Eburones, on a Roman fortress on the middle Moselle. It spread rapidly throughout most of northern and central Gaul. The Celts used guerrilla tactics against the Romans, ruthlessly burning their own villages and fields to deny the enemy food and then ambushing his vulnerable supply columns.
Vercingetorix
For two bloody years the uprising went on. Caesar surpassed his former cruelty and savagery in trying to put it down. When Celtic prisoners were taken, the Romans tortured them hideously before killing them. When the rebel town of Avaricum fell to Caesar’s legions, he ordered the massacre of its 40,000 inhabitants.
Meanwhile, a new leader of the Gallic Celts had come to the fore. He was Vercingetorix, king of the Arverni, the tribe which gave its name to France’s Auvergne region. His own name meant, in the Celtic tongue, “warrior king,” and he was well named. Vercingetorix came closer than anyone else had to uniting the Celts. He was a charismatic leader, and his successes against the Romans, particularly at Gergovia, the principal town of the Arverni, roused the hopes of other Celtic peoples. Tribe after tribe joined his rebel confederation, and for a while it seemed as if Caesar might be driven from Gaul.
Tragedy of Alesia
But unity was still too new an experience for the Celts, nor could all their valor make up for their lack of the long experience of iron discipline which the Roman legionaries enjoyed. Too impetuous, too individualistic, too prone to rush headlong in pursuit of a temporary advantage instead of subjecting themselves always to the cooler-headed direction of their leaders, the Celts soon dissipated their chances of liberating Gaul.
Finally, in the summer of 52 B.C., Caesar’s legions penned up Vercingetorix and 80,000 of his followers in the walled town of Alesia, on the upper Teaches of the Seine. Although an army of a quarter-million Celts, from 41 tribes, eventually came to relieve besieged Alesia, Caesar had had time to construct massive defenses for his army. While the encircled Alesians starved, the Celts outside the Roman lines wasted their strength in futile assaults on Caesar’s fortifications.
Savage End
In a valiant, self-sacrificing effort to save his people from being annihilated, Vercingetorix rode out of Alesia, on a late September day, and surrendered himself to Caesar. Caesar sent the Celtic king to Rome in chains, kept him in a dungeon for six years, and then, during the former’s triumphal procession of 46 B.C., had him publicly strangled and beheaded in the Forum, to the wild cheers of the city’s degraded, mongrel populace.
After the disaster at Alesia, the confederation Vercingetorix had put together crumbled, and Caesar had little trouble in extinguishing the last Celtic resistance in Gaul. He used his tried- and-true methods, which included chopping the hands off all the Celtic prisoners he took after one town, Uxellodunum, commanded by a loyal adjutant of Vercingetorix, surrendered to him.
Next: Germanic Expansion
Caesar did not live long enough to wreak the same havoc in Britain which he had in Gaul, but other Roman generals finished what he had started. During the first century A.D. Roman Britain was bloodily expanded to include everything in the British Isles except Caledonia (northern Scotland) and Hibernia (Ireland).
Decadent Rome did not long enjoy dominion of the Celtic lands, however, because another Indo-European people, the Germans, soon replaced the Latins as the masters of Europe.
Excerpted from the 14th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Both the fossil remains and the eyewitness accounts of Classical authors confirm that all these Indo-European peoples were racially Nordic. Because they settled in different areas after leaving the original homeland, and because they subsequently mixed with different races and to different extents, there are noticeable differences in various racial characteristics among their descendants today. But originally, Celt, German, Balt, and Slav were indistinguishably Nordic.
The Celts were the first group to make an impact on the Classical world, and so we will deal with them first.
The reason the Celts interacted with the Greeks and Romans before the other groups did is that their wanderings took them farthest south. They invaded and settled in a great crescent stretching across central Europe from eastern Hungary and Czechoslovakia through Austria, southern Germany, Switzerland, and France into the British Isles. At the eastern and western ends of their range, respectively, isolated bands of Celts penetrated into central Asia Minor and the Iberian peninsula, while in the center quite substantial numbers crossed the Alps into northern Italy.
The Roman conquest of southeastern Europe, Gaul, and Britain destroyed the greater part of Celtic culture, as well as doing an enormous amount of racial damage; the effects of the later German and Slavic incursions were largely limited to linguistic and other cultural changes.
But the Celts themselves, as much as anyone else, were responsible for the decline of their racial fortunes. They settled in regions of Europe which, although not so heavily Mediterraneanized as Greece and Italy, were much more so than the German, Baltic, and Slavic areas. And, as has so often been the case with the Indo-Europeans, for the most part they did not force the indigenous populations out of the areas they conquered, but made subjects of them instead. Thus, many people who think of themselves as “Celts” today are actually more Mediterranean than Celtic. And others, with Latin, Germanic, or Slavic names, are actually of nearly unmixed Celtic descent.
Fastidious, Fair, and Fierce
The early Celts were not literate, and we are, therefore, dependent on Classical authors for much of what we know about Celtic mores, lifestyles, and behavior, as well as the physical appearance of the Celts themselves. The fourth-century Byzantine writer, Ammianus Marcellinus, drawing on reports from the first century B.C., tells us that the Celts (or Gauls, as the Romans called them) were fastidious, fair, and fierce:
The Gauls are all exceedingly careful of cleanliness and neatness, nor in all the country… could any man or woman, however poor, be seen either dirty or ragged.
Nearly all… are of a lofty stature, fair and of ruddy complexion: terrible from the sternness of their eyes, very quarrelsome, and of great pride and insolence. A whole troop of foreigners would not be able to withstand a single Gaul if he called his wife to his assistance, who is usually very strong and with blue eyes…
The early Celts were not an urban people. Their dwellings, typically of timber construction, tended to be isolated farmsteads or, at most, clusters of a few buildings surrounded by a palisade.
In pre-Christian Ireland there was an intellectual class which had a social status approximately equal to that of the warrior-landowners. This class consisted of druids (priests), bards, physicians, artists, and skilled craftsmen, who moved freely from petty kingdom to petty kingdom in a way that was not possible for any other class, thereby helping to maintain cultural unity throughout a wide area. A similar class served the same functions on the continent.
Dark Side of Druidism
By the time of the Roman conquest, however, many extraneous elements had become inseparably blended into Celtic religion. The druids practiced not only solar rites, but some rather dark and nasty ones of Mediterranean origin as well. [Chechar’s note: today it’s known that the rites were not of Mediterranean origin—see below]
Celts, Germans Closely Related
Many later writers have not been as careful as Caesar was and tend to lump all Celtic-speaking populations together as “Gauls,” while sharply distinguishing them from the Germans. As a matter of fact, there was a much greater affinity between the Celts and the Germans, despite the language difference, than there was between the truly Celtic elements among the Gauls and the racially different but Celtic-speaking Mediterranean and Celtiberian elements.
In the British Isles the racial effects of the fifth-century B.C. Celtic invasions varied. In some areas indigenous Nordic populations were reinforced, and in others indigenous Mediterranean or mixed populations diluted the fresh Nordic wave.
Brennus Sacks Rome
Around 400 B.C. Celts invaded northern Italy in strength, establishing a permanent presence in the Po valley, between the Alps and the Apennines. They pushed out the resident Etruscans and Ligurians, founded the city of Milan, and began exploring possibilities for further expansion south of the Apennines.
In 390 B.C. a Celtic army under their chieftain Brennus defeated the Roman army and occupied Rome. The Celts were not prepared to stay, however, and upon payment of an enormous ransom in gold by the Romans they withdrew again to northern Italy. In the following centuries there were repeated clashes between adventurous Celts and the people of the Classical civilizations to the south.
But the Celts, unfortunately, despite their mobility and their intelligence, never formed a unified whole; they remained a collection of distinct tribes, as often hostile to one another as they were to non-Celts. This lack of unity brought their downfall.
Man against man, a Celt could usually beat a Roman; the Celts were at least as brave and as skilled in arms as the Romans, and the former were bigger and stronger, on the average, for the latter had by this time mixed for too many generations with southern races and lost most of the Nordic qualities of their forefathers. But the Romans had the supreme advantage of organization, without which little of lasting impact has ever been wrought in this world.
My comment:
With only the Romans’ word to go on human sacrifices performed by the Druids—the ancient Celts left no written record of their own—it has been easy for historians to dismiss such tales as wartime propaganda.
Recent archeological findings however are starting to unearth evidence of Druid sacrifices, sometimes on a massive scale. According to my “psychogenic” point of view (cf. my research on psychohistory), at the time of Caesar’s conquests of Gaul the Romans belonged to a more evolved “psychoclass” than the Gauls, which not only means more culturally evolved but also more integrated psychologically (with time the psychic development of the two psychoclasses, Celts and Latins, became homogenized).
An objective appraisal on the conflict between Romans and Aryan “barbarians” of more than two thousand years ago, therefore, ought to consider these two factors in any future study of the epoch: psychohistory and racial studies such as the one pioneered by Pierce.
Excerpted from the 13th article of William Pierce’s “Who We Are: a Series of Articles on the History of the White Race”:
Wealth inexorably undermined the old virtues. Decadence rotted the souls of the noble Romans. While the mongrel mobs were entertained by the debased spectacles in the Colosseum (not unlike the distraction of today’s rabble by non-stop television), the patricians indulged themselves with every new vice and luxury that money and a resourceful merchant class could provide. Pampered, perfumed, manicured, and attended by numerous slaves, the effete aristocracy of the first century A.D. was a far cry from the hard and disciplined ruling class of a few centuries earlier.
Just as there are Americans today who understand where the weakness and lack of discipline of their people are leading them and who speak out against these things, so were there Romans who tried to stem the tide of decadence engulfing the Republic. One of these was M. Porcius Cato, “the Censor” (234–149 bc), whose public career spanned the first half of the second century B.C.
Cato was born and raised on his father’s farm and then spent 26 years fighting in Rome’s legions before entering politics. Early in his career, having been appointed governor (praetor) of Sardinia, Cato set the pattern he would follow the rest of his life: he expelled all the moneylenders from the island, earning the undying hatred of the Jews and a reputation as a fierce anti-Semite.
Archreactionary
Later Cato was elected censor in Rome. The duties of a censor were to safeguard public morality and virtue and to conduct a periodic census of people and property for military and tax purposes. Cato took these duties very seriously. He assessed jewelry and other luxury items at ten times their actual value, and he dealt promptly and severely with disorder and degeneracy.
 In the Senate Cato spoke out repeatedly against the foreign influences in philosophy, religion, and lifestyle which were encroaching on the traditional Roman attitudes and manners. As a result, Rome’s “smart set” condemned him (privately, for he was too powerful to attack openly) as an archreactionary and an enemy of “progress.”
In the Senate Cato spoke out repeatedly against the foreign influences in philosophy, religion, and lifestyle which were encroaching on the traditional Roman attitudes and manners. As a result, Rome’s “smart set” condemned him (privately, for he was too powerful to attack openly) as an archreactionary and an enemy of “progress.”
In the field of foreign policy, Cato was adamantly opposed to the integration of the Semitic East into the Roman world. He wanted Rome to concentrate on the western Mediterranean and to deal with the Levant only at sword point. Unfortunately, there were few men of Cato’s fiber left among the Romans by the second century.
Declining Birthrate
One of the most fateful effects of decadence was the drastic decline in the birthrate of the Roman nobility. Decadence is always accompanied by an increase in egoism, a shifting of focus from race and nation to the individual. Instead of looking on bearing and raising children as a duty to the state and a necessity for the perpetuation of their gens and tribe, upper-class Romans came to regard children as a hindrance, a limitation on their freedom and pleasure. The “liberation” of women also contributed heavily to this change in outlook.
The failure of the patrician class to reproduce itself alarmed those Roman leaders with a sense of responsibility to the future. Emperor Augustus tried strenuously to reverse the trend by issuing several decrees regarding family life. Heavy penalties were set for celibacy or for marriage with the descendants of slaves. Eventually, Augustus ordered that every noble Roman between the ages of 25 and 60 must be married or, at least, betrothed.
Suicide of the Nobility
In 9 A.D. tax advantages and other preferences were granted to the parents of three or more children; unmarried persons were barred from the public games and could not receive inheritances, while the childless married person could receive only half of any inheritance left to him.
All these measures failed. Augustus’ own daughter, Julia, was a thoroughly liberated member of the “jet set” of her time, who considered herself far too sophisticated to be burdened with motherhood. In embarrassment, Augustus banished her to an island.
From the dictatorship of Julius Caesar to the reign of Emperor Hadrian, a century and a half, one can trace the destinies of 45 leading patrician families: all but one died out during that period. Of 400 senatorial families on the public records in 65 A.D., during the reign of Nero, all trace of half of them had vanished by the reign of Nerva, a single generation later.
Rise of Capitalism
As the patricians declined in numbers, the Roman peasantry also suffered, but for a different reason. The later years of the Republic saw the rise of agricultural capitalism, with wealthy entrepreneurs buying up vast estates, working them with slaves and driving the freeborn small farmers out of the marketplace.
By the tens of thousands the Latin and Sabine yeomen were bankrupted and forced to abandon their farms. They fled to the city, where most of them were swallowed up in the urban mob.
“New Romans”
The capitalist nouveaux riches who came to wield much of the power and influence in Rome lost by the dwindling patricians were an altogether new type of Roman. Petronius’ fictional character Trimalchio is their archetype. Tenney Frank wrote of these “new Romans”:
It is apparent that at least the political and moral qualities which counted most in the building of the Italian federation, the army organization, the provincial administrative system of the Republic, were the qualities most needed in holding the Empire together. And however brilliant the endowment of the new citizens, these qualities they lacked. The Trimalchios of the Empire were often shrewd and daring businessmen, but their first and obvious task, apparently was to climb by the ladder of quick profits to a social position in which their children, with Romanized names, could comfortably proceed to forget their forebears. The possession of wealth did not, as in the Republic, suggest certain duties toward the commonwealth.
Different Spirit
Many historians have remarked on the fact that the entire spirit of the Roman Empire was radically different from that of the Roman Republic. The energy, foresight, common sense, and discipline which characterized the Republic were absent from the Empire. But that was because the race which built the Republic was largely absent from the Empire; it had been replaced by the dregs of the Orient.
The change in attitudes, values, and behavior was due to a change in blood. The changing racial composition of Rome during the Republic paved the way for the unchecked influx of Levantine blood, manners, and religion during the Empire.
But it also set the stage for a new ascendancy of the same Northern blood which had first given birth to the Roman people. We will look at the conquest of Rome by the Germans. First, however, we must backtrack and see what had been happening in the North during the rise and fall of Rome.